Importing Custom Data
Import a single custom data file by defining the import template.
-
On the Home tab, in the
File group, click the
 Import icon. From the drop-down list, click the
Import icon. From the drop-down list, click the  Custom Data File icon.
Custom Data File icon.
- Browse to the location of the file and select a custom data file.
-
Under Delimiter, select one of the following delimiters
that separate the columns of data.
- Tab
- Space
- Comma
- Other
The data file may contain lines of text that are not part of the data to be imported.
- In the Start reading file at (line number) field, enter the line number at which data should be imported.
- In the Specify number of lines to read field, enter the number of data to read.
- If the data contains column title, select the Data contains column titles check box.
-
Click Next to continue with the template.
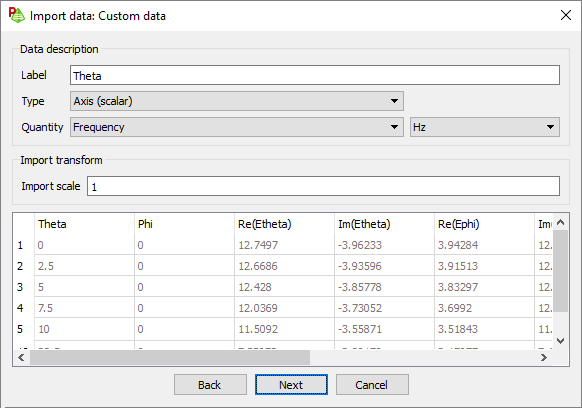
Figure 1. The Import data: Custom data dialog. - In the Label field, specify a descriptive label for the data.
-
In the Type
drop-down list, select one of the following and then a
relevant Quantity for the data column:
-
- Axis scalar
-
Select this option if the column is used as an independent axis on a graph.
Quantity: frequency, position, radius, angle, time or a user-defined quantity.
-
- Scalar
-
Select this option if any scalar result type may be used.
Quantity: far field, near field, voltage, current, power, specific absorption rate (SAR), impedance / admittance, scattering parameters, axial ratios, gain / directivity, radar cross section (RCS), voltage standing wave ratio, reflection coefficient, Poynting vector (magnitude) user-defined quantities and several other typical data types.
-
- Complex pair (Real + Imaginary)
-
Select this option of two adjacent columns contain the real and imaginary components of a complex number.
Quantity: far field, near field, voltage, current, impedance / admittance, scattering parameters, reflection coefficient, or a user-defined quantity.
-
- Ignore
- Select this option if a column is to be ignored during the import process.
-
- In the Import scale field, enter a value to scale the data.
- If the data in the column is in dB, select the Data is in dB (not linear) check box.
- Repeat 9 to 11 for the remaining columns.
- Click Done to import the data and to close the dialog.