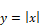
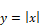
Block Category: Arithmetic
Inputs: Real, complex, or fixed-point scalars, or vectors or matrices.
Description: The abs block produces the absolute value of the input signal.
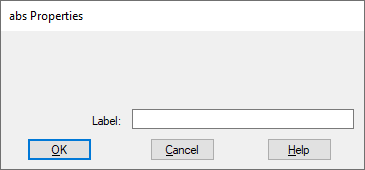
Label: Indicates a user-defined block label that appears when View > Block Labels is activated.
1. Absolute value of a scalar
Consider the equation y = abs (sin (t)) realized as:
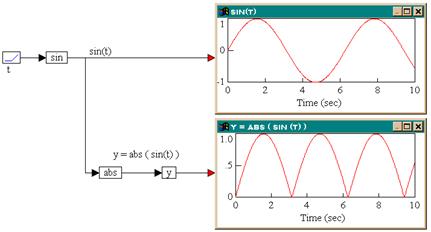
The results in the two plot blocks show that the abs block computes the absolute value of the input signal.
2. Absolute value of a vector
Consider the equation:
w = abs (x)
where x = [-7 1 -2.2] realized as:
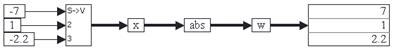
When the simulation runs, the abs block computes and outputs an element-by-element absolute value of the vector x.
3. Absolute value of a matrix
Consider the equation:
Z = abs(Q)
where:
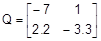
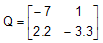
This equation is realized as:
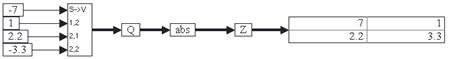
Four const blocks provide the vector element values of Q through a scalarToVector block. When the simulation runs, the abs block computes the element-by-element absolute value of the incoming matrix.