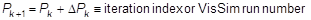
Global optimization is almost always a nonlinear problem and rarely is there a single best method for minimizing the cost function. You can choose from four optimization methods: Fletcher Reeves, Generalized Reduced Gradient, Polak-Ribiere, and Powell.
Regardless of the method you select, Embed produces a sequence of parameter updates on a per-run basis that decreases the value of the cost function. The basic parameter update equation is:
Pk+1 = Pk + rPk Ξ iteration index or Embed run number
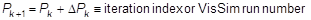
The difference between each method is the way 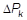
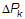 is generated. For more information on these
methods, see numerical
recipes.
is generated. For more information on these
methods, see numerical
recipes.
To perform global optimization
1. Choose System > Optimization Properties.
2. In the Optimization Properties dialog box, activate the Perform Optimization option; choose the method you want and click OK; then start the simulation.
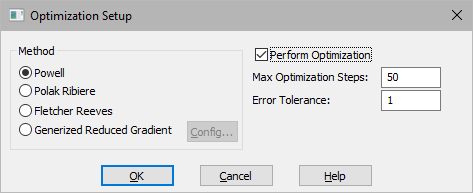
Error Tolerance: Indicates the maximum error between the results of two successive iterations. The default value is 10.
Fletcher Reeves: Specifies a conjugate gradient algorithm that requires fewer iterations to convergence. This algorithm is slower than Powell’s method.
Generalized Reduced Gradient: Specifies a generalized reduced gradient algorithm that performs constrained optimization. When you select this method, you can click Config to adjust tolerances and algorithmic options, and generate a report file.
Polak Ribiere: Specifies a conjugate gradient algorithm that is a bit more sophisticated than Fletcher Reeves for arriving at the supposed minimum of the quadratic form.
Powell: Specifies a direction-set algorithm that typically runs faster because it does not explicitly calculate the gradient.
Max Optimization Steps: Indicates the maximum number of optimization steps.
Perform Optimization: This parameter must be activated to perform global optimization.
Config: Invokes an editable table to adjust tolerances and algorithmic options that control the behavior of the Generalized Reduced Gradient algorithm. You are not required to take any action to use the default settings; however, at times, it may be necessary to set one or more of the parameters to a new value to make the optimizer more efficient or make it possible to solve a difficult problem. The new values remain in effect for the duration of the session.