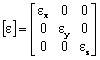Isotropic / anisotropic materials
Introduction
The studied materials can be isotropic or anisotropic. In other words, the magnetic behavior of the material is as follows:
- independent of the direction of the applied field (isotropic material)
- dependent on the direction of the applied field (anisotropic material)
These two cases are presented in the following sections.
Isotropic materials
Isotropic materials are characterized by a law independent of the direction of the applied field.
The ![]() and
and ![]() vectors
are always collinear.
vectors
are always collinear.
The dependence between ![]() and
and ![]() is a
scalar relationship, which is written as: D= ε .E
is a
scalar relationship, which is written as: D= ε .E
Anisotropic materials
Anisotropic materials are characterized by a law, which is dependent on the direction of the applied field.
The ![]() and
and ![]() vectors
are not collinear.
vectors
are not collinear.
The dependence between ![]() and
and ![]() is a
vector relationship, which is written as:
is a
vector relationship, which is written as: ![]()
with ε permittivity tensor: 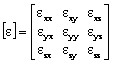
… in Flux
The model provided in Flux is a simplified model.
The vector dependence between ![]() and
and ![]() which is written as:
which is written as: ![]() can therefore be expressed in the form of three curves:
Dx(Ex), Dy(Ey),
Dz(Ez)
can therefore be expressed in the form of three curves:
Dx(Ex), Dy(Ey),
Dz(Ez)
The permittivity tensor is then written: