About the EDEM Analyst
The Analyst is the post-processor used to analyze and visualize the results of your simulation. You can play back the simulation, graph results, save a still image, create a video or export data.
- Analyst Tree
- Viewer
- Section Details
- Toolbar and Menu Bar
- Data Browser
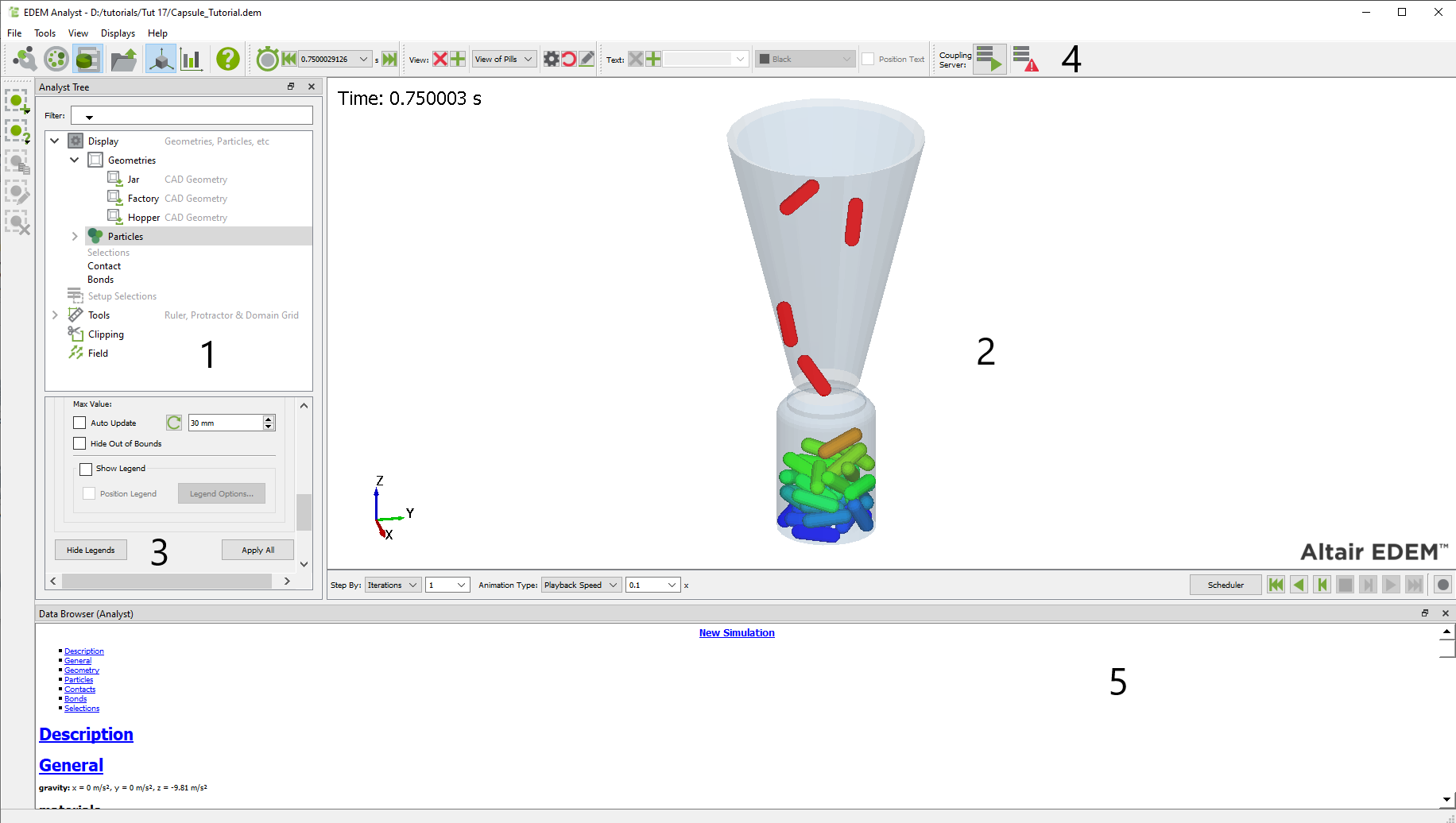
Analyst Tree
The Analyst Tree is displayed on the left side of the EDEM window. It has five Sections: Display, Setup Selections, Tools, Clipping, and Field.
