ACU-T: 7010 Shape Optimization using HyperStudy
Prerequisites
Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory HyperWorks tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 HyperWorks UI Introduction, and have a basic understanding of HyperMesh, AcuSolve, and HyperView. To run this simulation, you will need access to a licensed version of HyperMesh and AcuSolve.
Since the HyperMesh database (.hm file) contains meshed geometry, this tutorial does not include steps related to geometry import and mesh generation.
Problem Description
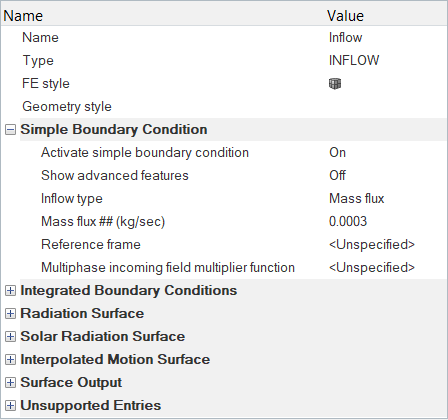
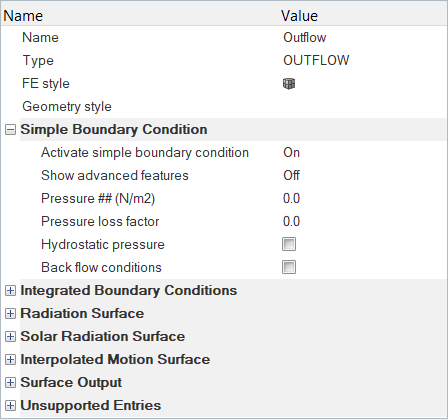
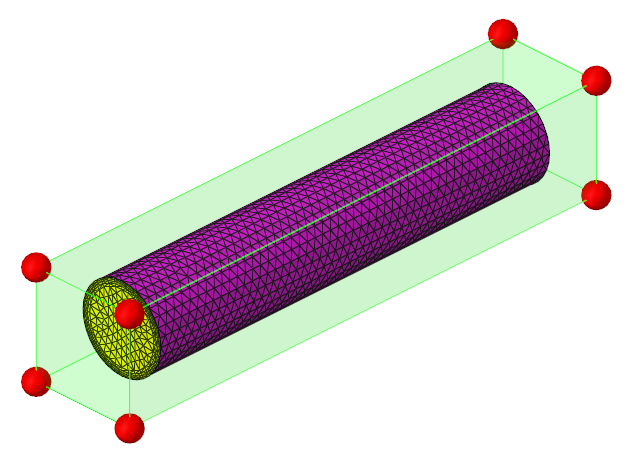
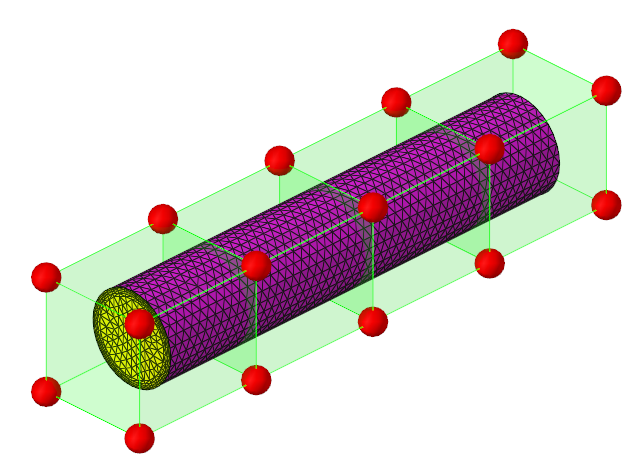
