MultiSphere Particles
Add a Particle Shape
A particle is defined using one or more spheres. Multiple sphere surfaces can be overlapped to create multi-sphere particles.
Right click on the Bulk Material and choose Add MultiSphere Particle or use the  icon. This creates a new particle shape in the Creator Window:
icon. This creates a new particle shape in the Creator Window:
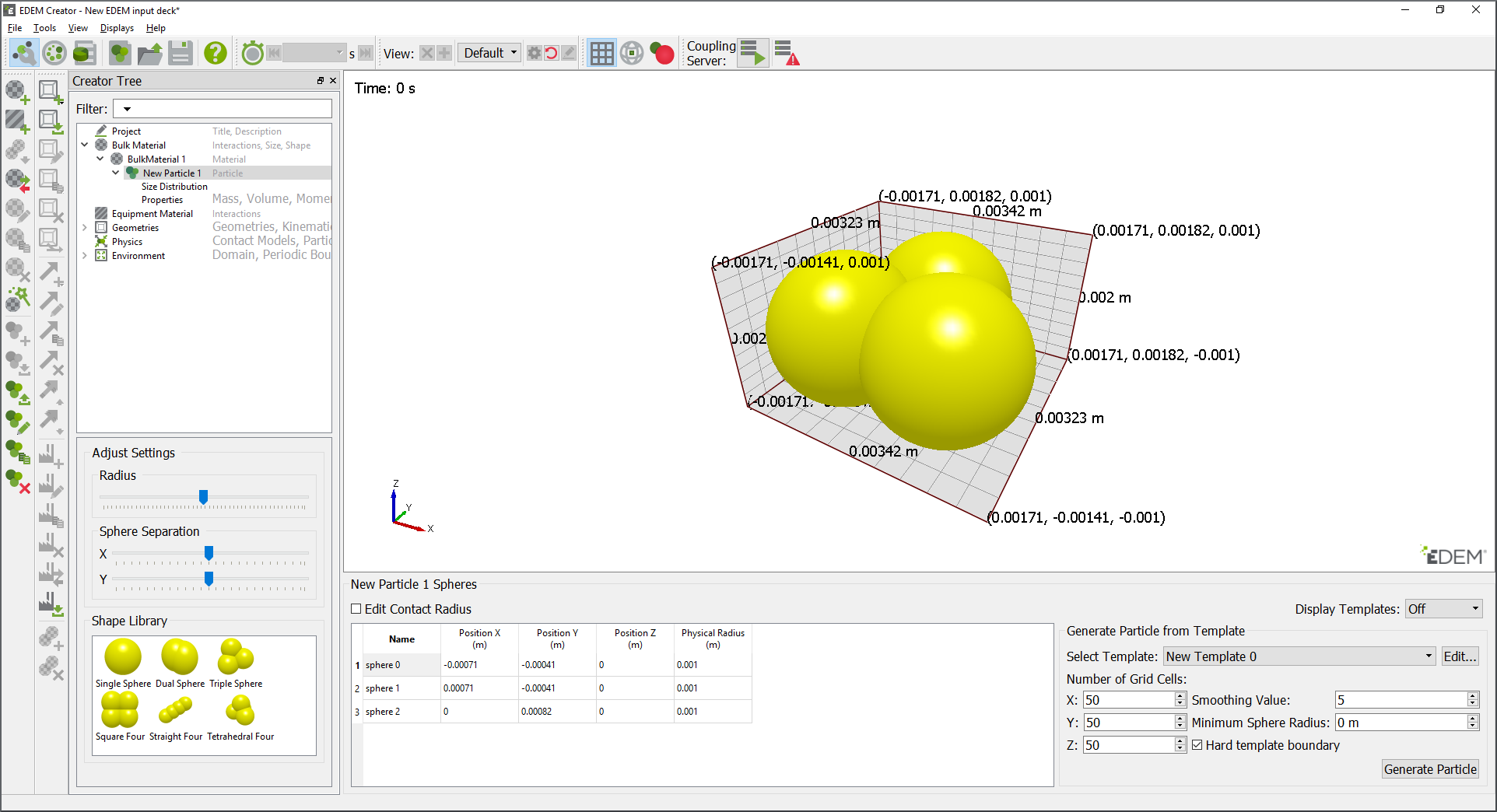
A MultiSphere particle can be made from multiple spheres. In the image above each sphere is called sphere N where N is between 0 and the ‘number of spheres -1’.