Right clicking on any section of the Analyst Tree allows you to expand/collapse all the corresponding Subsections.
Viewer
The Viewer displays 3D representations of your particles, geometry, and fields (if applicable). The rotation, position and zoom factor of the Viewer are controlled using the mouse.
A number of animation controls appear just below the Viewer.
Section Details
The Section Details space contains all the information and configuration options for each of the Sections shown in the Analyst Tree: Display, Setup Selections, Tools, Clipping and Field. The options shown within the Section Details will vary accordingly with the section or subsection being highlighted in the Analyst Tree.
Analyst Toolbar
| Icon | Name | Description |
|
|
Creator |
Click to switch to the Creator. |
|
|
Simulator |
Click to switch to the Simulator. |
|
|
Analyst |
Click to switch to the Analyst. |
|
|
Open |
Click to open an existing model. |
|
|
3D Viewer |
Click to switch to the 3D Viewer. |
|
|
Create Graph |
Click to switch to the Graph Creator. |
|
|
Help |
Click to view the online help. |
|
|
Jump to Start |
Move to the first time step in the simulation. |
|
|
Animate Backwards |
Click to continually change time steps backwards. |
|
|
Step Backwards |
Click to step backwards. |
|
|
Stop Animation |
Click to stop animation. |
|
|
Step Forwards |
Click to step forwards. |
|
|
Animate Forwards |
Click to continually change time steps forwards. |
|
|
Jump to End |
Move to the last time step in the simulation. |
|
|
Record Animation |
Click to open animation dialog box. |
|
View: |
Save View |
Save the current View settings. |
|
View: |
Delete View |
Delete the selected View settings. |
|
|
Start Coupling Server |
Click to start Coupling Server. |
|
|
Server Awaiting Connection |
Shows the Server is started but not connected. |
|
|
Server Connected |
Shows the Server is connected. |
|
|
Coupling Server Disabled |
Shows the Server is not running. |
|
|
Stop Server |
Click to stop the Coupling Server. |
|
Text: |
Add Text |
Click to add text to viewer. |
|
Text: |
Delete Text |
Click to delete text from the viewer. |
|
|
Add Selection |
Add a Selection to the analysis. |
|
|
Manual Selection |
Add Manual Selection. |
|
|
Grid Bin Group |
Add Grid Bin. |
|
|
Geometry Bin |
Add Geometry Bin. |
|
|
Mass Flow Sensor |
Add Mass Flow Sensor. |
|
|
Total Mass Sensor |
Add Total Mass Sensor. |
|
|
Velocity Profile Sensor |
Add Velocity Profile Sensor. |
|
|
Segregation Sensor |
Add Segregation Sensor. |
|
|
Density Sensor |
Add Density Sensor. |
|
|
Imported Geometry Bin |
Add Imported Geometry Bin. |
|
|
Copy Selection Group |
Copy Selection Group. |
|
|
Rename Selection Group |
Rename Selection Group. |
|
|
Delete Selection Group |
Delete Selection Group. |
Analyst Menu Bar
File Menu
-
Open. Open an existing model.
-
Truncate File. Remove sections of data from your model.
-
Export. Opens a sub-menu with the following options:
-
Simulation Deck. Export a single full time step from your simulation to create a copy as a new EDEM simulation deck (you cannot export from partial save time steps). Exporting a deck allows it to be transferred to another location and run again using identical simulation parameters. To export a simulation deck:
-
In the Analyst use the ‘Animate Forwards’ or ‘Animate Backwards’ tool to change the simulation time step to the value that you want to export. EDEM will save this p as a new simulation.
