ACU-T: 4200 Humidity – Pipe Junction
Prerequisites
Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory HyperWorks tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 HyperWorks UI Introduction. To run this simulation, you will need access to a licensed version of HyperMesh and AcuSolve.
Since the HyperMesh database (.hm file) contains meshed geometry, this tutorial does not include steps related to geometry import and mesh generation.
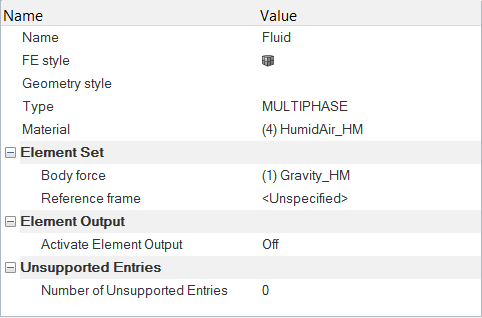
Problem Description
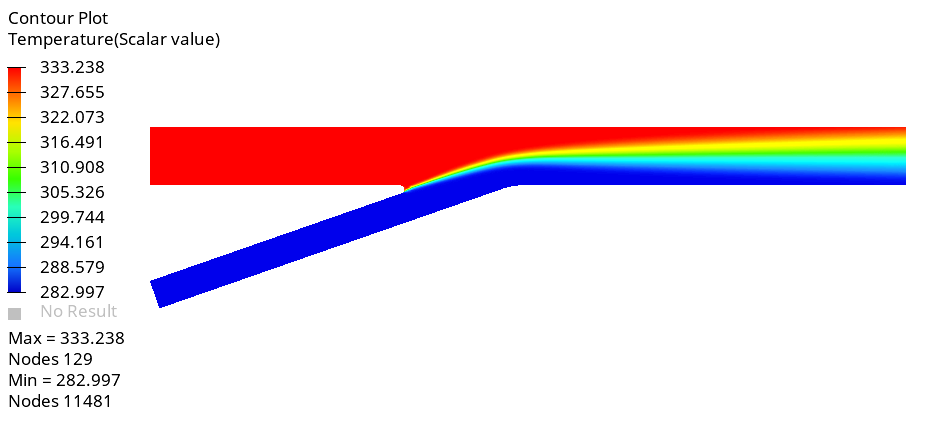
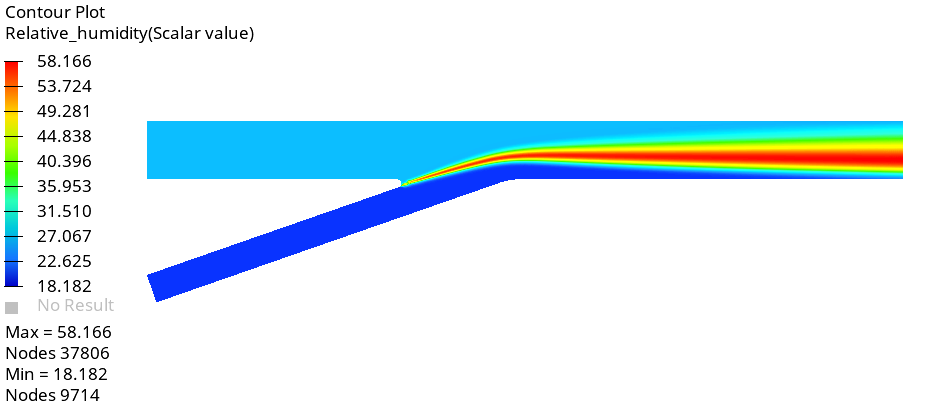
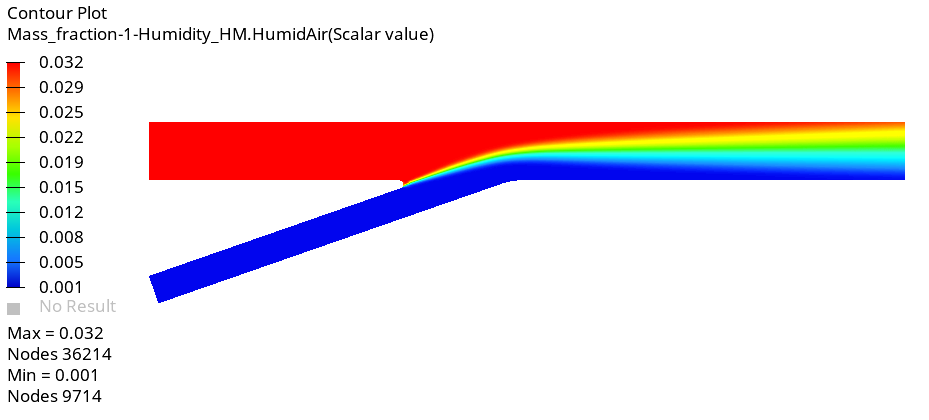
The problem to be addressed in this tutorial is shown schematically in Figure 1. As an example, a pipe junction problem is attached here to show the capability of the Humidity modelling in AcuSolve. In this problem, there are two inlets with different flow, thermal, and humidity conditions. As the flow proceeds downstream of the pipe, two pipes merge into a single pipe to create a single outlet and a distinct profile of temperature and humidity is attained. The geometry is symmetric about the XZ midplane of the pipe, as shown in the figure.
