ACU-T: 6103 AcuSolve - EDEM Bidirectional Coupling with Heat Transfer
This tutorial introduces you to the workflow for setting up and running a basic bidirectional coupling (two-way) simulation with heat transfer using AcuSolve and EDEM. Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory HyperWorks tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 HyperWorks UI Introduction, and have a basic understanding of HyperWorks CFD, AcuSolve, and EDEM. To run this simulation, you will need access to a licensed version of HyperWorks CFD, AcuSolve, and EDEM.
Problem Description
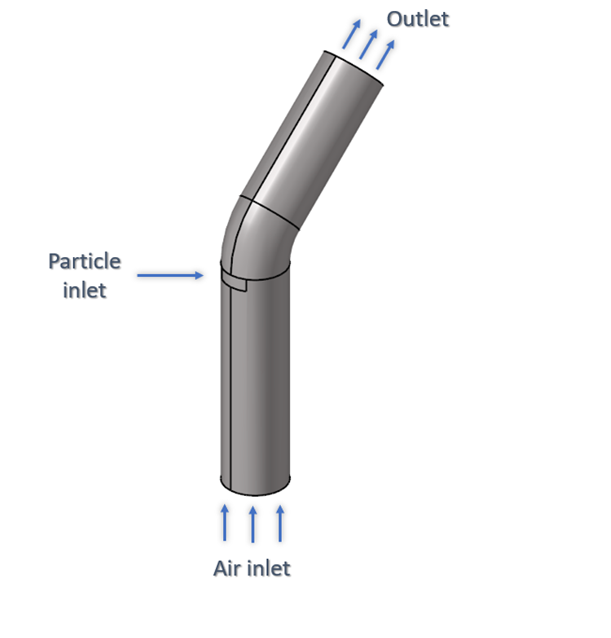
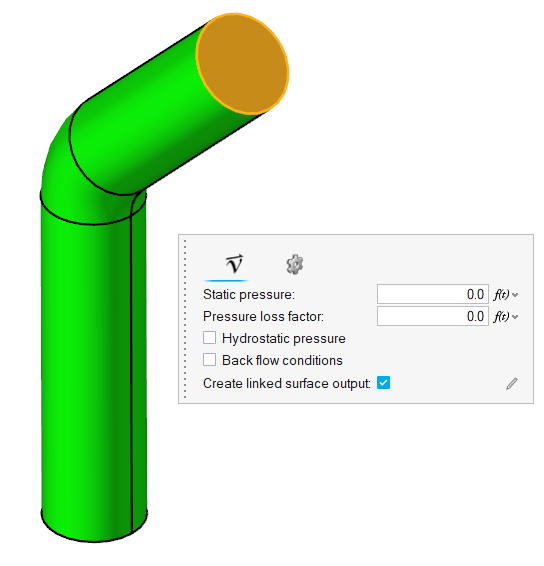
Figure 1.
