Post-processing quantities: rotation motion
Introduction
This paragraph deals with physical quantities computed for rotating motion .
Kinematic variables
The list of kinematic variables used for solving and the names of the corresponding Flux parameters are given in the table below; in this table MS indicates the concerned mechanical set.
| Kinematic variable | Name | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angular position: |
AngPos(MS) | degree |
| Angular speed: |
AngSpeed(MS) | degree/s |
| Angular acceleration: |
AngAcc(MS) | degree/s² |
Physical quantities
The list of physical quantities computed in the post-processing module and the names of the corresponding Flux parameters are given in the table below; in this table MS indicates the concerned mechanical set.
| Torque | Name | Unit | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic torque: |
TorqueElecMag(MS) | N.m | |
| Internal system | |||
| Friction torque: |
TorqueFrInt(MS) | N.m |
|
| Spring return torque: |
TorqueSpInt(MS) | N.m |
|
| Inertia torque: |
TorqueInInt(MS) | N.m |
|
| Resistant torque*: |
TorqueReInt(MS) | N.m |
|
| External system | |||
| Friction torque: |
TorqueFrExt(MS) | N.m |
|
| Spring return torque: |
TorqueSpExt(MS) | N.m |
|
| Inertia torque: |
TorqueInExt(MS) | N.m |
|
| Resistant torque *: |
TorqueReExt(MS) | N.m |
|
- either the sum of the friction torque + the spring return torque
- or the resistant torque defined using a formula
Reminder of the solved mechanical equation
The solved mechanical equation for rotating motion is: ![]()
where:
- J is the moment of inertia:
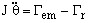
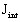 is the moment of
inertia of the moving mechanical set itself (internal system)
is the moment of
inertia of the moving mechanical set itself (internal system)
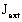 is the moment of
inertia of the external load (external system)
is the moment of
inertia of the external load (external system)
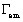 is the
electromagnetic torque
is the
electromagnetic torque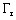 is the resistant
torque:
is the resistant
torque: 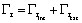
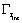 is the resistant
torque acting on the moving mechanical set (internal system)
is the resistant
torque acting on the moving mechanical set (internal system)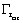 is the resistant
torque acting on the external load (external system)
is the resistant
torque acting on the external load (external system)
Important note
When there are symmetries or periodicities, the computed values of the torque correspond to the entire device.