List of Flux 2021.2 new features
a short description of each new features and improvements of this version.
New features dealing with Environment
| New features | Description |
|---|---|
| Flux in SimLab | Flux is being progressively integrated in SimLab
to benefit of the easy common environment. In SimLab 2021.2
Several applications have started to be integrated with
limitations:
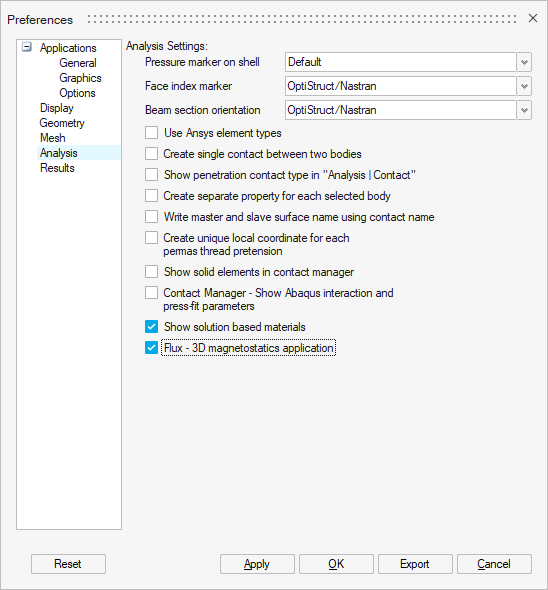
Note: The 3D Magnetostatic solution is
not activated by default because it lacks robustness and
the results cannot be guaranteed for all use cases of
the implemented process. Nevertheless you can already
activate this solution (see the following note), use it,
and give us feedback that will allow us to improve it.
We plan to have the 3D Magnetostatic solution available
by default for the next release of SimLab 2022.
Note: To activate the 3D Magnetostatic
solution:
|
New features dealing with Physics
| New features | Description |
|---|---|
| Generalized projective method to compute forces in the Import / Export data context |
A new method called Generalized projective method to create force collections is now available in the Import / Export data context. This kind of collection allows to compute forces on a generic mesh with the aim to be exported to OptiStruct to setup a NVH analysis of electrical devices, such as rotating machines. This collection may be seen as an extension of the Simplified projective method dedicated to rotating machines previously named Force collection dedicated to rotating machine (for more details, consult Generalized projective method). |
New features dealing with Solving
| New features | Description |
|---|---|
| Free-shape optimization (beta version) |
The first version of free-shape optimization has been implemented in Flux 2021.2. Currently, three types of responses to optimize can be chosen in Flux: flux, torque or force. During the optimization, Flux computes the sensitivities of each responses from the adjoint method on the lines to optimize and then launches OptiStruct to run the free-shape optimization process. To run the free-shape optimization, OptiStruct must be installed and the OptiStruct installation path must be set in the FluxSupervisor Options in the Coupled software section. The free-shape optimization moves the mesh nodes of the line you want to optimize to maximize or minimize your responses. This feature will allow the design of new shapes for your devices and will bring better performances. Available in Beta mode and only in Windows, the free-shape optimization can be run from the Solving menu. Before running an optimization, it is necessary to define the optimization problem (minimization or maximization), the responses (flux, torque or force) the objective function to optimize (a predefined function like avg, maxabs or rms for example or a Compose function defined in an oml file) and the constraints. |
New/Updated examples
As a reminder, all examples are accessible via the Flux supervisor, in the context of Open an example.
| New/Updated examples | Description |
|---|---|
| Updated | Flux-SimLab: electric motor NVH analysis |
| Flux-Activate: IPM motor speed control | |
| New | Improving SRM efficiency with shape optimization method |
New macros
| New macros | Description |
|---|---|
| Axial_Flux_Machine_MACRO | This macro gives to the users the possibility to create an AFIR (Axial Flux Motor Rotor) with almost all combinations of poles pairs and slots, while editing most of the geometric parameters. It loads subsidiary macro to enable study and analysis of the machine created. |
|
AFIR_BACK_EMF__COGGING _TORQUE |
The macro AFIR_BACK_EMF__COGGING_TORQUE is used to determine the Back EMF and the cogging torque of an AFIR (Axial Flux Inner Rotor Motor); it is loaded automatically after loading Axial_Flux_Machine_MACRO. |
|
AFIR_CST_SPEED_SIM |
The macro AFIR_CST_SPEED_SIM is used primary to determine the torque at a speed of an AFIR (Axial Flux Inner Rotor Motor); it is loaded automatically after loading Axial_Flux_Machine_MACRO. |
|
Table_LD_LQ_OnePosition |
This macro intends to create look up table of flux dq, Ld, Lq and torque versus Id, Iq and rotor position. The goal is for analysis on the system part (like with Activate for instance). It will create a new Magneto-Static project from the magnetic transient one. In the Magneto-Static project the current is driven with Id and Iq allowing to extract easily all the needed tables. At the end of the oml file in comment there is the possibility to display Ld, Lq and torque versus Id and Iq with Altair Compose. In addition, oml files with FluxD and FluxQ are available for plotting efficiency maps. |
|
Table_LD_LQ _MultiplePositions |
This macro intends to create look up table of flux dq, Ld, Lq and torque versus Id, Iq and rotor position. At the end of the oml file in comment there is the possibility to display Ld, LQ torque versus Id and Iq with Altair Compose. In addition, oml files with FluxD and FluxQ are available for plotting efficiency maps. The primary difference with Table_LD_LQ_OnePosition is that the simulation is made at several position and it takes the mean value of Flux_Q and Flux_D to plot the efficiency map. |
|
AFIR_STARTING |
This macro can determine the transient state of the machine before it reaches the steady state. |
|
AFIR_SHORT_CIRCUIT |
This macro allows the user to simulate the course of the AFIR when a short circuit occurs. There is the three type of short circuit. |