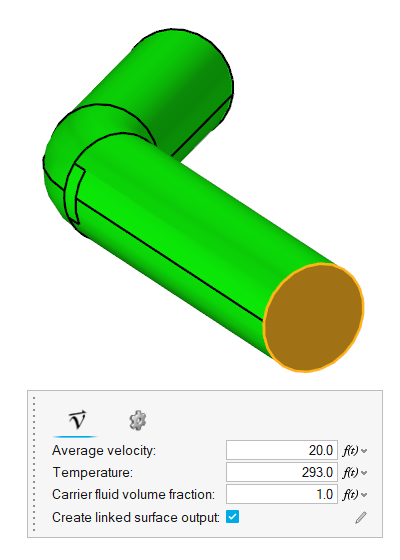
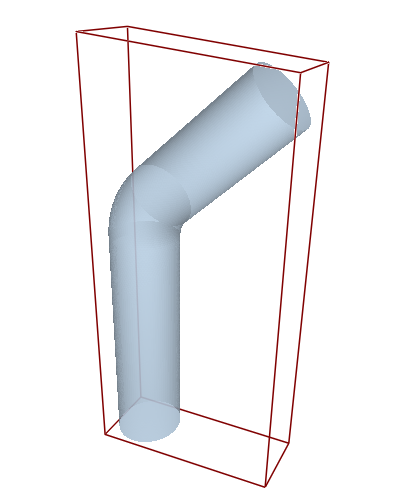
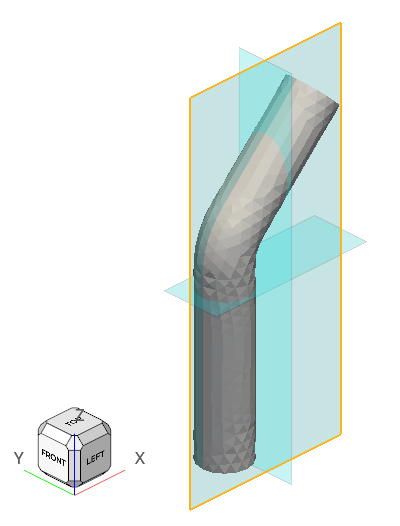
The model consists of a cylindrical pipe with a 45-degree bend. The radius of the pipe is 0.25 m and the particle inlet is located midway through the length of the pipe.
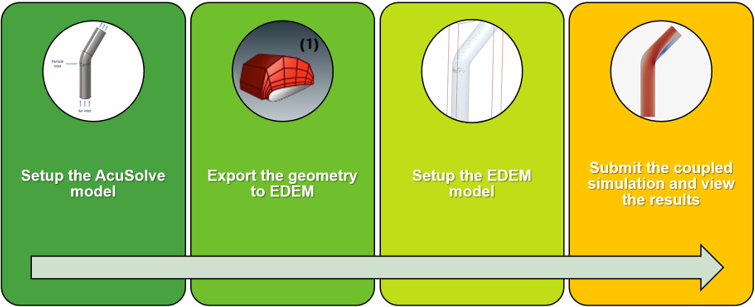
Figure 2.
Accordingly, the tutorial consists of two parts:
- AcuSolve setup and geometry export
- EDEM setup and simulation
The AcuSolve model will be set up using HyperWorks CFD. Once the AcuSolve setup is complete, the EDEM deck with the geometry will be exported from HyperWorks CFD. This input deck will be opened in EDEM and will be used to complete the EDEM setup. Once the EDEM deck is set up, you will launch the coupled simulation.
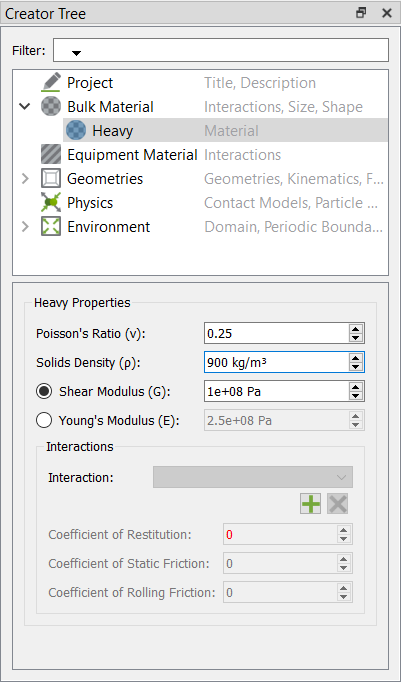
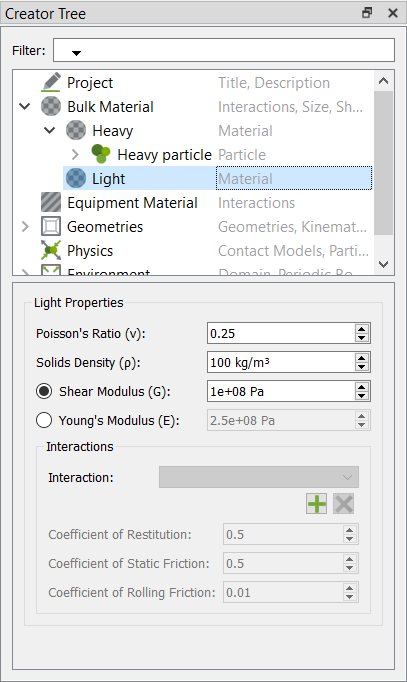
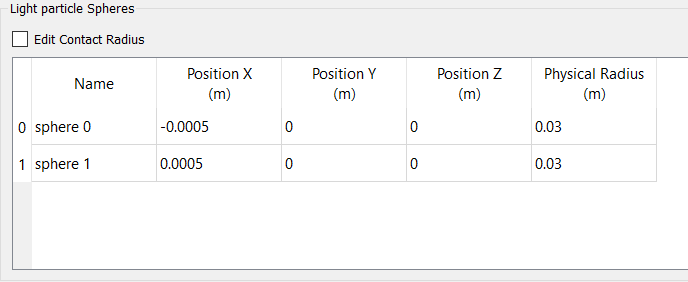
Two different bulk materials used in the EDEM simulation and their properties are listed below:
