ACU-T: 2300 Atmospheric Boundary Layer Problem – Flow Over Building
Prerequisites
Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory HyperWorks tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 HyperWorks UI Introduction
Since the HyperWorks CFD database (.hm file) contains meshed geometry, this tutorial does not include steps related to geometry import and mesh generation.
Problem Description
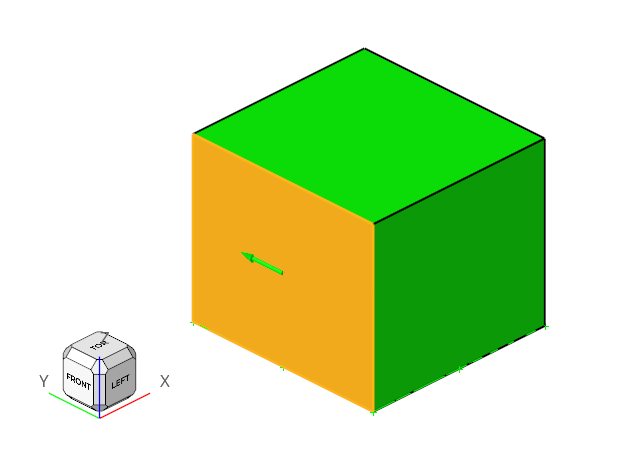
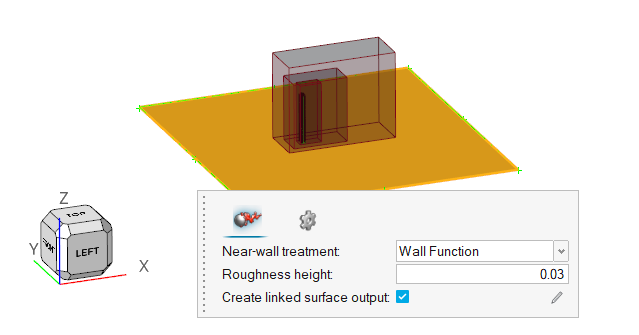
The problem to be addressed in this tutorial is shown schematically in Figure 1. As an example, this problem shows the capability of Atmospheric Boundary Layer modelling in AcuSolve.
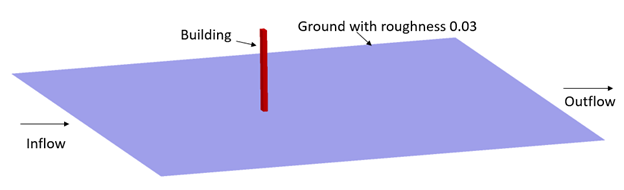
Figure 1.
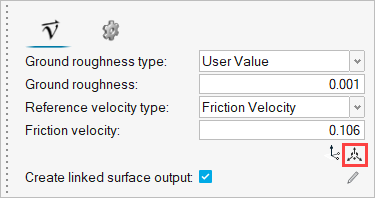
In this tutorial, you will simulate the air flow over a building with a ground roughness of 0.03 m. In this case, User Defined Atmospheric Roughness Type is considered.
Start HyperWorks CFD and Open the HyperMesh Database
Validate the Geometry
The Validate tool scans through the entire model, performs checks on the surfaces and solids, and flags any defects in the geometry, such as free edges, closed shells, intersections, duplicates, and slivers.

Figure 3.
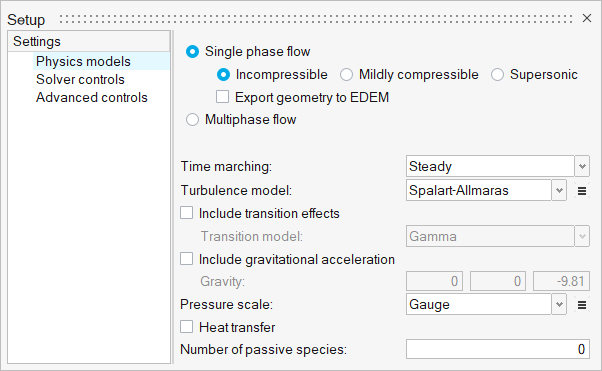
Set Up Flow
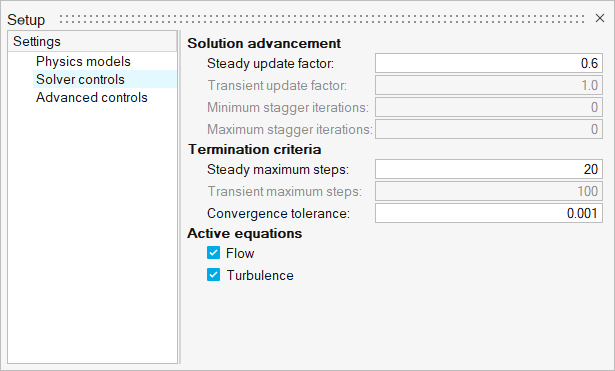
Set Up the Simulation Parameters and Solver Settings
Assign Material Properties
Define Flow Boundary Conditions
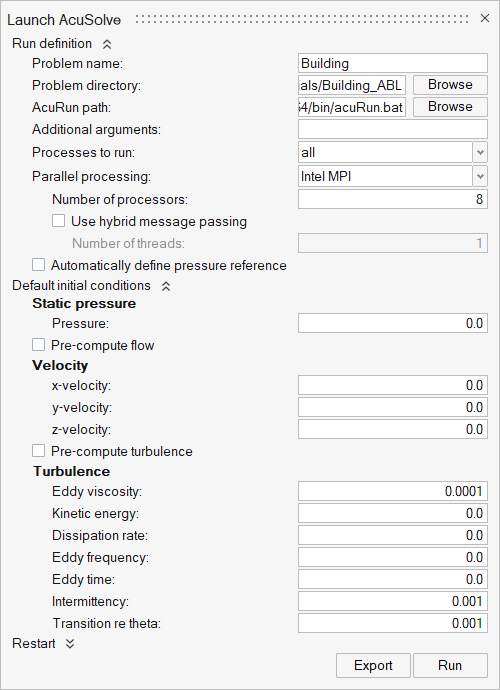
Run AcuSolve
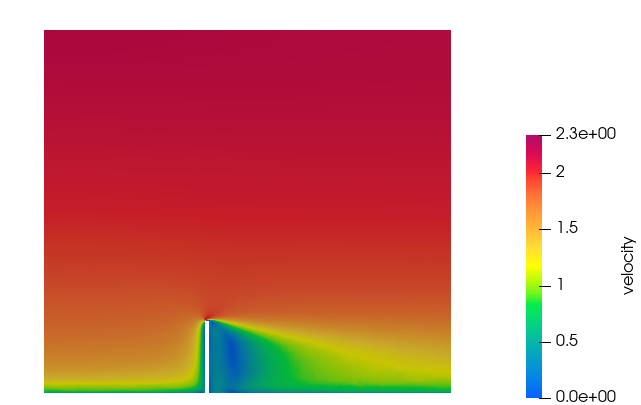
Post-Process the Results with HW-CFD Post
Summary
In this tutorial, you successfully learned how to set up and solve a simulation involving an atmospheric boundary condition using HyperWorks CFD. You started by opening the HyperWorks CFD input file with the geometry and then defined the simulation parameters, fluid material, and boundary conditions. Once the solution was computed, you visualized the results of the velocity magnitude on a plane.