OS-E: 0600 Steady-state Thermal Analysis with Convection Loading of a Structure with Insulator
Heat sink with fins are commonly used in engineering applications to dissipate heat. The 3D geometry of an aluminum heat sink designed for cooling. The cross-sectional view of a furnace constructed from two materials.

Figure 1. FE Model
Model Files
Refer to Access the Model Files to download the required model file(s).
The model file used in this example includes:
HEAT_CONVECTION_Solid.fem
Model Description
The inner part is made of copper and the outer heat sink wall is made of aluminum. The outer heat sink wall comes into contact with the ambient air and heat convection.
The Finite element model consists of three different materials.
- FE Model
- Element Types
- CHEXA
- Aluminum
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.2
- Heat Capacity Per Unit Mass
- 921.0
- Density
- 2.9E-9
- Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient
- 0.001
- Cooper
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.5
- Heat Capacity Per Unit Mass
- 385.0
- Density
- 6.0E-9
- Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient
- 0.0037
- For Insulator
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.001
- Heat Capacity Per Unit Mass
- 410.0
- Density
- 1.02E-9
- Free Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient
- 0.00017
Results
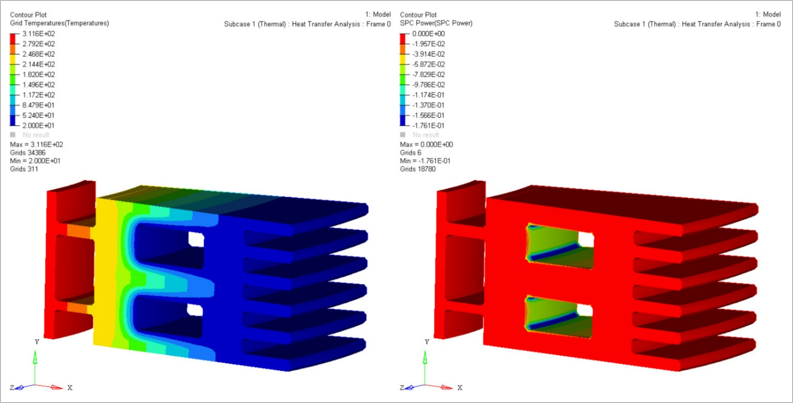
Figure 2. Grid Temperature and SPC Power Contour