| Name | Density (kg/m3) | Particle radius (m) | Average mass of individual particle (kg) | Rate of generation (particles per sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy particle | 900 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 100 |
| Light particle | 100 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 100 |
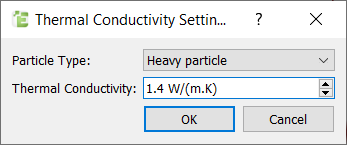
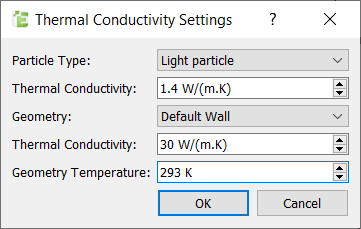
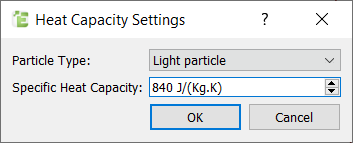
The thermal material properties used for the particles are listed in the table below:
| Name | Thermal conductivity (W/m-k) | Specific heat capacity (J/kg-K) | Temperature (K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particles | 1.4 | 840 | 363 (initial) |
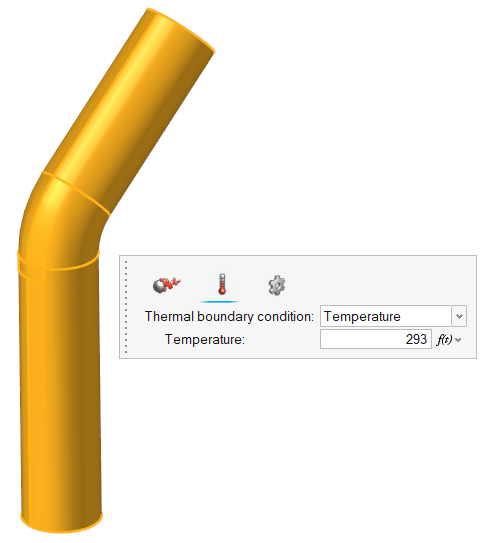
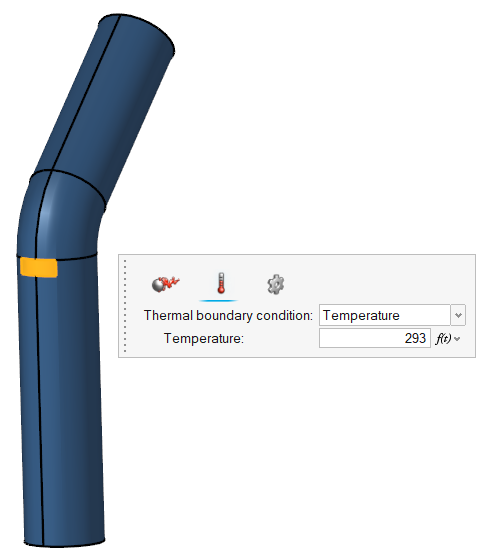
| Walls | 30 | - | 293 |
Part 1 - AcuSolve Simulation
Start HyperWorks CFD and Open the HyperMesh Database
Validate the Geometry
The Validate tool scans through the entire model, performs checks on the surfaces and solids, and flags any defects in the geometry, such as free edges, closed shells, intersections, duplicates, and slivers.