-
Go to File > Export > Simulation Deck.
-
Enter a name for the deck then click Save.
-
From the Export Options dialog, select the content options:
-
Un-tick the Export Custom Properties option to exclude any custom property data from the deck.
-
Nullify Stored Factory Activities: Choose this option if you want to remove the factory history from the exported simulation file. For example if a dynamic factory is set to create X kg of a material starting at 1 s and the factory has run so that this mass of material has been created, EDEM sets the factory as completed. If you export with the Nullify tick-box selected then the factory will no longer be set as completed, and if the Start Time is set prior to the factory start time then this factory will restart in the new Simulation Deck.
-
Set Simulation Time: Choose this option if you want to change the displayed simulation time of the exported input deck. This does not change simulation results. This is designed to help when coupling to other CAE tools with different simulation time. Enter a starting time in seconds.
-
-
Click OK to save the simulation deck.
-
-
Breakage Analysis
-
Results Data. Export specified data for analysis.
-
SimSolid Data. Export force data on a specific geometry in a text format suitable for SimSolid import.
-
Timestep Selection: select Start Timestep and End Timestep. Data can be exported for a single time step (where Start and End time steps are equal or ‘Timestep per file’ is selected) or as time-averaged values (where the Start and the End time steps differ and ‘Average to file’ is selected) to minimize the effects of spiking.
-
Force Export:
-
Orient and transpose to initial CAD position. For each time step the force data is mapped to the initial CAD position. This setting allows the a structural analysis to be carried out in SimSolid even if the geometry has moved position in EDEM.
-
Contact Force: check this box in order to export force data per particle-geometry contact point.
-
Element Force: check this box in order to export force data per geometry mesh element.
-
Geometry: select the geometry part for which data is to be exported.
-
-
Material Center of Mass Export: check this box and select a pre-defined particle manual selection in order to export the X, Y and Z co-ordinates of the center of mass and the total mass for the selection.
-
Export: clicking on this button will write the .csv file containing the load data for importing into SimSolid and the file containing the information on the particle manual selection.
-
-
HyperMesh Workbench Data. Export pressure and force data on a specific Geometry in a text format suitable for HyperMesh import.
-
Timestep Selection: select Start Timestep and End Timestep. Data can be exported for a single time step (where Start and End timesteps are equal or ‘Timestep per file’ is selected) or as time-averaged values (where the Start and the End time steps differ and ‘Average to file’ is selected) to minimize the effects of spiking.
-
Force and Pressure Export:
-
Geometry: select the Geometry part for which data is to be exported.
-
Element Pressure: check this box in order to export pressure data per Geometry mesh element.
-
Element Force: check this box in order to export force data per Geometry mesh element.
-
Contact Force: check this box in order to export force data per particle-Geometry contact point.
-
Orient and transpose to initial CAD position. This setting allows a transient analysis to be performed in HyperMesh without the Geometry moving from its initial position. For each time step the force and pressure data is mapped to the initial position.
-
-
Material Center of Mass Export: check this box and select a pre-defined particle manual selection in order to export the X, Y and Z co-ordinates of the center of mass and the total mass for the selection.
-
Export: clicking on this button will write the .csv file containing the load data for importing into HyperMesh and the file containing the information on the particle manual selection.
-
-
ANSYS Workbench Data. Export pressure and force data on a specific Geometry in a text format suitable for ANSYS import.
-
Timestep Selection: select Start Timestep and End Timestep. Data can be exported for a single time step (where Start and End timesteps are equal or ‘Timestep per file’ is selected) or as time-averaged values (where the Start and the End time steps differ and ‘Average to file’ is selected) to minimize the effects of spiking.
-
Force and Pressure Export:
-
Geometry: select the Geometry part for which data is to be exported.
-
Pressure: check this box in order to export pressure data.
-
Force: check this box in order to export force data.
