fanplot
Creates a surface and a set of 3D lines defined by the x, y, and z matrices.
Syntax
h = fanplot(x, y, z)
[sh lh th] = fanplot(..., property, value, ...)
Inputs
- x, y, z
- Range of the x, y, and z axes..
- property, value
- Only the following properties are accepted:
- 'curves'
- Vector of indices. Specifies the visible curves.
- 'text'
- A cell of strings. Specifies the names of the visible curves.
Outputs
- sh
- Handle of the surface graphics object.
- lh
- Vector containing the handles of the line graphics objects.
- th
- Vector containing the handles of the text graphics objects.
Examples
clf;
x = repmat(1:10,15,1)';
y = repmat(linspace(0,5,15),10,1);
z=sin(x).*cos(y);
sh=fanplot(x, y, z);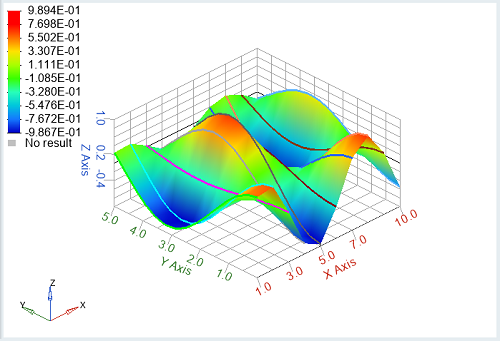
Figure 1. Simple fanplot
clf;
x = repmat(1:10,15,1)';
y = repmat(linspace(0,5,15),10,1);
z=sin(x).*cos(y);
[sh lh th]=fanplot(x, y, z,'curves',[1:2:10],'text',{'line x = 1.0','line x = 3.0', 'line x = 5.0', 'line x = 7.0','line x = 9.0'});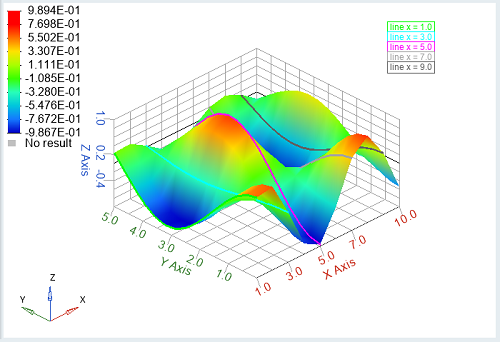
Figure 2. fanplot with 'curves' and 'text' properties set
Comments
If there are no axes, one is created first. Matrices x, y, and z must have the same dimensions MxN, where M is the number of curves and N is the number of points in each curve.