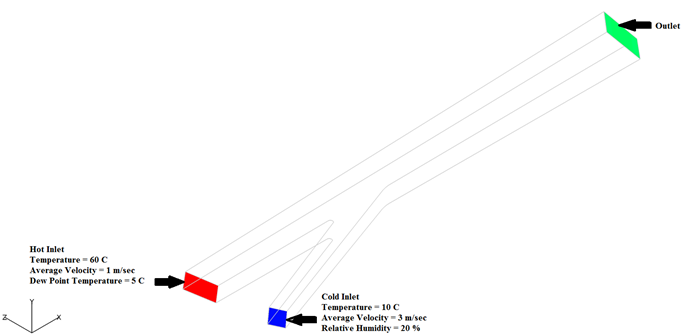
Figure 1.
Open the HyperMesh Model Database
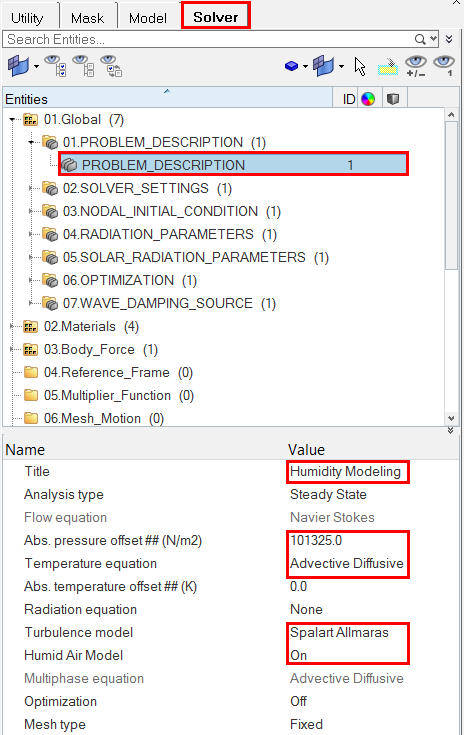
Set the General Simulation Parameters
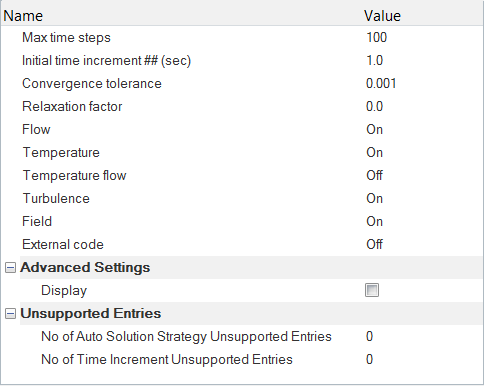
Set the Analysis Parameters
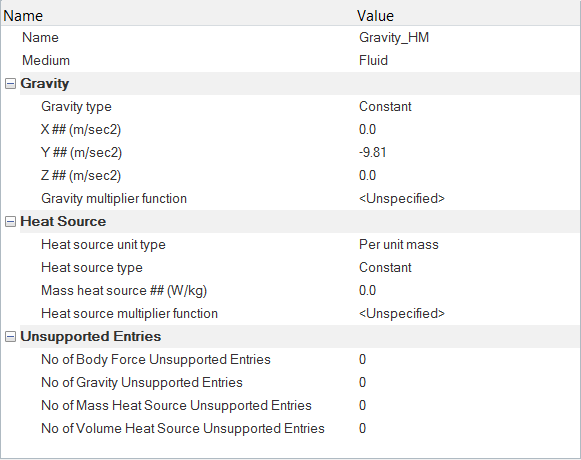
Set Up Body Force Parameters
Set Up Boundary Conditions and Nodal Initial Conditions
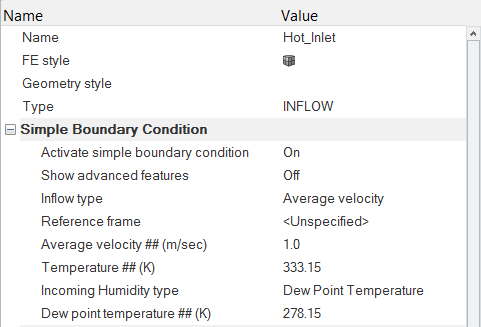
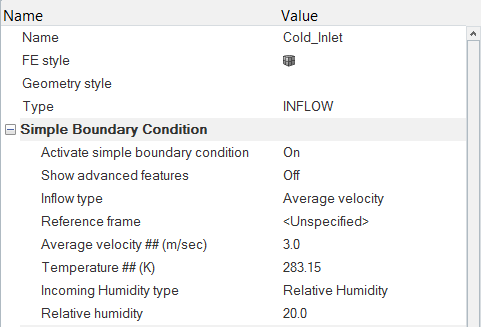
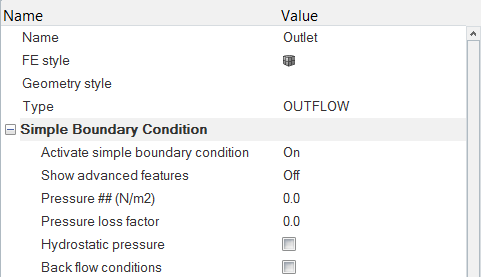
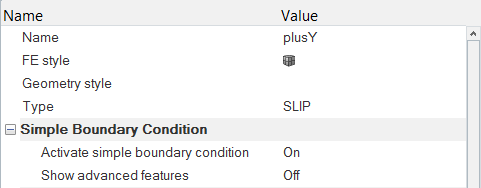
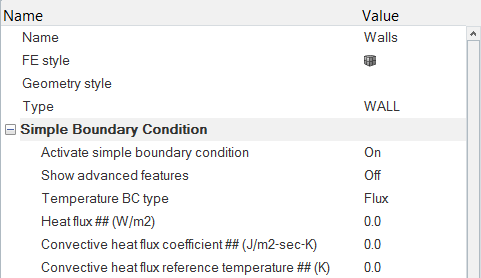
Set the Boundary Conditions
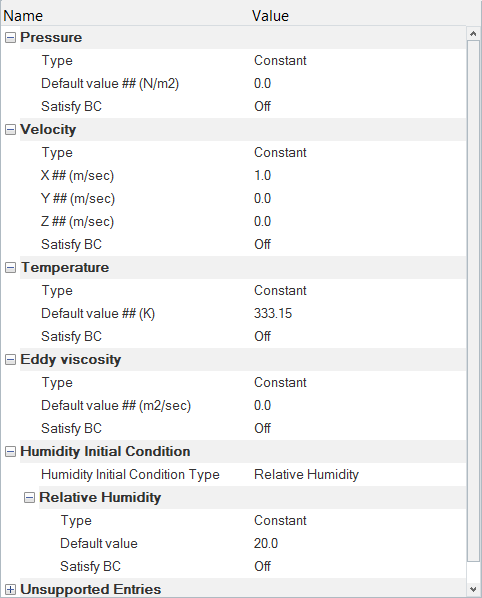
Set the Nodal Initial Conditions
Compute the Solution
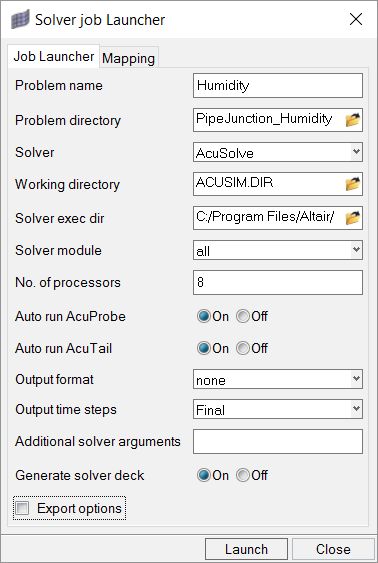
