ACU-T: 5100 Modeling of a Fan Component Using the Fan Component - Coefficient Method
Prerequisites
This simulation provides instructions for running a steady state simulation of flow inside a pipe with an interior fan placed at the middle of the pipe. Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 HyperWorks UI Introduction, and have a basic understanding of AcuSolve and HyperMesh. To run this simulation, you will need access to a licensed version of HyperMesh and AcuSolve.
Since the HyperMesh database (.hm file) contains meshed geometry, this tutorial does not include steps related to geometry import and mesh generation.
Problem Description
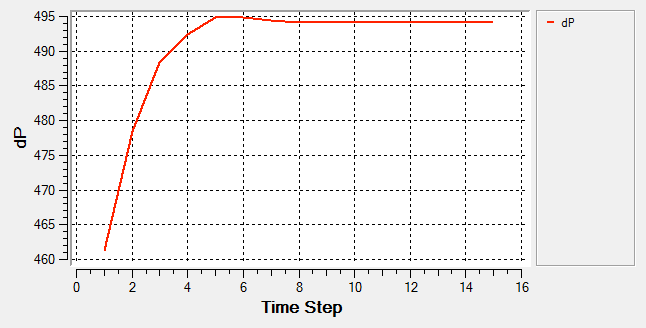
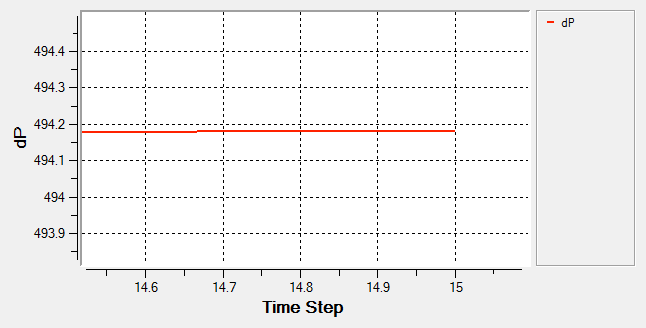
The problem to be solved in this tutorial is shown schematically in the figure below. It consists of an interior fan which rotates at a speed of 377 rad/sec (~3600 RPM) and has a thickness of 0.06 m and a tip radius of 0.11 m. The volumetric flow rate at the inlet is 0.146 m3/sec (~525.35 m3/hr). The problem is simulated as a steady state run and the pressure rise across the fan region is computed.

Figure 1.
Open the HyperMesh Model Database
Set the General Simulation Parameters
Set the Boundary Conditions
Compute the Solution
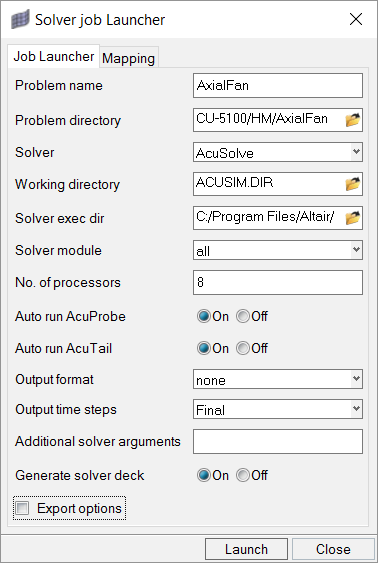
In this step, you will launch AcuSolve directly from HyperMesh and compute the solution.
Run AcuSolve
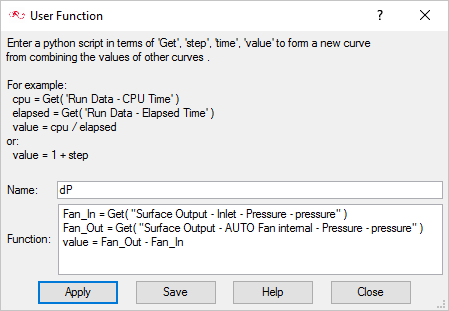
Post-Process with AcuProbe
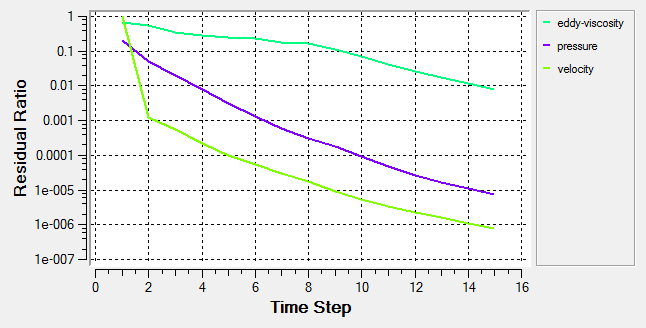
As the solution progresses, the AcuProbe window is launched automatically. AcuProbe can be used to monitor various variables over solution time.
Summary
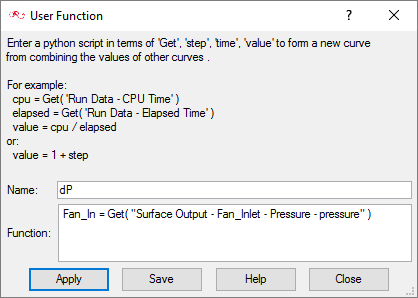
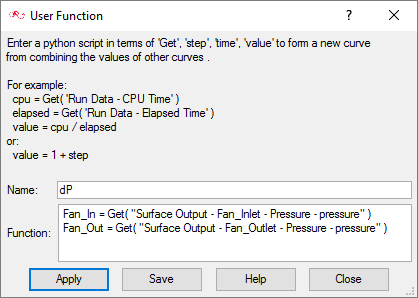
In this tutorial you successfully learned how to set up and solve a simulation involving a fan component. You imported the meshed geometry and then assigned the material properties and boundary conditions to all the regions. Once the solution was computed, you defined a user function to create a plot of the pressure rise across the fan component volume.