Category: Toolbox > eDrives and Systems > eMotors > Sensors
Description: The Linear Variable Displacement Transducer block models an LVDT sensor with the aspects of carrier demodulator noise, filtering, linearity, null offset, and range limitations.
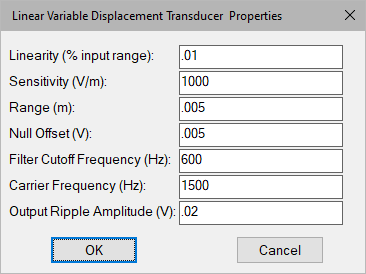
Carrier Frequency: Defines the LVDT modulator carrier frequency in hertz.
Filter Cutoff Frequency: Indicates the bandwidth of a two-pole analog filter used to remove the carrier. Units are in hertz.
Linearity: Simulates symmetric curvilinear input-output characteristic of a LVDT as a percent of the transducer input range.
Null Offset: Defines the offset voltage at 0 displacement in volts.
Output Ripple Amplitude: Defines the influence of the carrier on the output signal as the amplitude of a sinusoidal voltage signal in volts.
Range: Defines the measurable stroke of the transducer in meters. Inputs that exceed the input range cause output saturation.
Sensitivity: Defines the linear gain of the transducer in volts output per meter displacement.
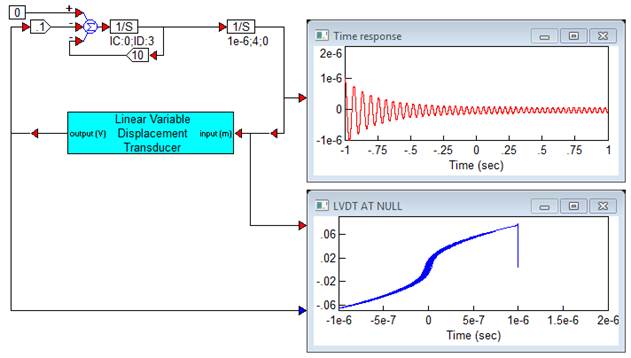
Diagram name: Linear Variable Displacement Transducer
Location: Examples > eDrives and Systems > eMotors > Sensors
The following simplified simulation shows a dynamic system in which an LVDT block is used to feedback measured position. The LVDT block is adjusted to include a fairly severe nonlinearity. The high gain resulting at null from this nonlinearity creates a sustained oscillation, or limit cycle, at steady state.