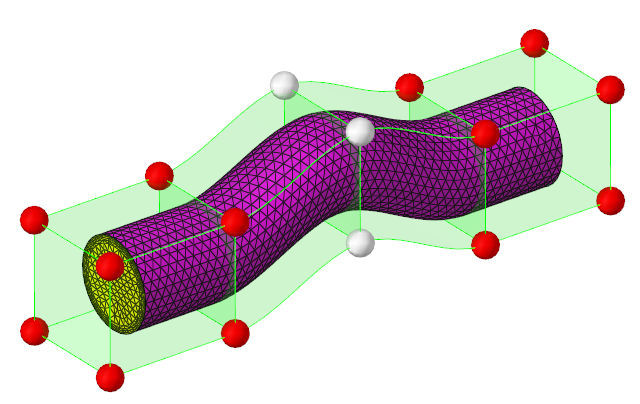
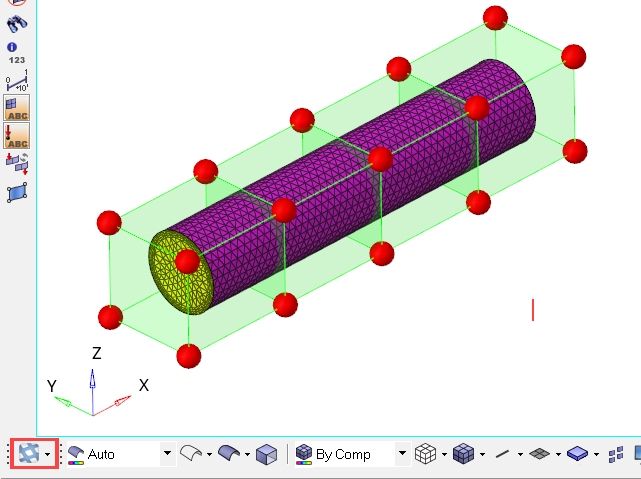
The geometry for this problem consists of a simple pipe channel with perfectly circular cross-section as the base shape. Water enters the Inlet at the rate of 0.0003 kg/s and the outlet is a standard pressure outlet at zero relative pressure. Walls of the channel are no-slip walls.

Figure 1.
Open the HyperMesh Model Database
Specify the Boundary Conditions
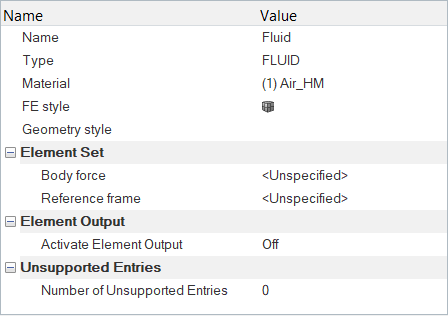
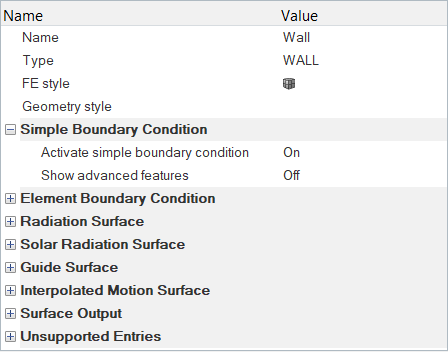
By default, all components are assigned to the wall boundary condition. In this step, you will change them to the appropriate boundary conditions and assign material properties to the fluid volumes.
