Bonding (legacy)
Please note that EDEM has two Bonding Models. The original (legacy) model as described here is not GPU compatible and is marked as deprecated to be removed in a later version. An updated model Bonding V2 has been included which is GPU compatible. The Bonding V2 model also has updated physics capabilities and is recommended over the legacy Bonded model.
The Bonding contact model bonds spheres together. To use, enable the bonding model for particle-particle interactions.
The Bonding contact model can be used to bond particles with a finite-sized “glue” bond. This bond can resist tangential and normal movement up to a maximum normal and tangential shear stress, at which point the bond breaks. Thereafter the particles interact as hard spheres. This model is based on work of Potyondy and Cundall (Potyondy and Cundall 2004). This model is particularly useful in modeling concrete and rock structures.
Bonds are created between particles at the formation start time:
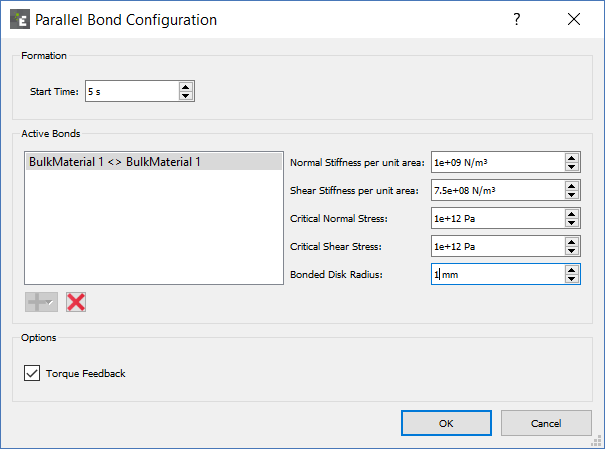
If the bulk material Active Bonds are defined and the Particles that comprise of the Bulk Material are in contact at the formation start time then the bonds are formed according the bond parameters. This occurs once per simulation and once the bond time has passed no new bonds will be formed.
After bonding, the forces (Fn,t)/torques (Tn,t) on the particle are set to zero and are adjusted incrementally every time step according to:
where:
RB is the radius of the “glue”, Sn,t are the normal and shear stiffness respectively and δt is the time step. vn,t are the normal and tangential velocities of the particles and ωn,t the normal and tangential angular velocities.
The bond is broken when the normal and tangential shear stresses exceed some predefined value:
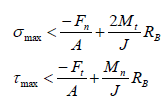
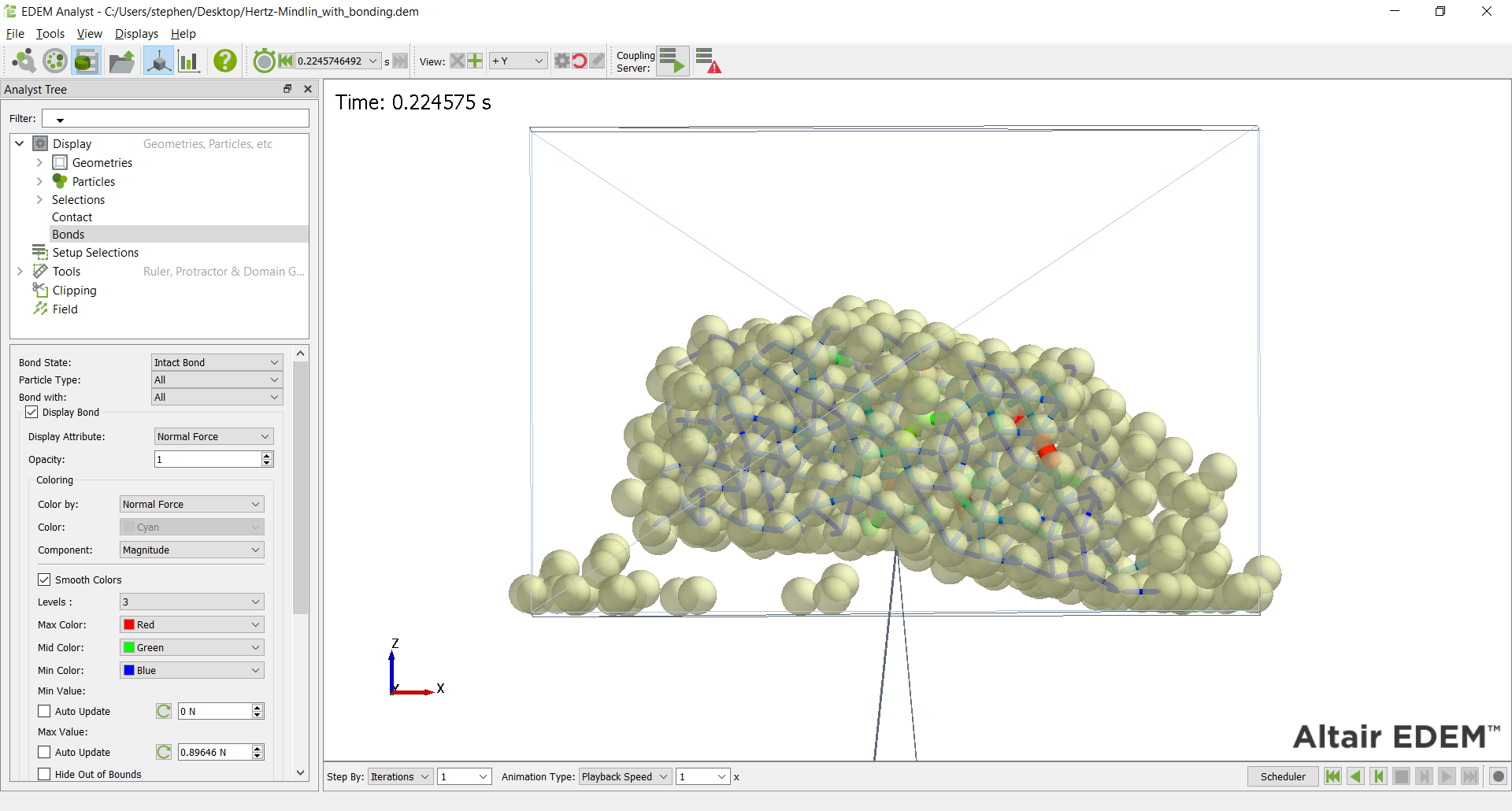
These bond forces/torques are in addition to the Base Contact Model. Since the bonds involved in this model can act when the particles are no longer physically in contact, the contact radius should be set to higher than the actual radius of the spheres. This model may only be used between particles.
| Interaction | Configurable Parameters | Position |
|
Particle to Particle |
Select an active bond then set the Bond Formation Time and the following parameters:
Set the bond stress and stiffness values to represent the material that is been modeled. A high stiffness value will produce high bond forces and stresses. A lower than normal time step may be required to accurately capture these high forces.
When the Bond Formation Time is reached, all defined particles in contact will be bonded together. Before this time, particles interact based on the Hertz-Mindlin contact model.
Note that a bond between two particles will cease to exist whenever one or both of the bonded particles leaves the simulation domain. If periodic boundaries are applied when the particle leaves the domain, then the particle will exist on the opposite side of the domain; in this case the two particles will remain bonded across the periodic boundary.
When Torque Feedback is selected the bonded structure has a greater resistance to bending when considering a bond between two spheres, for a bonded structure where rotation is limited this setting has less impact. |
Last |
Bonds can be post-processed in the EDEM Analyst under Bond information. Please note that the Bonded V2 model uses Custom Contacts, as such the post-processing uses Contact information in the Analyst.