In this step, you will launch AcuSolve directly from HyperMesh and compute the solution.
Run AcuSolve
Post-Process the Results with HyperView
Open HyperView and Load the Model and Results
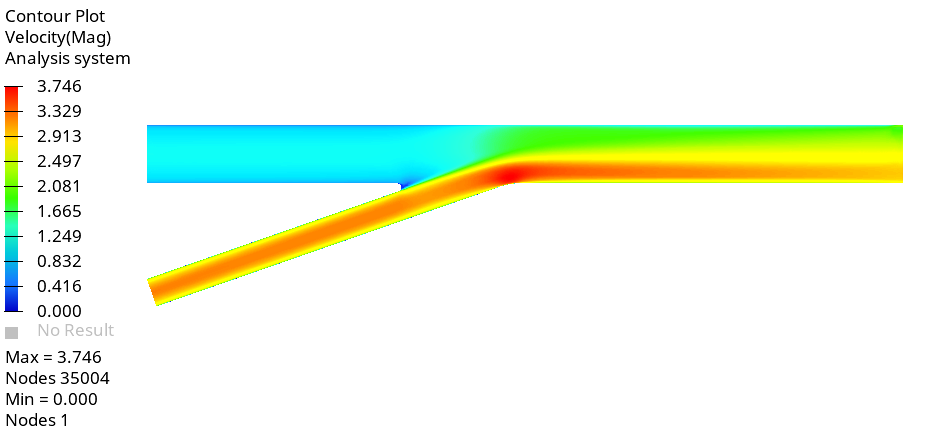
Create Contour Plots
Summary
In this tutorial, you worked through a basic workflow to set-up a CFD model, carried out a CFD simulation, and then post-processed the results using HyperWorks products, namely AcuSolve, HyperMesh and HyperView. You started by importing the model in HyperMesh. Then, you defined the simulation parameters and launched AcuSolve directly from within HyperMesh. Upon completion of the solution by AcuSolve, you used HyperView to post-process the results and create contour plots.