Figure 4.
Set Up Flow
Set the General Simulation Parameters
Assign Material Properties
Define Flow Boundary Conditions
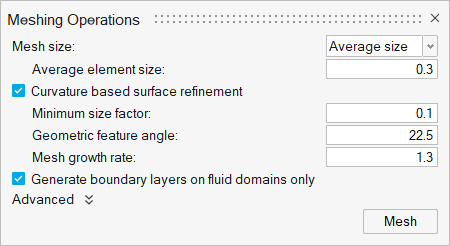
Generate the Mesh
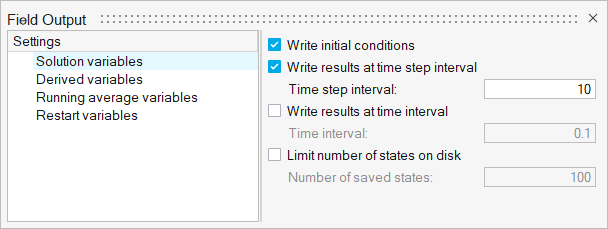
Define Nodal Outputs
Once the meshing is complete, you are automatically taken to the Solution ribbon.
Export the Solver Deck
- From the menu bar, go to .
- Name the file windshifter_heat and make sure that AcuSolve (*.inp) is selected as the file type.
- Click Save.
Part 2 - EDEM Simulation
Start Altair EDEM from the Windows start menu by clicking .
Open the EDEM Input Deck
As mentioned earlier, when the AcuSolve simulation was launched, HyperWorks CFD created a set of EDEM files in the problem directory. You will open that EDEM input deck and setup the DEM simulation
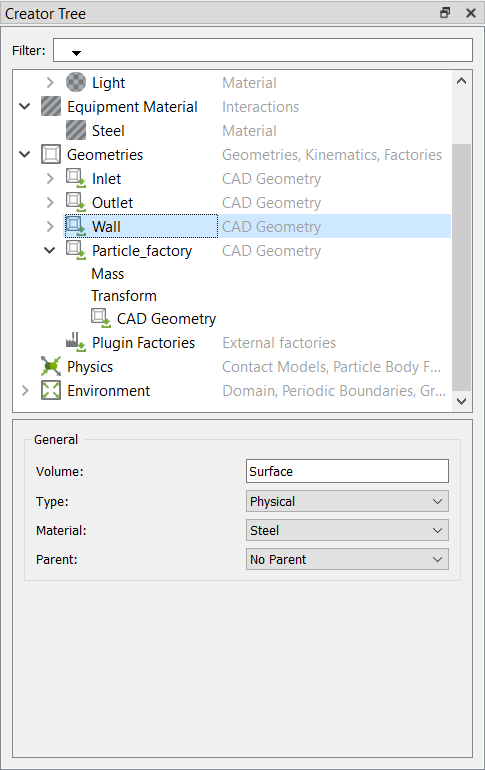
Define the Bulk Materials and Equipment Material
In this step, you will define the material models for the heavy and light bulk material and the equipment material.
