R Transform
An R script can be executed as a data transformation step in the data pipeline. Specifically:
q Data is retrieved from an underlying source
q The returned data table is translated into an R data frame
q The R data frame, and supplied R Script are passed to an external R process running Rserve
q The external Rserve process returns a resulting R data frame
q The returned data frame is translated into a Panopticon table for visualization rendering
For this to occur, both R and Rserve must be installed, and initialized.
|
NOTE |
· When used with streaming data sources (e.g., message bus), the Real Time Limit of a streaming data source should be set to a value longer than the time taken to perform the R data transform. For example, if the transform operation takes 2 seconds, the Real Time Limit should be set to 2500 milliseconds. · When used for non-streaming data sources (e.g., Database), the data table Auto Refresh period should be set to a value longer than the time taken to perform the R data transform. For example, if the transform operation takes 2 seconds, the data table Auto Refresh period should be set to 3 seconds.
|
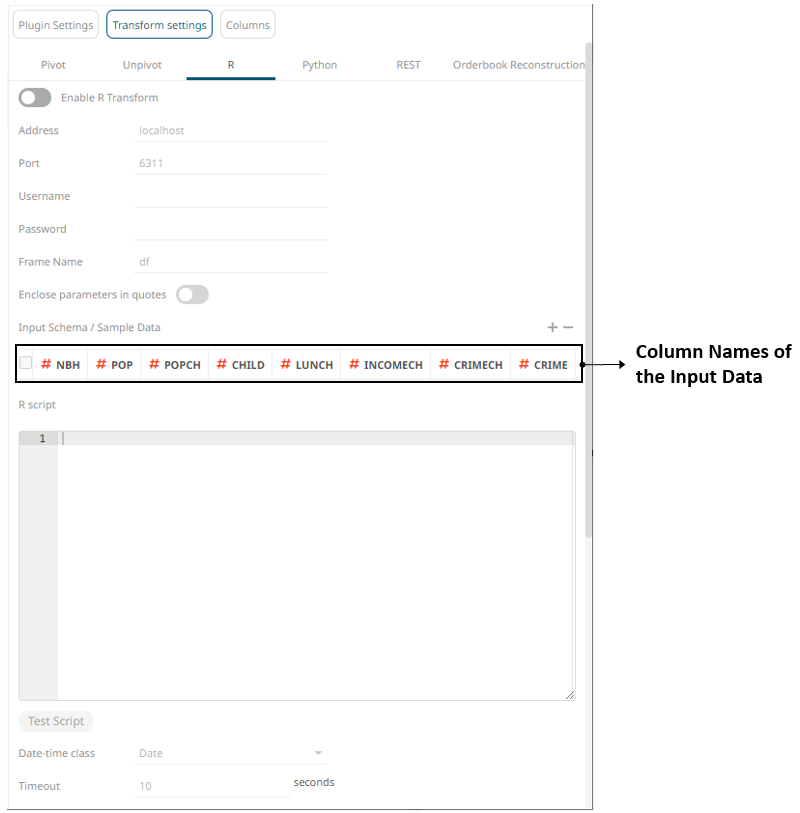
When the R button is selected, the Transform Settings pane changes to show:
Steps:
1. Tap the Enable R Transform slider to turn it on.
The
Transform Settings button and R tab change to  and
and  , respectively.
, respectively.
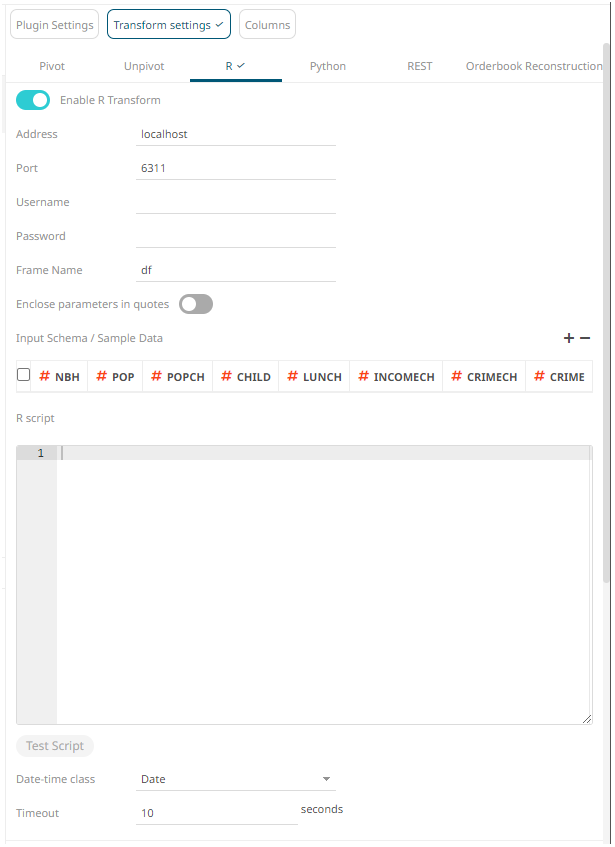
The default Address (i.e., localhost) and Port (i.e., 6311) fields are displayed.
2. Specify the Username and Password if authentication is enabled on the Rserve process.
|
NOTE |
The Address, Port, Username, and Password fields will be hidden if their corresponding properties are set in the Panopticon.properties file.
|
3. The Frame Name that Panopticon will produce, and then be utilized by the R scripts should be specified. Default is df.
4. Specify whether to Enclose Parameters in Quotes.
5. On the Input Schema/Sample Data section, the column names of the input data source are displayed. You can opt to add sample data to ensure transform is applied in case the input database, files, or infrastructure becomes unavailable.
To add or manage the sample data, you can use the following icons:
|
Icon |
Description |
|
|
Add sample data for the input column names. |
|
|
Check a box of a sample data row and click to delete, or check the topmost box and click to delete all of the sample data rows. |
6. Enter the R Script. This R script should reference the input frame name and return a data frame. Just like an underlying SQL query, the R Script itself can be parameterized.
|
NOTE |
This step will work for small and simple use cases. However, when you have several transforms, or when each transform is applied to several data tables, it is highly recommended to follow the instructions in the Best Practices on Working with R Transform in Panopticon section. |
7. Click
 : If
successful, the output schema is displayed.
: If
successful, the output schema is displayed.
Otherwise, a notification is displayed with the cause of the error. Update the script.
8. Select the Date-time class that will be applied to the transform:
· Date is the simplest data type to use for calendar dates. It is stored as integers and is represented as the number of days since 1970-01-01, with negative values for earlier dates.
· chron that can be used for chronological objects which can handle dates and times.
· POSIXct is built-in POSIXt date-time data type with ct that stands for calendar time. It stores the number of seconds since the origin.
9. The Timeout is set to 10 seconds by default to ensure that slow running R scripts do not impact other areas of the product. You can opt to enter a new value.
10. Click  to
see the output columns from the R transform.
to
see the output columns from the R transform.
11. Refer to Enable Time Series Analysis for more information in enabling this feature.