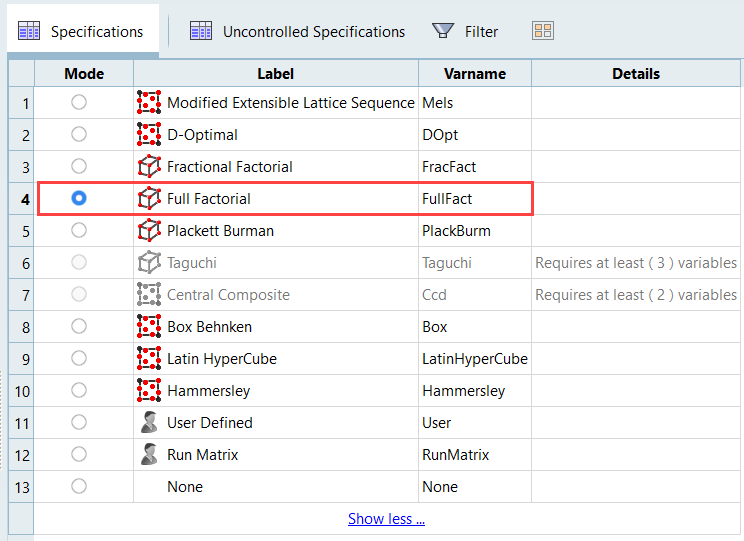
Set the Optimization Parameters
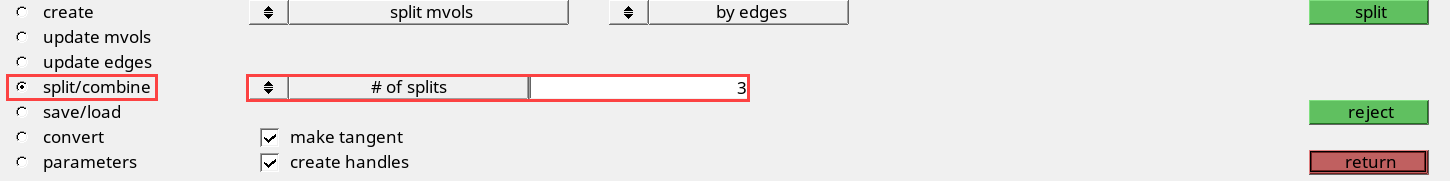
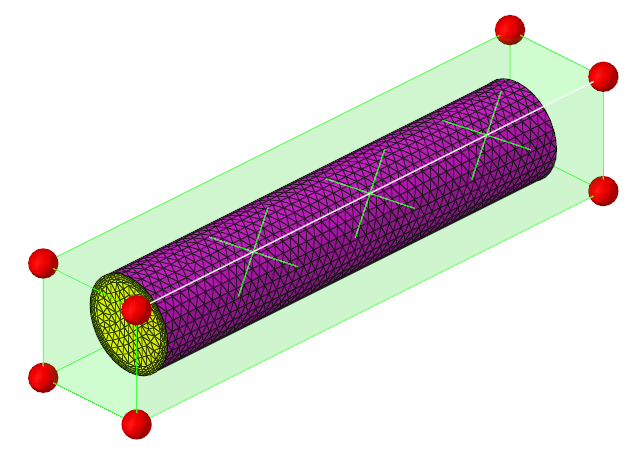
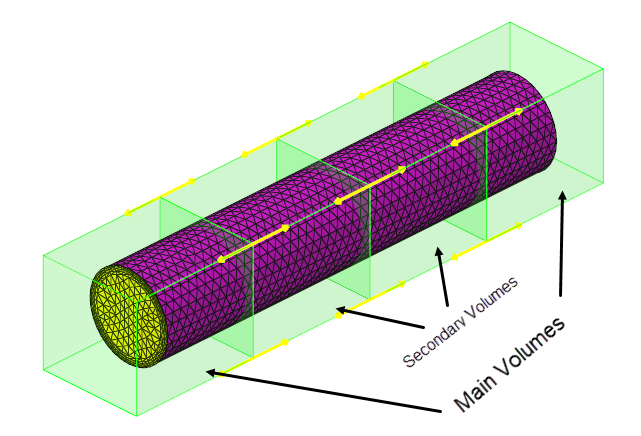
Generate and Export Morph Shapes
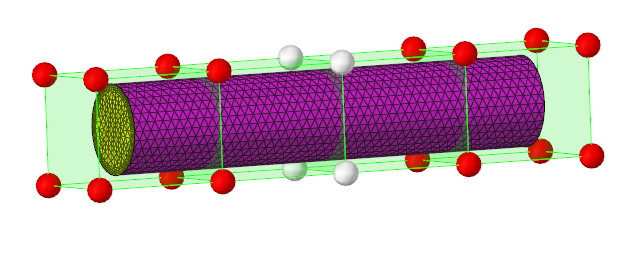
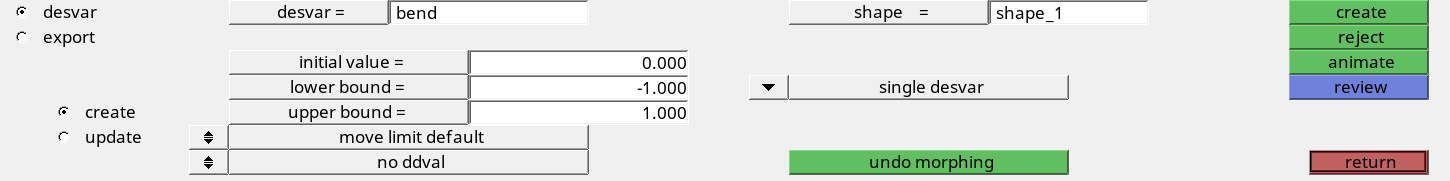
Define the Design Variable
