Infinite Planes and Half-Spaces
Use an infinite plane or half-space to model a ground plane efficiently. The number of triangles in the model is reduced as the ground plane is not discretised into triangles.
On the Construct tab, in the Structures
group, click the ![]() Planes/arrays icon. From the drop-down list, select
Planes/arrays icon. From the drop-down list, select ![]() Plane / ground.
Plane / ground.
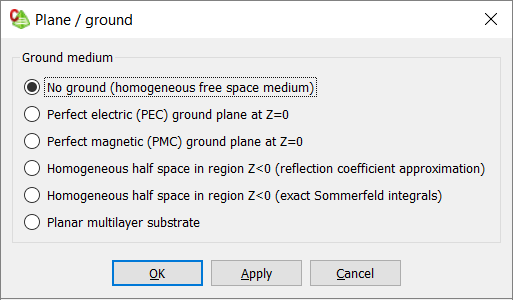
Figure 1. The Plane / ground dialog.
No Ground (Homogeneous Free Space Medium) [Default]
The model is solved in a homogeneous environment filled with free space medium. Edit the properties of free space if required.
Perfect Electric (PEC) Ground Plane at Z=0
Perfect Magnetic (PMC) Ground Plane at Z=0
Homogeneous Half Space in Region Z<0 (Reflection Coefficient Approximation)
- For the reflection coefficient approximation ground, the structures must be above (Z>0) and at least away from the ground plane, where is the free space wavelength.
- This technique is faster and potentially less accurate than the exact Sommerfeld integrals method.
Homogeneous Half Space in Region Z<0 (Exact Sommerfeld Integrals)
- A dielectric face may not coincide with the Z=0 half-space boundary.
- A metallic face may coincide with the Z=0 half-space boundary.
- Structures may cross the Z=0 half-space boundary.
- Structures may be inside (Z<0) the half-space boundary.
Planar Multilayer Substrate
- Supports arbitrarily shaped structures inside the substrate. Structures may cross multiple layers.
- Enclose the substrate in a MoM / SEP region to create a finite planar multilayer substrate.