OS-V: 1210 Contact with Friction
A deformable block is slid over a fixed rigid plate using enforced velocities and the problem is solved using an explicit dynamic analysis in OptiStruct. The results from OptiStruct are compared with an equivalent model in Radioss.
図 1. Finite Element Model
Benchmark Model
The finite element model consists of a deformable block on which enforced velocities are applied causing it to slide over a rigid fixed block.
Both blocks are meshed with first-order CHEXA elements and frictional contact is defined between the blocks with a friction coefficient = 0.05. The bottom block is constrained in all directions. One side of the top block is constrained along Y direction, while the opposite side is subjected to an enforced velocity and constrained along the X, Y, and Z rotational degrees of freedom. The upper side of the top block is subjected to an enforced velocity and is constrained along the X, Y, and Z rotational degrees of freedom.
| Direction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Y | 565 mm/s | 0.009 s |
| Z | -102 mm/s | 0.001 s |
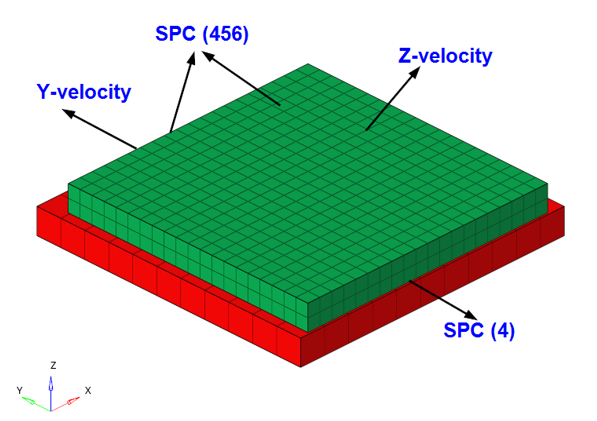
図 2. Boundary Conditions
- Property
- Value
- Elastic modulus
- 193000 N/mm2
- Poisson’s ratio
- 0.3
- Density
- 7.75 E-09 tonn/mm3
Results
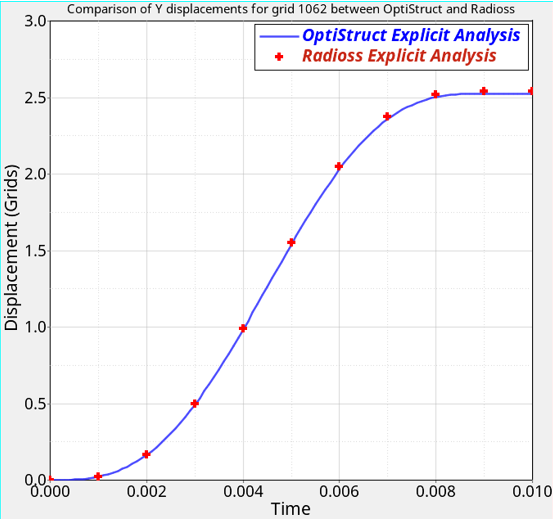
図 3. Comparison of Y displacement for a particular grid (1062)
Model Files
必要なモデルファイルのダウンロードについては、モデルファイルへのアクセスを参照してください。
The model file used in this problem includes:
contact_with_friction.fem