For certain applications, a transfer function representation of the linearized system may be more desirable than a state-space representation. The Transfer Function Info command presents a linearized system in transfer function form and includes the following information:
•The numerator and denominator polynomials are presented in powers of the complex variable s defined as:
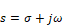
Where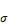
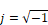
•The gain of the transfer function
•The factors of the numerator (called zeros) and the denominator (called poles). The zeros and poles may appear in the following format:
(real-part, imaginary-part)
The transfer function is computed from the state-space matrices using a similarity transformation. The poles and zeros are computed by converting the numerator and denominator polynomials to square matrices and computing the corresponding eigenvalues. If numerical round-off errors occur during the factoring process, they can be corrected by using Analyze > Preferences.