Design of Experiment-style Studies with the EDEM Coupling Interface
With Version 2_1_0 and onwards of the EDEM Coupling Interface was expanded to enable geometry sections to be imported and deleted at any point in a simulation. This allows equipment designs to be evolved through co-simulation with Design-Of-Experiment (DOE) style programs or parametric CAD packages. This capability in the EDEM Coupling Interface also allows the automatic creation of many simulations for batch mode running containing variations on geometry or geometry dynamics.
Importing a Geometry
The loadGeometry Method will create a new geometry section in the EDEM simulation and name it using the CAD file name which is read in. The import process will use the same default parameters as shown in the EDEM Creator Geometry import dialog, any changes to the defaults can be specified via the setGeometryImportParameters Method, which should be invoked prior to calling the loadGeometry Method.
Assigning a Material to a Geometry
Prior to loading a geometry, you must specify the material to assign to the geometry section that's about to be loaded. The relevant ID is obtained via a call to getMaterialId.
Deleting a Geometry
Use the name of the target geometry to delete it from the simulation via a call to removeGeometry.
Assigning Kinematics to Geometry
The EDEM Coupling Interface has the ability to assign built-in kinematics to a target geometry. The kinematics are assigned using addLinearTranslationKinematic, addLinearRotationKinematic, addSinusoidalTranslationKinematic, addSinusoidalRotationKinematic, addConveyorTranslatonKinematic and addConveyorRotationKinematic.
The parameters for each of the dynamics represent the values that are available in the configuration section of ‘Add Kinematic’ GUI for the chosen kinematic type.
Compiling Coupling Interface Code to an Executable
This guide highlights how to compile a simple user-written code into a stand-alone executable to work with the coupling interface. To compile the EDEM-FLUENT coupling please see the ‘Coupling EDEM with ANSYS Fluent’ E-Learning guide found on the Altair Website. To access the E-Learning Login and go to eLearning Courses > EDEM > Coupling EDEM with ANSYS Fluent.
Windows
To create a simple executable a 3rd party compiler is required to compile C++ code. EDEM Altair does not support any specific compiler however Microsoft Visual Studio is commonly used and Visual Studio Community 2017 is shown in this example. When installing Visual Studio it is important to choose to install the C++ toolset (Universal Windows Platform development and Desktop development with c++), depending on the install these may be installed by default or additional options in the installer.
-
Place the .cpp files that you have written in a working directory, e.g. C:\code\Dynamics_Coupling. In this instance a Free_Body.cpp file is used which can be found on the EDEM Forum.
-
Start Visual Studio.
-
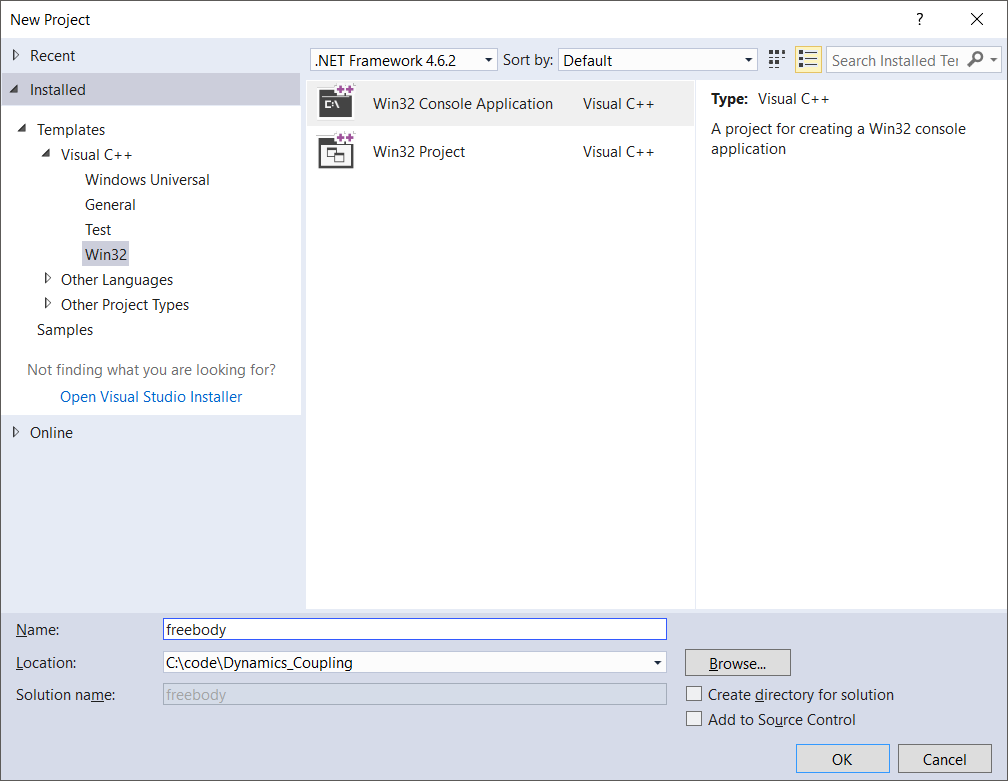
Create a New Project (Win32 Console Application Visual C++)
-
Go to File > New > Project
-
Set name: freebody
-
Set location C:\code\Dynamics Coupling
-
Click OK.