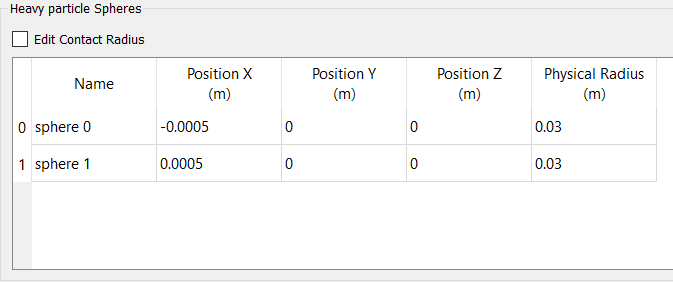
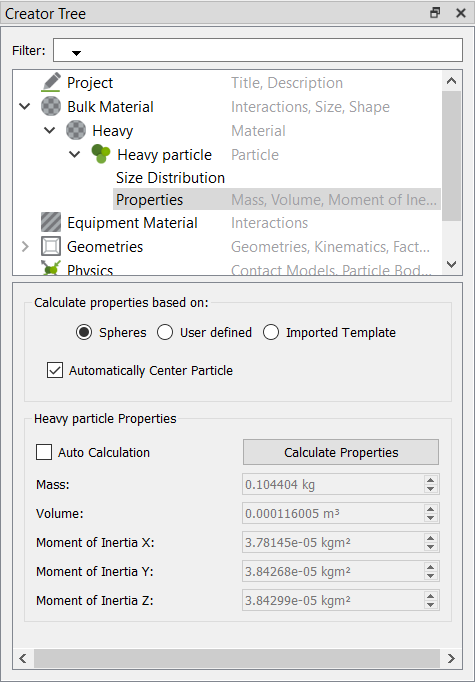
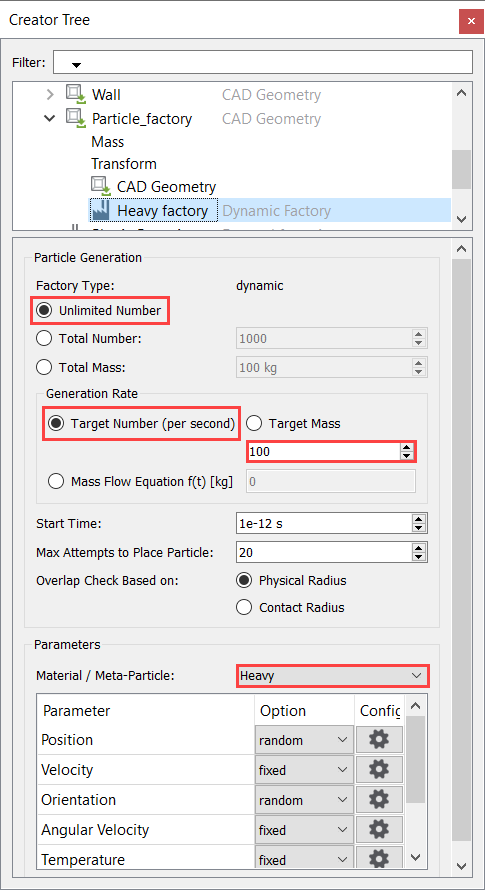
Create the Particle Factory
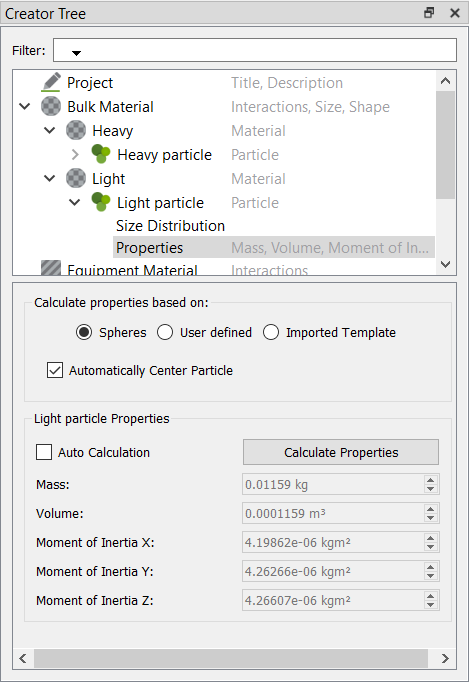
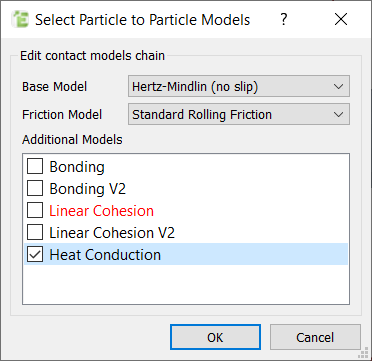
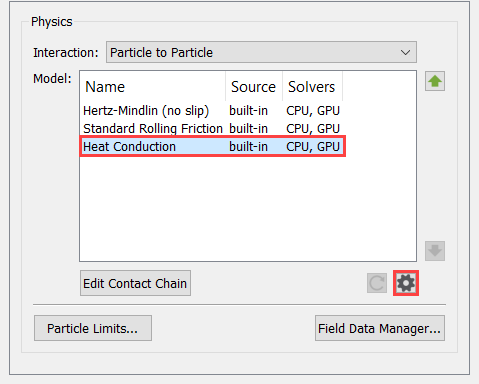
Define the Heat Transfer Paramaters
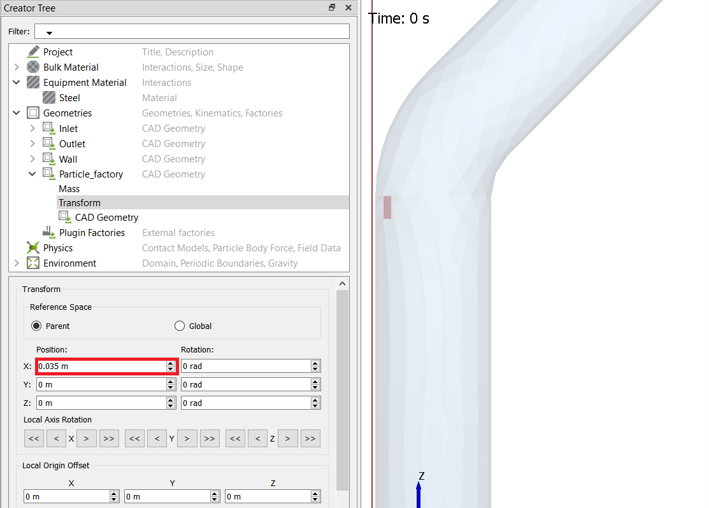
Define the Particle Factory