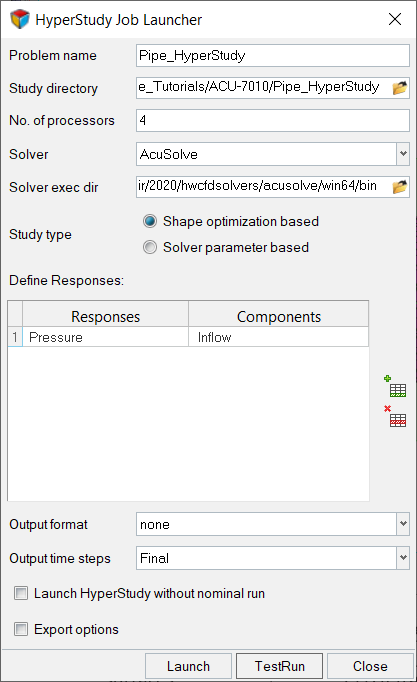
Launch the DOE Study Using HyperStudy
Start the Nominal Run
In the HyperStudy window, check step by step by clicking on each setup from the Explorer menu to ensure that everything was properly defined.
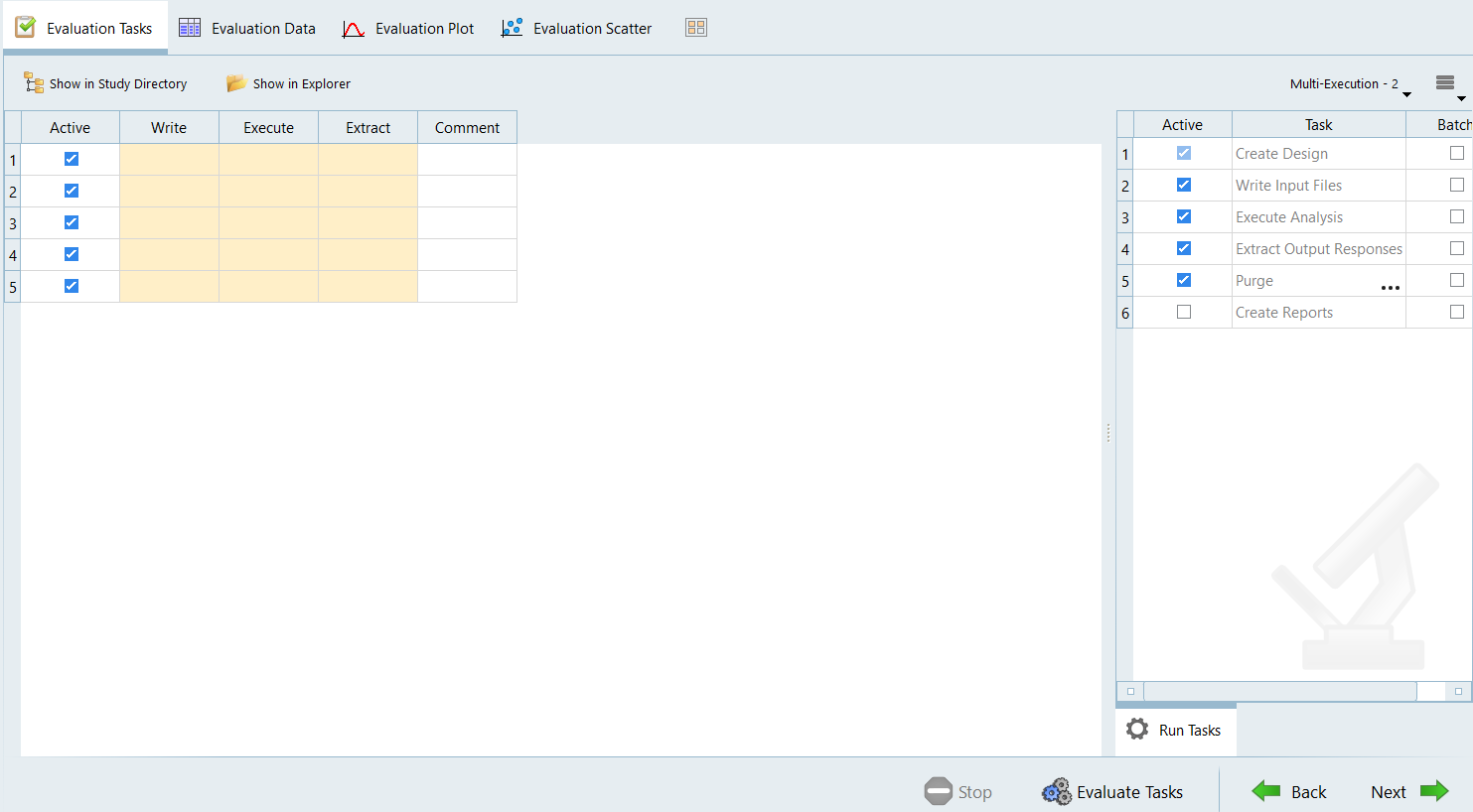
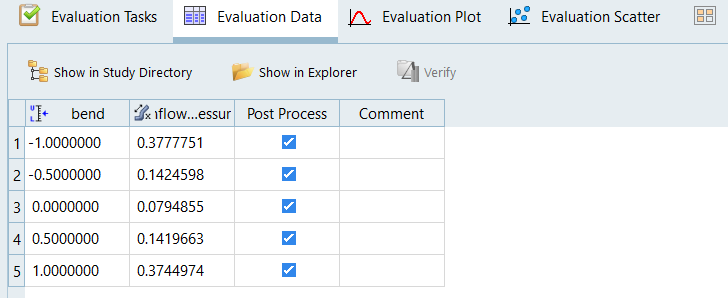