The user can modify the X,Y,Z position of each sphere for the particle shape, user can also add, copy or remove a sphere from the particle using the icons  ,
,  ,
,  or the right click menu. Duplicating a sphere adds a new sphere in the list, the radius and position can then be modified by the user.
or the right click menu. Duplicating a sphere adds a new sphere in the list, the radius and position can then be modified by the user.
The sphere table can be copied and pasted from an external source. The table must match the format of the table in EDEM.
Select Contact Radius when the particle has a different interaction (contact) which is not on its physical surface, such as contact radius due to other (long-range) forces acting upon it or inter-particle bonds. This option should only be used with a relevant user-defined contact model. When two contact radii overlap the contact force calculation is entered into; the physical radius of the spheres is used to calculate the magnitude of the physical contact force however user-defined forces can be applied when the contact radii overlap.
For multiple spheres, use the Position X, Y and Z options to define their relative positions. Note that multi-sphere particles should be centered on the origin along the principle axes to ensure that the moments of inertia are calculated correctly.
Copy Particle
Select the particle and choose Copy Particle  , this makes a copy of the particle, and associated spheres, with the name New Particle N.
, this makes a copy of the particle, and associated spheres, with the name New Particle N.
Add a Particle Shape from Library
A particle can be added and described manually or can be chosen from a list of shapes using the Add Shape From Library option.
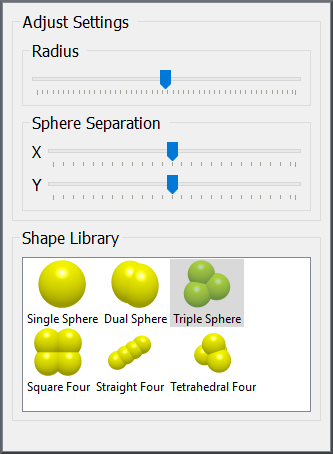
On choosing this option the radius, X, Y, Z position and sphere separation (in the X and Y axes) of each shape can be set.
Modify Particle Shape
A particle shape can be modified by changing the values in the table. In addition, selecting the Particle and choosing Modify Shape will show the following toolbar:
The Radius slide bar changes the radius (scale) of the shape while maintaining the same shape profile. Surface Separation will change the surface separation (shape profile) by modifying the sphere positions in the X axis or Y axis.
Export Particle Shape
Once a particle has been defined it can be exported for use in other EDEM simulations. Right click on the particle and choose Export Particle  and save the file to your Particles folder (as specified using Tools > Options > File Locations). Files are exported in the .dem format.
and save the file to your Particles folder (as specified using Tools > Options > File Locations). Files are exported in the .dem format.
Import a Particle Shape
Any particle created in EDEM can be exported for use in other models. To import a particle click the Import button  and navigate to your chosen file, only particles exported from EDEM simulations can be imported.
and navigate to your chosen file, only particles exported from EDEM simulations can be imported.
Calculate Particle Properties
The particle mass, volume and inertia need to be set. These can be calculated automatically by EDEM or input manually.
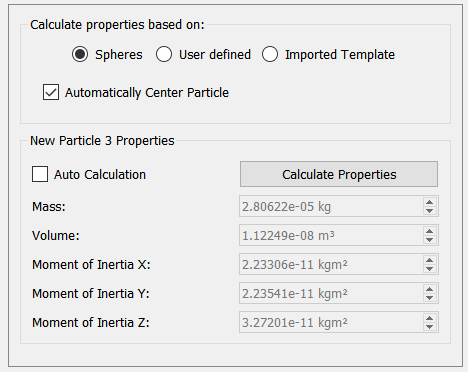
Automatically Calculate Properties:
- Select whether to calculate using the spheres that make up your particle, or (preferably) from an imported template.
- Check whether you want to automatically center the particle when calculating the moments of inertia. Unchecking this option may result in non-physical results.
- Click Calculate Properties to calculate the mass, volume, and moments of inertia for the current particle.
- If Auto Calculation is selected then any changes to the defined Particle size or shape will automatically trigger the Calculate Properties tool.
Since random sampling is used to calculate particle properties, re-calculating for particles with multiple surfaces may result in slightly different values.
User Defined Properties:
Type values for each property into the relevant field. If a value turns red it is not recommended.
| Properties | Description |
|
Mass |
Mass of the particle. |
|
Volume |
Volume of the particle measured. |
|
Moment of Inertia X/Y/Z |
The moment of inertia is a measure of a body's resistance to angular acceleration. A particle consists of a number of spheres, i, each with mass mi and radius ri. If each sphere is a distance di from a particular axis of rotation, then the moment of inertia of the particle about that axis is given by: You can input different values for the moment of inertia to take into account particles of varying material properties (such as hollow spheres). |