Ityp = 1
Block Format Keyword This law enables to model a liquid inlet condition by providing data from stagnation point. Liquid behavior is modeled with linear EOS.
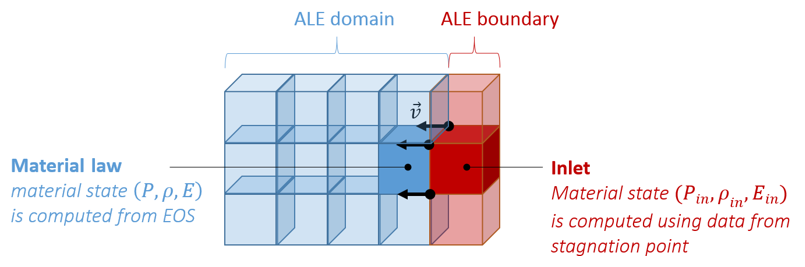
Figure 1.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /MAT/LAW11/mat_ID/unit_ID or /MAT/BOUND/mat_ID/unit_ID | |||||||||
| mat_title | |||||||||
| Ityp | Psh | FscaleT | |||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| node_IDV | C1 | Cd | |||||||
| fct_IDp | |||||||||
| fct_IDE | |||||||||
| Blank Format | |||||||||
| Blank Format | |||||||||
| fct_IDT | fct_IDQ | ||||||||
Definitions
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| mat_ID | Material
identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| unit_ID | Unit Identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| mat_title | Material
title. (Character, maximum 100 characters) |
|
| Initial stagnation
density. 3 (Real) |
||
| Reference density used in
E.O.S (equation of state). Default (Real) |
||
| Ityp | Boundary condition type.
1
(Integer) |
|
| Psh | Pressure shift. 2 (Real) |
|
| FscaleT | Time scale factor. 3 (Real) |
|
| node_IDV | Node identifier for velocity computation. 4
(Integer) |
|
| C1 | Liquid bulk modulus. 9 (Real) |
|
| Cd | Discharge coefficient.
5 Default = 0.0 (Real) |
|
| fct_ID | Function
identifier for stagnation
density. 3
(Integer) |
|
| fct_IDp | Function
identifier for stagnation
pressure. 3
(Integer) |
|
| Initial stagnation
pressure. 3 (Real) |
||
| fct_IDE | Function
identifier for stagnation
density. 3
(Integer) |
|
| Initial specific volume
energy at stagnation point. 3
8 (Real) |
||
| fct_IDT | Function
identifier for inlet
temperature. 3
6
(Integer) |
|
| fct_IDQ | Function
identifier for inlet heat
flux. 3
6
(Integer) |
Comments
- Provided gas
state from stagnation point
is used to compute inlet gas state. Bernoulli is
then applied.
(1) This leads to inlet state:(2) - The Psh parameter enables shifting the output pressure, which also becomes P-Psh. If using Psh=P(t=0), the output pressure will be , with an initial value of 0.0.
- If no function is defined, then related quantity remains constant and set to its initial value. However, all input quantities can be defined as time dependent function using provided function identifiers. Abscissa functions can also be scaled using FscaleT parameter which leads to use f (Fscalet * t) instead of f(t).
- Inlet velocity is used in Bernoulli theory.
- Discharge coefficient accounts for
entry loss and depends on shape orifice.
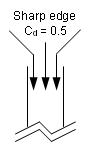
Figure 2. - With thermal modeling, all thermal data ( , ...) can be defined with /HEAT/MAT.
- It is not possible to use this boundary material law with multi-material ALE laws 37 (/MAT/LAW37 (BIPHAS)) and 51 (/MAT/LAW51 (MULTIMAT)).
- Definition of stagnation energy is
optional. Default value recommended:
; since linear EOS
does not depends on energy pressure is not
affected and the initial energy is also set by you.
Specific volume energy E is defined as , where is the internal energy. It can be output using /TH/BRIC.
Specific mass energy e is defined as . This leads to . Specific mass energy e can be output using /ANIM/ELEM/ENER. This may be a relative energy depending on user modeling.
- Liquid bulk modulus is usually set to , where is sound speed.