Board to Net Clearance
This DFE rule checks for the distance between signal traces and board edges.
In order to be protected from RF or EMI (Electromagnetic Interference), ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) or EOS (Electrostatic Overstress) from inner layer or outside of PCB, routing pattern should have enough distance from board edges.
- Item: Enter the item name.
- Net Group: Select a target net group or groups.
- Clearance: Assign a clearance between nets in net group and board edges.
- Outline: The board outline consists of two lines. Select outline reference. (Edge/Center)
- Edge: Select out most board out line as a reference.
- Center: Select center of two board outlines as a reference.
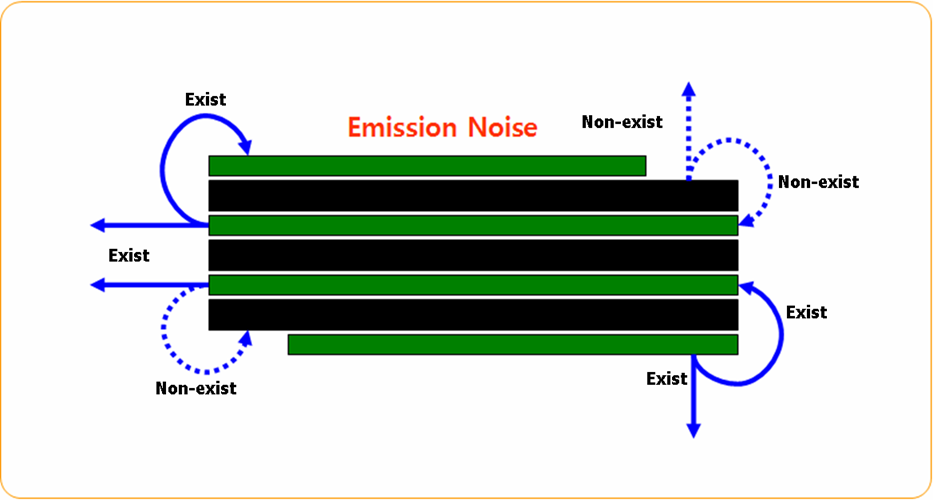
Figure 1.
Rule In Signal Trace Routing
- Keep clock signal and high frequency signal trace apart.
- Solve EMI/EMC troubles before auto-routing.
- Follow the 3-W Rule.
- Follow the 20-H Rule.
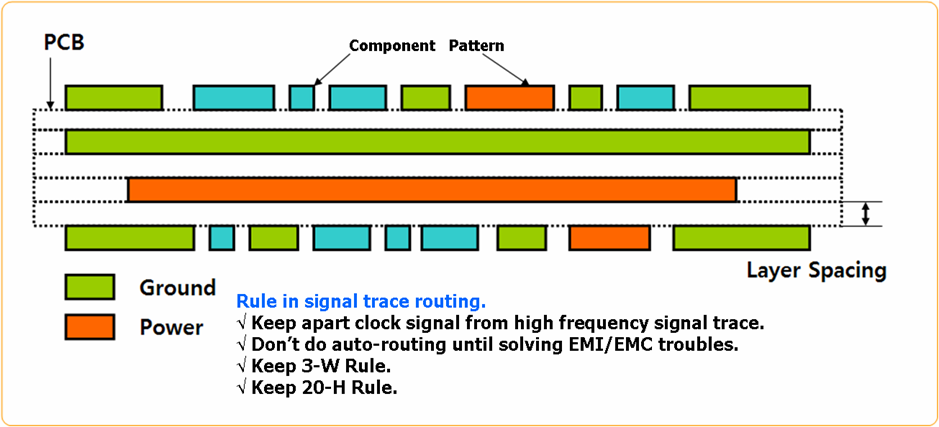
Figure 2.
3-W Rule
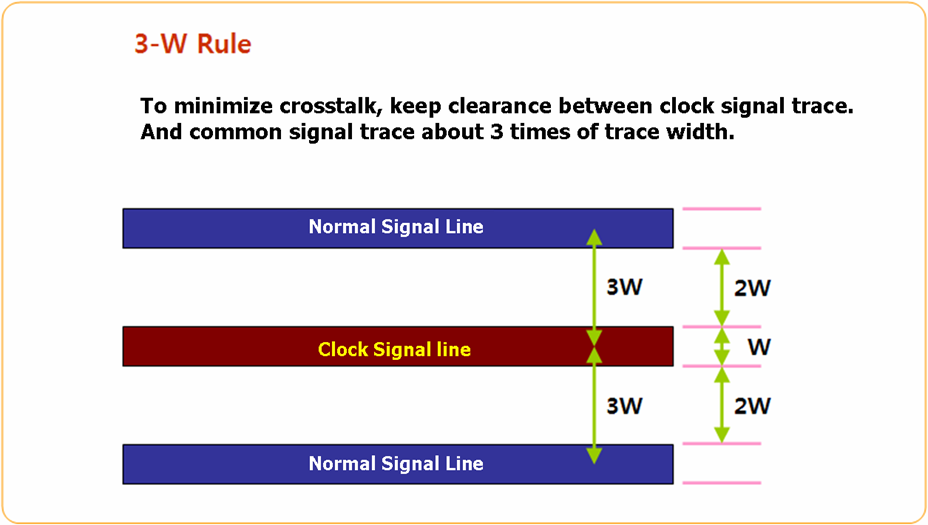
Figure 3.
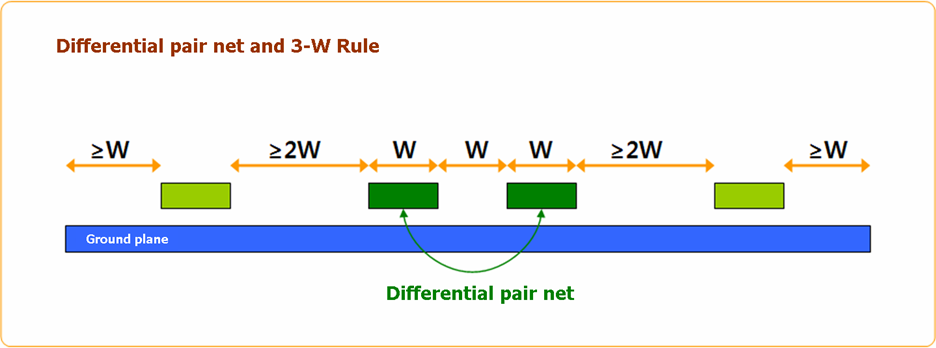
Figure 4.
20-H Rule
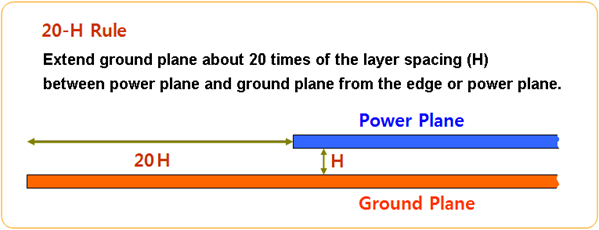
Figure 5.