/SPHBCS
Block Format Keyword Describes the SPH symmetry conditions.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /SPHBCS/type/sphbcs_ID | |||||||||
| sphbcs_title | |||||||||
| Dir | frame_ID | grnd_ID | Ilev | ||||||
Definitions
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| type | Symmetry condition type:
(Text) |
|
| sphbcs_ID | Symmetry condition
identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| sphbcs_title | Symmetry condition
title. (Character, maximum 100 characters) |
|
| Dir | Direction:
(Text) |
|
| frame_ID | Reference frame
identifier. Must be fixed. (Integer) |
|
| grnd_ID | Nodes group identifier for
kinematic boundary condition reinforcement. (Integer) |
|
| Ilev | Formulation level.
(Integer) |
Comments
- The SPH symmetry conditions are insured through the automatic creation of ghost particles, symmetric to the real particles with respect to the symmetry plane.
- Dir =
,
,
Condition is a symmetry condition with respect to the plane going through the origin of the frame and normal to the local direction Dir of the frame.
Particles should lie into the positive semi-space:(1) Where,- Origin of the frame
- Local direction Dir of the frame (Figure 1).
- The frame must be fixed.
- For mass consistency, it is recommended for the symmetry plane to be coincident to a plane of the initial net (particles to lie on the symmetry plane at the time t =0).
- The nodes group identifier for
kinematic boundary condition reinforcement is useful when modelizing axi-symmetry or
spherical symmetry conditions through the use of several SPH symmetry conditions.
For a description of how to use SPH symmetry conditions to model axi-symmetry or
spherical symmetry conditions, refer to SPH Symmetry Conditions.
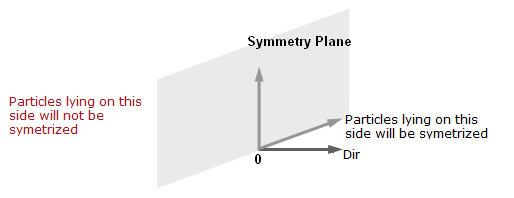
Figure 1. Symmetry Plane for the SPH Symmetry Condition