Constant Value Arguments
When an argument is passed as a constant, it is converted to a constant value table by the Expression Builder.
- The argument is a value table.
- The argument is of a specific format (scalar, vector, or tensor).
- The argument is bound to a specific entity type.
Operators that accept general value types will not accept constant value arguments. Examples of operators that fail to meet these criteria are unary operators in the Math Library (which accept scalar, vector, or tensor types, bound to any entity type). These restrictions are necessary in order to create a constant value table.
The composite failure theory example below requires five material-bound scalar value tables in order to function (Xt, Xc, Yt, Yc, and S).
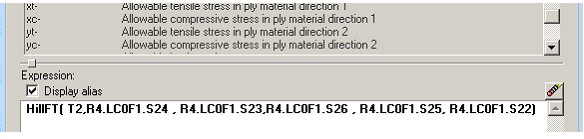
Figure 1.
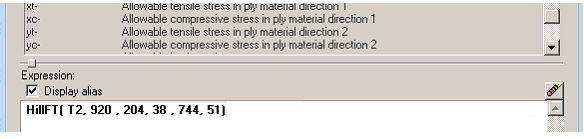
Figure 2.