Creating MongoDB Input Data Source
The MongoDB connector is an interface used to import MongoDB’s schema-less BSON documents into a table schema that Panopticon Streams can interpret and analyze. It uses many BSON structure types and MongoDB query features.
Steps:
1. In the New Data Source page, select Input > MongoDB in the Connector drop-down list.
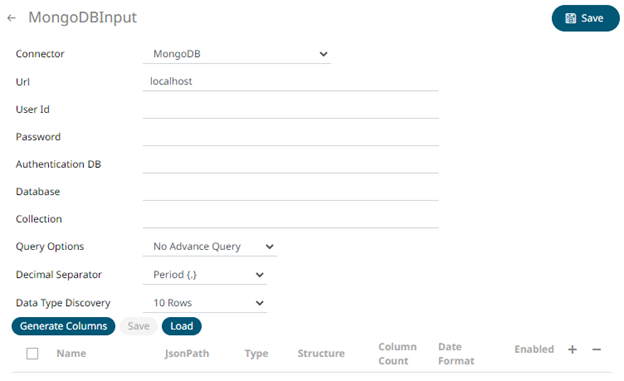
2. Enter the following properties:
|
Property |
Description |
|
URL |
Enter either: · localhost if the database resides on the same computer, or · enter the IP address and port of the computer where MongoDB is installed (e.g., 192.168.1.1:27017). If no port is specified, the default is 27017. |
|
User Id |
The user Id that will be used to connect to MongoDB. |
|
Password |
The password that will be used to connect to MongoDB. |
|
Authentication DB |
The database where the user is created. |
|
Database |
The database that will be used. |
|
Collection |
The collection that will be used. |
3. You can also opt to make the Query Document feature of MongoDB to be available in Panopticon Streams. Select Use Query Document in the Query Options drop-down list.
This also displays the Method drop-down. Select either Find (Default) or Aggregate.
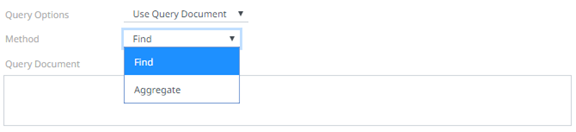
When Aggregate is selected, you can add all the columns generated by aggregation in the schema.
In addition, the MongoDB command line interface displays query operations with a JSON style syntax.
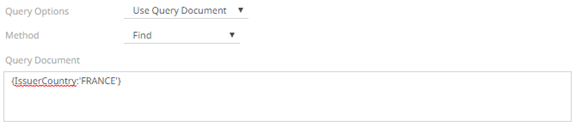
Enter your desired JSON query document. Refer to http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/tutorial/query-documents/ for more information on the Query Documents feature on MongoDB.
For example:
Queries from the documentation look like this: db.inventory.find ( {type: “snacks”} ). The database and collection are already defined in the UI and the Find operation is handled in the code. The user only needs to enter the query document:
{ type : “snacks” }
This query must include surrounding curly braces as well as matching internal braces should the user decide to make a more advanced query.
4. Instead of using Use Query Document, select the Parameterize query option.
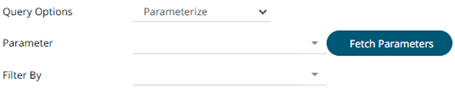
Click Fetch Parameters to populate the Parameter drop-down and select a value. Then select what column to filter on in the Filter By drop-down.
5. Select either the period (.) or comma (,) as the Decimal Separator.
|
NOTE |
Prepend 'default:' for the elements falling under default namespace.
|
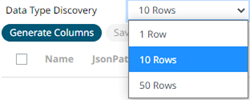
6. Select
the Data Type Discovery.
This property specifies how many rows to fetch from the input data
source, when auto generating the schema after clicking  .
.
7. You can also opt to load or save a copy of the column definition.
8. You can also opt to click  . A
new row displays in the JSON list box. Enter the necessary information
for each column.
. A
new row displays in the JSON list box. Enter the necessary information
for each column.
|
Property |
Description |
|
Name |
The column name of the source schema. NOTE: It is recommended to name the column the same as its JSON path for clarity and uniformity. |
|
JsonPath |
The JsonPath of the source schema. |
|
Type |
The data type of the column. Can be a Text, Numeric, or Time |
|
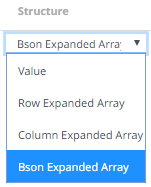
Structure |
Used for more advanced features and are covered in the Row-Wise Array Expansion, Column-Wise Array Expansion, and Bson-Wise Array Expansion sections. Value is the default structure and will always display data regardless of actual structure.
|
|
Column Count |
Enabled when Column-Expanded Array structure is selected.
Enter the number of columns for the plugin to generate as columns for that array. |
|
Date Format |
The format when the data type is Time. NOTE: To parse and format times with higher than millisecond precision, the format string needs to end with a period followed by sequence of upper case S. There can be no additional characters following them. For example: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSSSS |
|
Enabled |
Determines whether the message field should be processed. |
To delete a column,
check its  or
all the column entries, check the topmost
or
all the column entries, check the topmost  , then click .
, then click .
9. Click . The new data source is added in the Data
Sources list.