Run the DOE Study
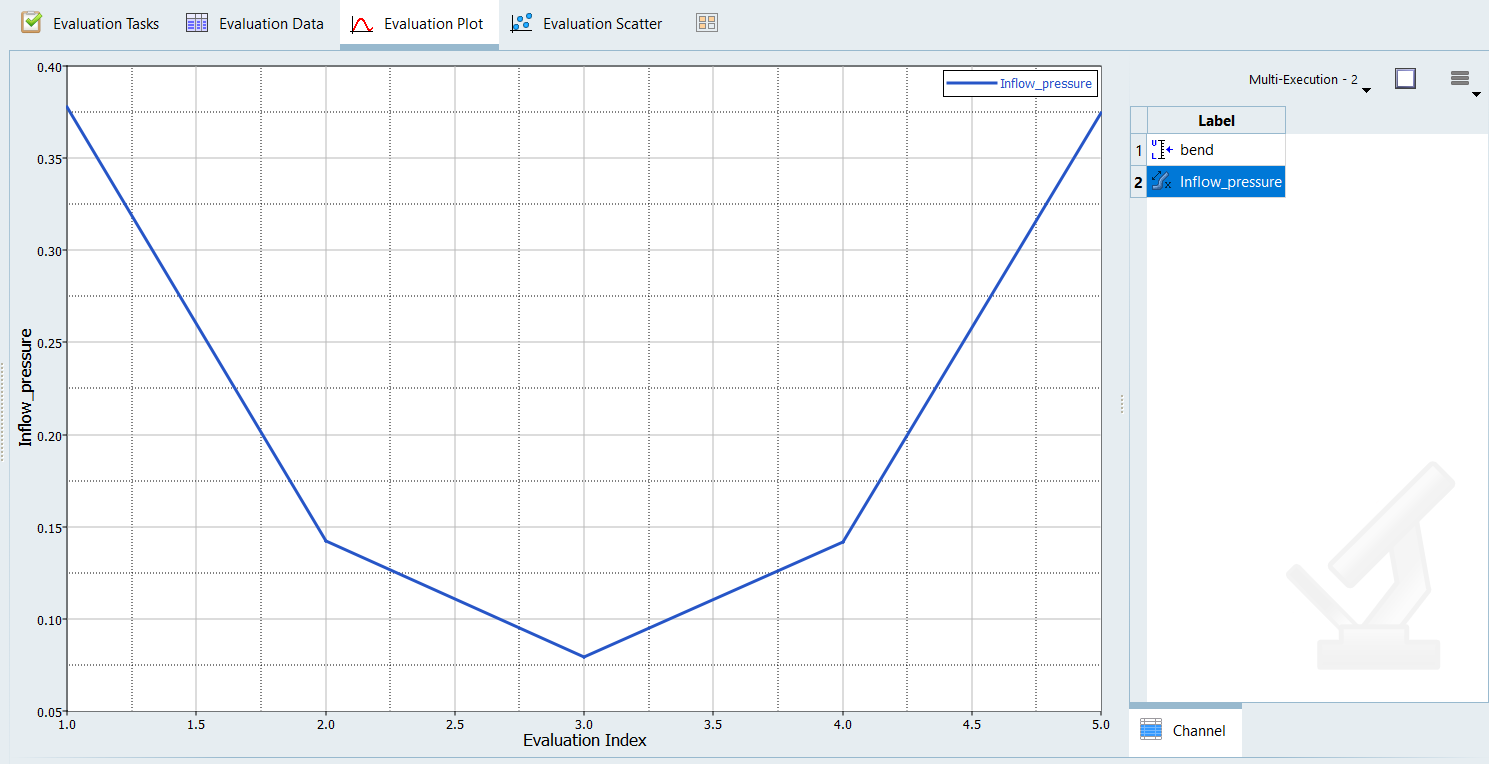
Post-Process the Results with HyperView
Switch to the HyperView Interface and Load the AcuSolve Model and Results
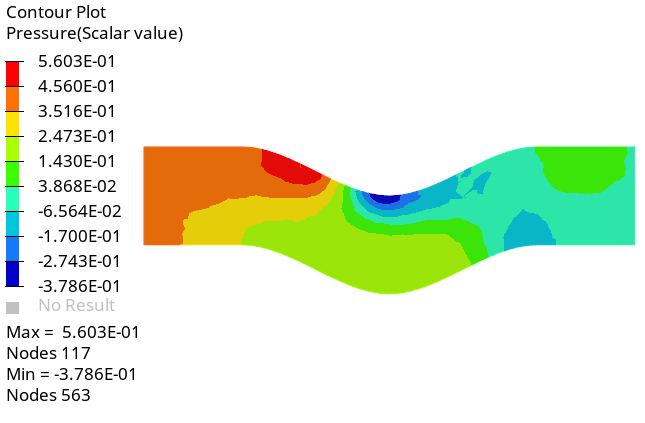
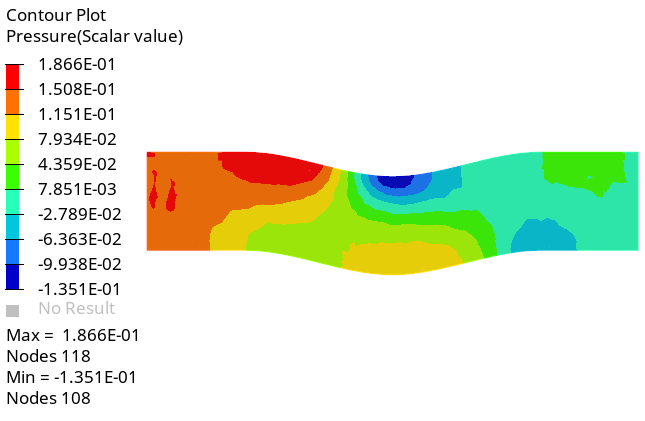
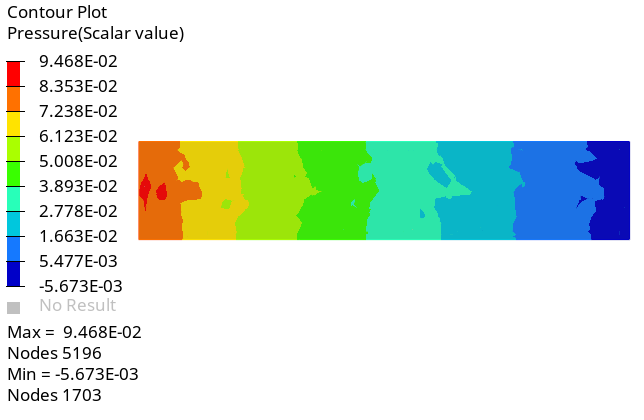
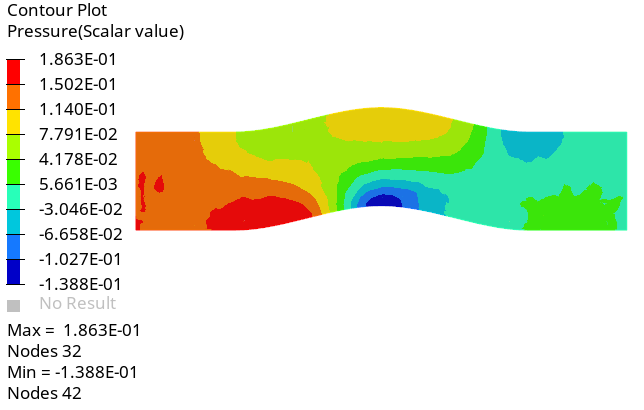