-
Orient and transpose to initial CAD position. This setting allows a transient analysis to be performed in ANSYS without the Geometry moving from its initial position. For each time step the force and pressure data is mapped to the initial position.
-
-
Material Center of Mass Export: check this box and select a pre-defined particle manual selection in order to export the X, Y and Z co-ordinates of the center of mass and the total mass for the selection.
-
Export: clicking on this button will write the .axdt file containing the load data for importing into ANSYS and the file containing the information on the particle manual selection.
-
-
Image. Save a copy of the image currently displayed in the Viewer.
-
Breakage Particle Size Distribution
-
Timestep. Define the timestep which breakage should be analysed at.
-
Breakage Particle. Particles which break.
-
Postpro Particle. Dummy particle.
-
Lambda.Lambda is a material parameter involved in the distribution of fines. EDEM provides an automatic estimate based on other material parameters (see Tavares and Changas 2020)
-
Output file (.csv). Select the location where the csv file should be saved.
-
Display Graph of Results. This option plots a graph of the Particle Size Distribution.
-
Save Graph of Results. Select a location where you want to save the graph of the particle size distribution.
-
Select Geometry Bin. Note geometry bins with rotation are not supported.
-
-
Data to Stl. Export geometries and particles to a CAD file.
-
Particles:
-
Export either spheres or templates. Sphere will export Multi-Sphere shape. Template will apply a template to the particle, an input template CAD is required.
-
Particle Output file. Generate a name for the exported .stl
-
Global Particle Scale. Applies a single value scale to the spheres/templates. This will use the correct particle position but adjust the size of the particles based on the input scale.
-
Time step Selection. Select the appropriate time step for the particle export.
-
-
Geometries:
-
Geometry Output file. Generate a name for the exported .stl
-
Merge Output Files. Combines all exported geometries into a single file. If not selected each geometry will be exported as an individual file.
-
Geometry Time step. Select the appropriate time step for the geometry export. NB. deformed geometries are not exported.
-
-
-
-
Print Image. Print a copy of the image currently displayed in the Viewer.
-
Running an EDEMpy Script: An EDEMpy Script can be run from the analyst. The option to run a script can be found under File > Run EDEMpy script. From this interface a previously generated EDEMpy script can be selected. Additional arguments used in the script can be passed to python in the Arguments section.
-
Import Config. Import a config (*.dfg) file.
-
Export Config. Export a config (*.dfg) file.
-
Creator. Select to switch to the Creator.
-
Simulator. Select to switch to the Simulator.
-
Analyst. Select to switch to the Analyst.
-
Recent Files. A list of recently opened files. Select a file to open it.
-
Quit. Quit EDEM.
Tools Menu
- The Analyst’s Tools Menu is the same as for the Simulator.
- Abaqus Co-Simulation
Abaqus Co-Simulation is displayed when the “Abaqus Coupling” check box is enabled in Tools > Options > Coupling Options. Selecting this option opens the Abaqus Co-Simulation dialogue for running Abaqus FEA simulation decks using EDEM contact data as an input. Abaqus Co-Simulation is supported for Abaqus 6.16 and newer.
Abaqus Co-Simulation Interface: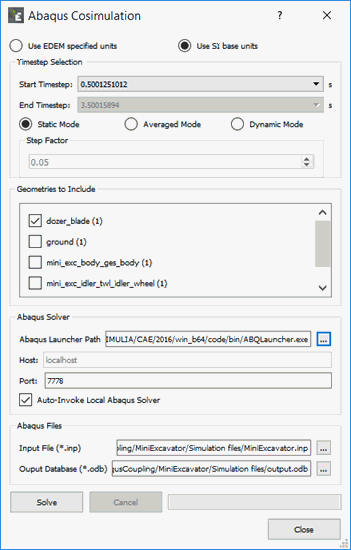
-
Units:
The user has the option to use EDEM specified units or SI units. -
Timestep Selection:
Select start and end time steps for analysis. For Static Mode cases Start time step defines the time that contact data in EDEM is used for input in the Abaqus FEA analysis. Start and end time steps define the start and end times for Averaged Mode (loads averaged over time) and Dynamic Mode (dynamic loads over time). Step Factor defines the sampling frequency to use for averaged and dynamic cases. -
Geometries to Include:
Select the geometries in EDEM to include in the analysis. Only contacts on selected geometries are transferred to Abaqus. -
Abaqus Solver:
Define path to Abaqus launcher and if Abaqus is to be solved remotely define the Host and Port for this connection. Select Auto-Invoke Local Abaqus Solver for cases solved on the local machine – Abaqus solvers must be manually invoked if they are run remotely. -
Abaqus Files:
Define Abaqus input (.inp) and output (.odb) files.