-
-
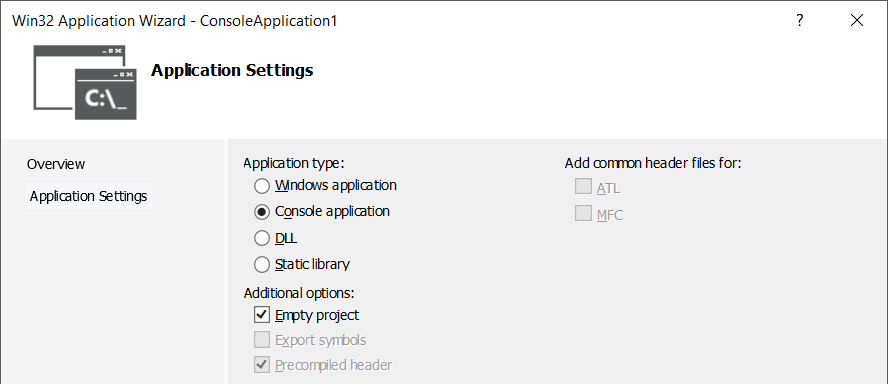
Select Application Settings and then do the following:
-
Select Console Application.
-
Select Empty Project.
-
Click Finish.
-
-
Add the file Free_Body.cpp to the project
-
Copy this file to C:\code\Dynamics_Coupling\freebody.
-
Right-click Source Files > Add > Existing Item > Free_Body.cpp > Add.
-
- Go to Project > Properties and set the following:
- Configuration to All Configurations.
- Platform to All Platforms.
- Select Configuration Properties > C/C++ > General
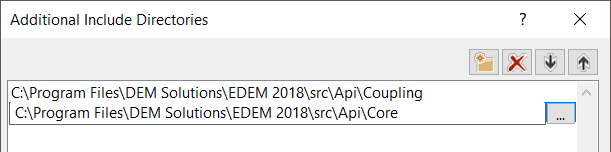
- Select Additional Include Directories > <Edit…>.
- Add the following paths then click OK.
C:\Program Files\Altair\2022.2\EDEM\bin\src\Api\Coupling
C:\Program Files\Altair\2022.2\EDEM\bin\src\Api\Core
-
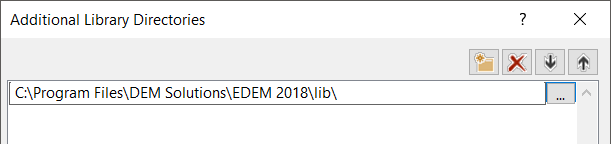
Select Configuration Properties > Linker > General > Additional Library Directories > edit
-
Include
C:\Program Files\Altair\2022.2\EDEM\bin\lib\
-
-
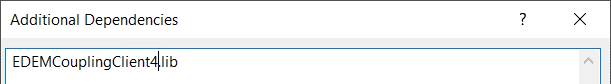
Select Configuration Properties > Linker > Input > Additional Dependencies > Edit.
-
Add EDEMCouplingClient4.lib.
-
Click OK.
-
-
Go to Project > Properties > Configuration Manager and set the following:
-
Active solution configuration to Release or Debug.
-
Active solution platform to x64 > close.
-
Build the solution (Build > Build Solution) to create the .exe file
-
Linux
To compile coupling interface applications for use with EDEM running on Linux, it is recommended to use the GNU Compiler Collection, more referred to as gcc.
Compiling with gcc
If you have the source code <source_code>.cpp file in your working directory, the following two commands will compile the source code:
g++ -std=c++11 -c -g -DDEMLINUX -I ~/2022.2/altair/EDEM/src/API/Core -I ~/2022.2/altair/EDEM/src/API/Coupling/ -MMD -MP -MF <output>.o.d -o <output>.o <source_code>.cpp
followed by:
g++ -std=c++11 -o <compiled> <output>.o -L ~/2022.2/altair/EDEM/lib -lEDEMCouplingClient4 -L ~/2022.2/altair/EDEM/bin -lQt5Core -lQt5Network
where <source_code>, <output>, and <compiled> are filenames of your choice. EDEM_XXXX is replaced with the version of EDEM you have installed, libEDEMCouplingClientXXXXX is replaced with the coupling client Library version associated with it, and the libQtXXXX entries use the Qt version associated with that EDEM release. For reference, the coupling client Library and Qt versions can be found below:
|
EDEM Version |
Coupling Client Library version |
libQt Version |
| 2022 |
libEDEMCouplingClient4.so |
5.12 |
| 2021 | ||
|
2020 |
||
|
2019 |
5.6 | |
|
2018 |
||
|
2017.2 |
libEDEMCouplingClientV3_2_0.so |
|
|
2017.1 |
libEDEMCouplingClientV3_1_0.so |
|
|
2017.0 |
libEDEMCouplingClientV3_0_0.so |
Running an Application
When running your compiled application, you will need to ensure that the EDEM libraries can be correctly picked up, by adding the location of the EDEM libraries to the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable. To do this, you will need to enter the following:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/DEMSolutions/EDEM_XXXX/lib/
Where, again, XXXX is replaced with your EDEM version. If entering this into a console, this will only be applied in the current session. If you want to add the EDEM Library path to LD_LIBRARY_PATH permanently, you will need to add this line to your .bashrc file.