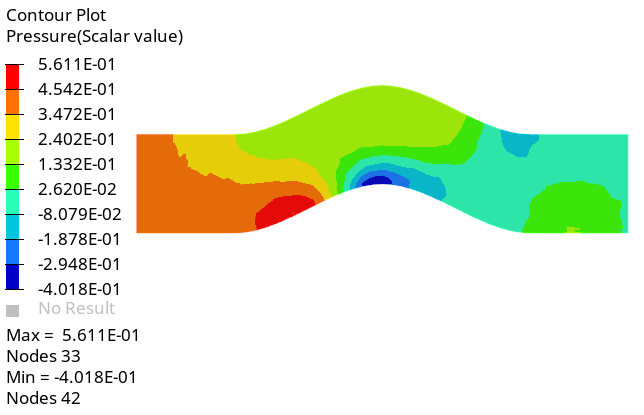
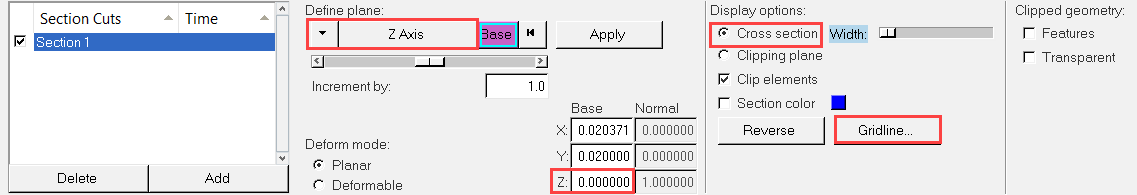
Create a Pressure Contour on a Cut Plane
Summary
This tutorial introduced you to running a DOE study using Altair products, namely HyperMesh, AcuSolve, HyperStudy and HyperView. You started by importing a HyperMesh database and then set up the simulation parameters for AcuSolve and created a morph shape using HyperMorph. Next, you set up the design variable and linked the morph shape to it. Then, you proceeded to set up the DOE study. Once the results were obtained, you processed the results using HyperView.



 on the Standard Views toolbar.
on the Standard Views toolbar.