-
View Menu
-
Show Particles: Activate/deactivate to see the particles in the Viewer.
-
Themes: Show the EDEM interface with Legacy Theme (default) or Dark Theme.
Displays Menu
-
Show 1 Display: Shows the model in 1 window in the Analyst.
-
Show 2 Displays: Shows two side-by-side views of the model, each view can be configured by dragging the view window and changing the model orientation.
-
Show 3 Displays: Shows two side-by-side views and one full length view below.
-
Show 4 Displays: Splits the display into 4 equal sized view windows.
-
Split Display Horizontally.
-
Split Display Vertically.
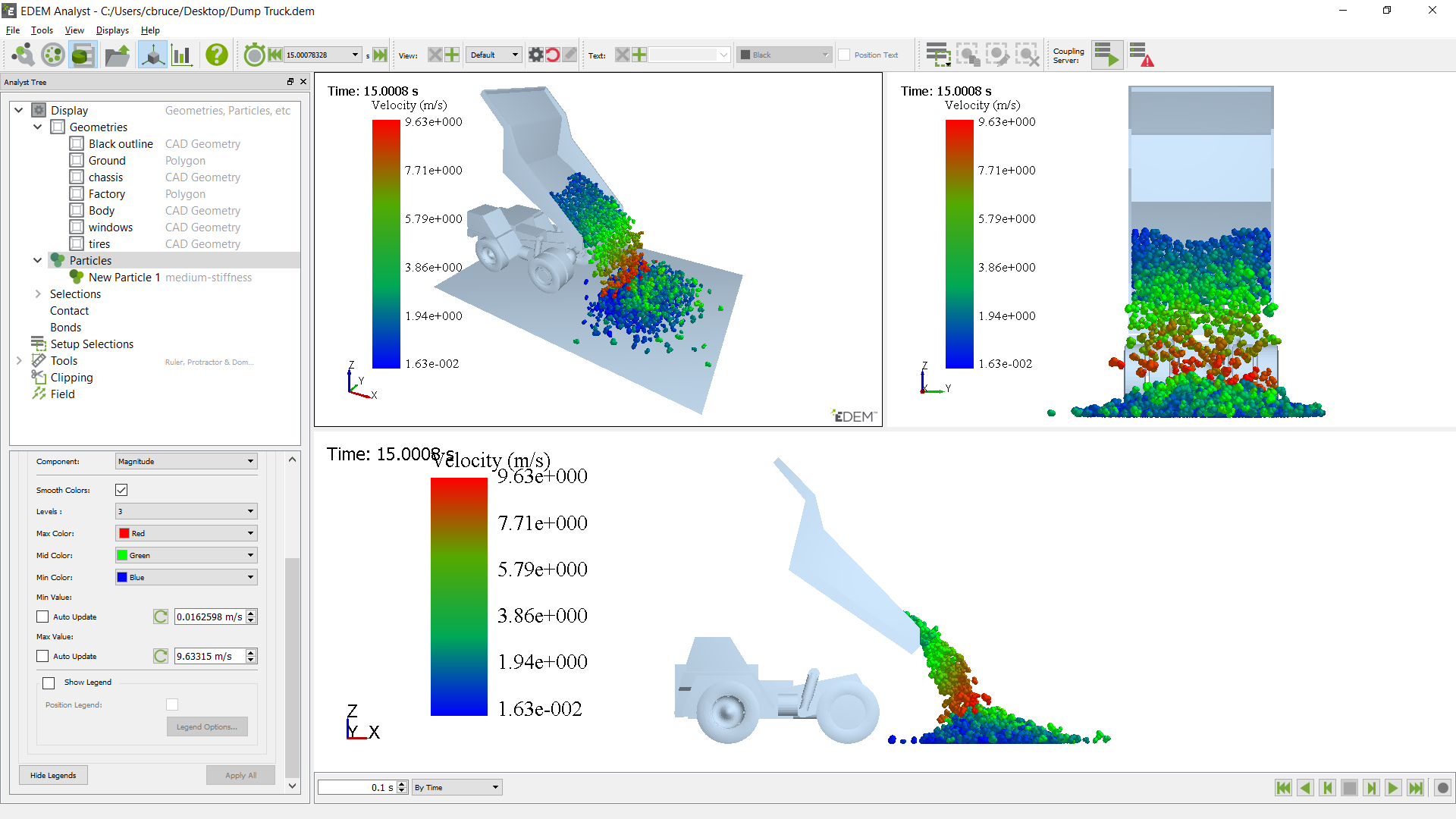
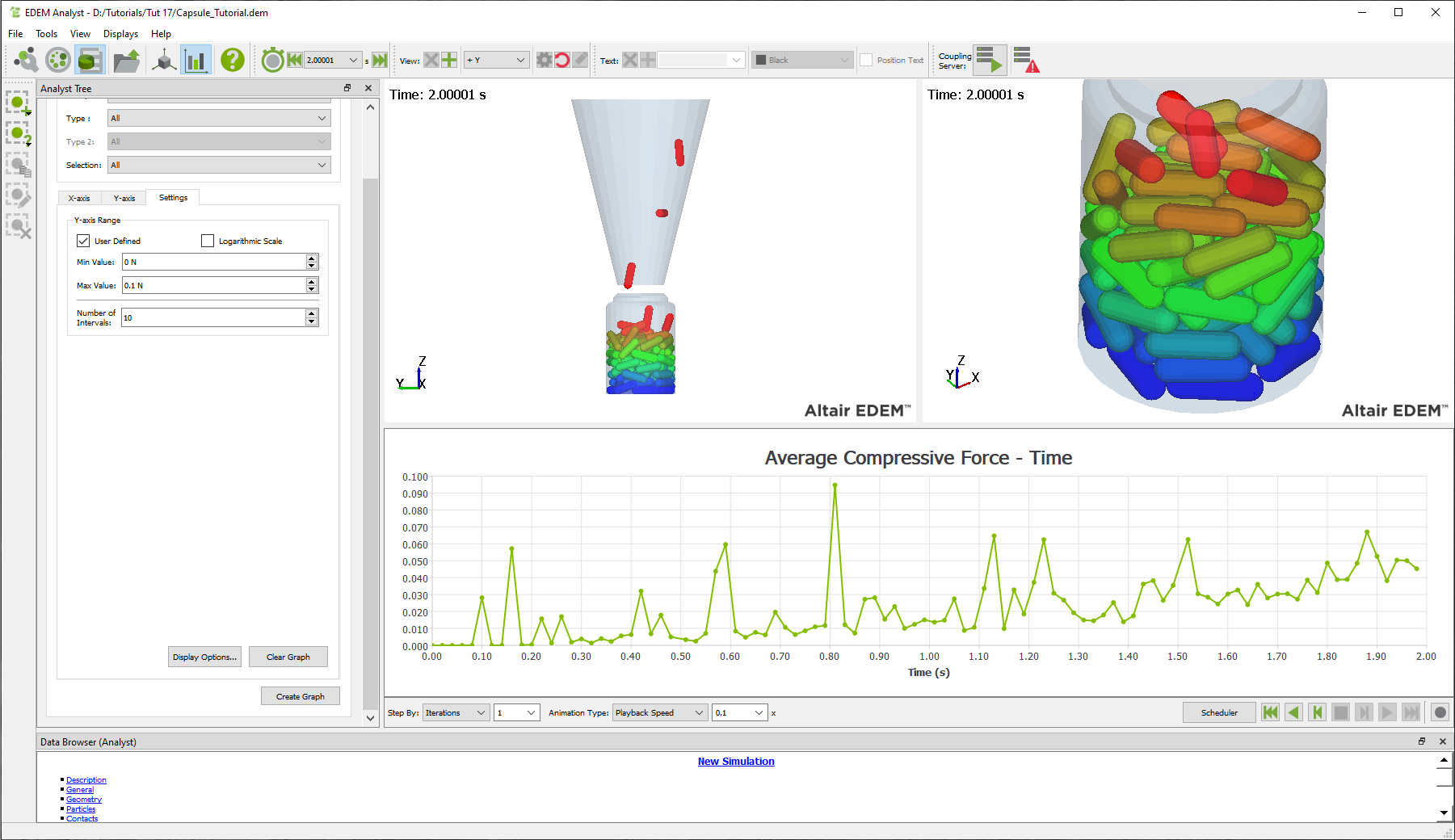
Showing 3 displays, either using "show 3 displays" or "split displays vertically" followed by "split displays horizontally".
Views and graphs can also be displayed side by side using split displays so that simulations may be simultaneously reviewed qualitatively and quantitatively on the same display.
The example below shows particles visualized by mass from two view points and a line graph of total compressive force acting on the body of the Dump Truck:
Image and video exports maintain the same display layout so that exported images and videos combine views and graphs.
Choosing an option from the display setting option overwrites the previous display settings.
Help Menu
- Help: The help menu brings up the relevant information regarding the EDEM interface.
