RD-T: 3030 Buckling of a Tube Using Half Tube Mesh
This tutorial simulates buckling of a tube using half tube mesh with symmetric boundary conditions.
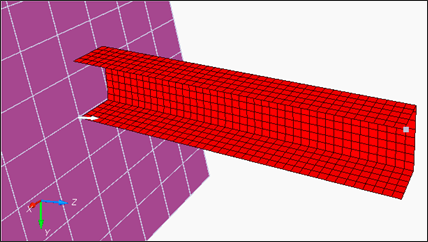
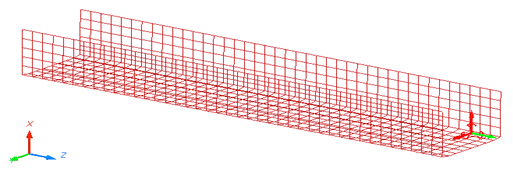
Figure 1. Model
The model description is as follows:
- UNITS: Length (mm), Time (ms), Mass (kg), Force (kN) and Stress (GPa)
- Simulation time: Engine [0 - 10 ms]
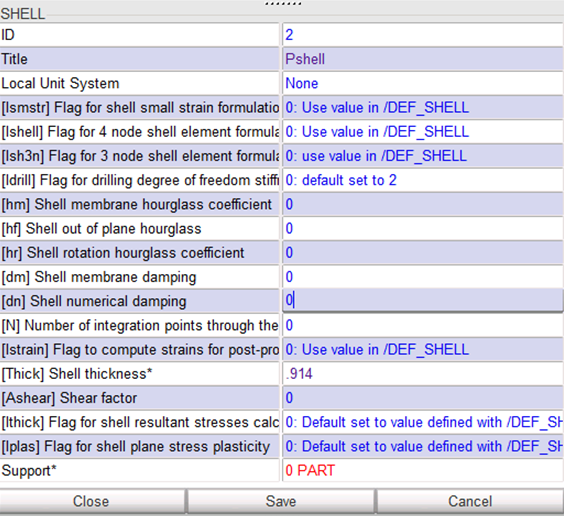
- The tube thickness is 0.914 mm.
- An imposed velocity of 13.3 mm/ms (~30 MPH) is applied to the right end of the tube
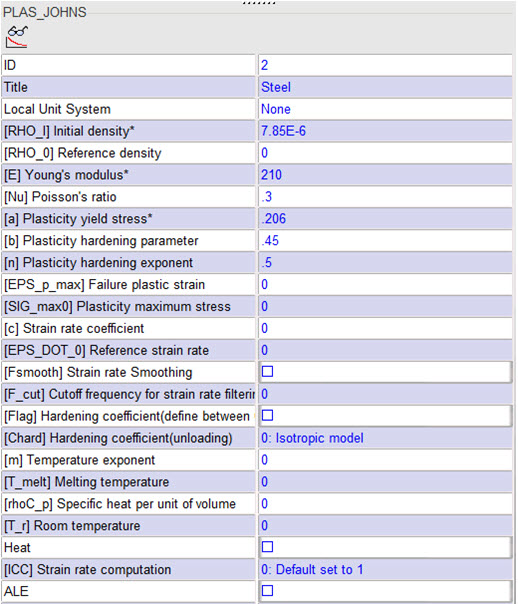
- Elasto plastic material using Johnson-Cook law /MAT/PLAS_JOHNS (STEEL).
[Rho_Initial] Initial density = 7.85e-6 Kg/mm3
[E] Young's modulus = 210 GPa
[nu] Poisson coefficient = 0.3
[a] Yield Stress = 0.206 GPa
[b] Hardening Parameter = 0.450 GPa
[n] Hardening Exponent = 0.5
Model Files
Start HyperCrash
- Open HyperCrash.
- Set the User profile to RadiossV2022 and the Unit system to kN mm ms.kg.
- Set User Interface style as New.
- Set your working directory to where the downloaded file is located.
- Click Run.
- Click .
- In the input window, select BOXTUBE_0000.rad.
- Click OK.
Create and Assign a Material
Create and Assign a Property
Define the Rigid Body
Define Boundary Conditions
Define Boundary Conditions Representing Symmetry
Define the Imposed Velocity
Define a Rigid Wall
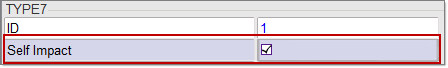
Create a Self Contact for the Tube
Export the Model
Open Compute Console from the Windows Start Menu
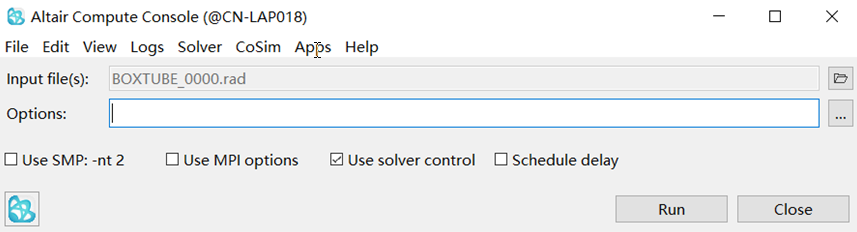
Figure 17.
Review the Results
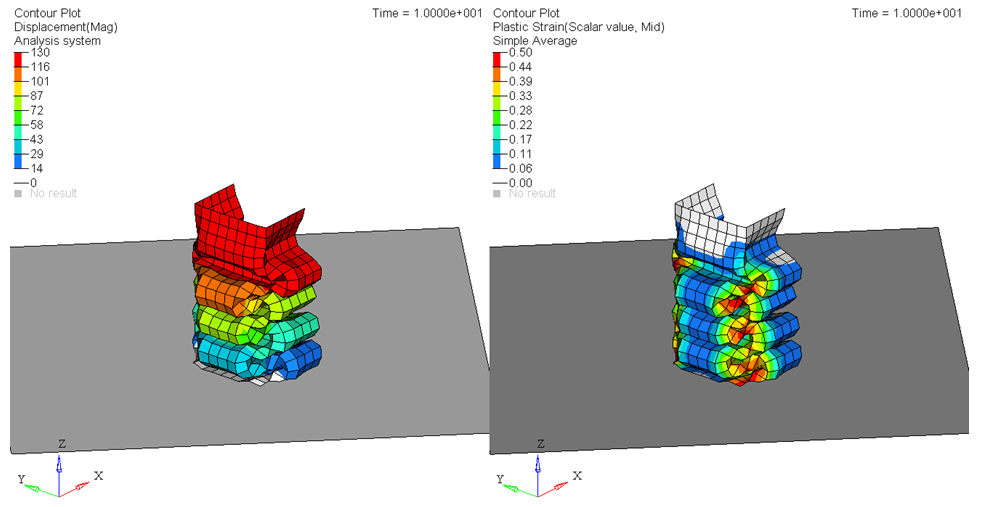
Figure 18.
 and select boxtube
in the
and select boxtube
in the 
 to select the nodes in the
to select the nodes in the 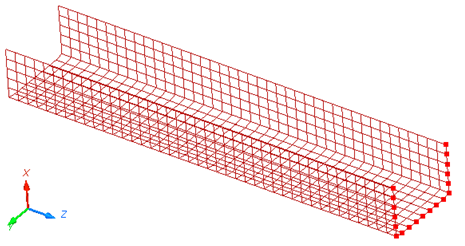
 in the toolbar, and select the rigid body main node
in the
in the toolbar, and select the rigid body main node
in the