- About: The about box provides information about the current version of EDEM, the EDEM Version and Revision number are useful information to provide EDEM technical support when discussing support cases.
Data Browser
The Data Browser is a .html page that displays detailed information about your model. The information displayed differs between the Creator, Simulator and Analyst. Right click anywhere within the Data Browser and choose Save to save the information in an .html file.
The Data Browser within the Analyst has the following sections: Description, General, Geometry, Particles, Contacts, Bonds, and Selections.
Description
-
Description. The description as defined in the EDEM Creator > Project.
General
-
Dimensions. The number of dimensions in your domain.
-
Gravity. Details of the gravity acting in your model as specified in the Globals pane.
-
Materials. A list of all materials used in the model and their properties, as specified in the Materials Editor.
-
Energy. The total energy in the model at the current time. It is the sum of the kinetic energy, potential energy and the energy in any contacts taking place.
Geometry
-
Domain. The dimensions of the domain as specified in the Geometry pane.
-
Geometry Totals. Details of the number of elements that make up each section of Geometry.
-
Sections. Each section in the model and its properties are listed. Properties are as specified in the Geometry pane.
Particles
-
Particles. A list of each particle type used in the model and their properties. Details of each surface within the particle are also listed. Properties are as specified in the Particles pane.
-
Factories. Details of each factory used in the model and their properties. Properties are as specified in the Factory pane. The total number of particles created by each factory is also listed.
-
Particle totals. The total number of particles in the model at the current time. Totals for each particle type are also listed.
Contacts
-
Interactions. A list of the interaction types taking place in the model as specified in the Materials Editor.
-
Contacts. Lists the total number of contacts in progress at the current time. The contacts are broken down into contact types: for example, the number of particle A - particle B contacts or particle B - surface A contacts. The total number of collisions that have taken place during the time step are also listed.
Bonds
-
Bond totals. A list of the bond totals, indicating total number of bonds, total number of intact bonds, total number of broken bonds, and total intact and broken bonds for each particle type.
Selections
-
All selections are listed. This section has links to pages with information on the selection and its associated queries, list of particles, and geometry elements (if applicable).