Now that the bulk material, geometry sections, and equipment materials are defined, you need to create a particle factory to generate the particles. You will create one factory for each bulk material.
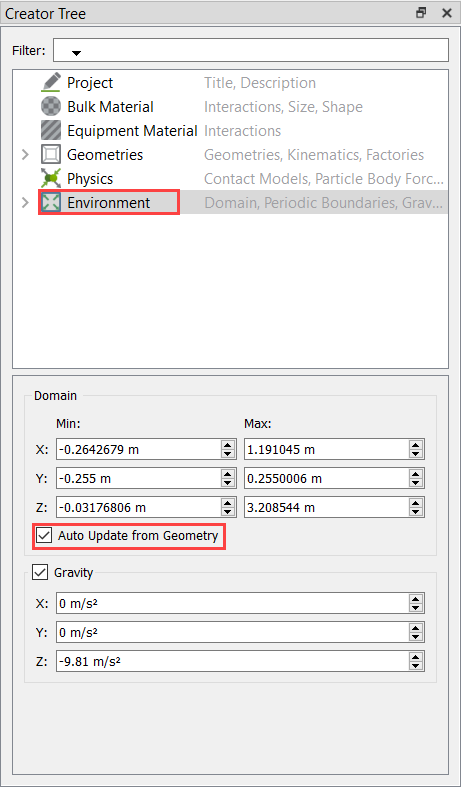
Define the Environment
In this step, you will define the extents of the domain for the EDEM simulation and the direction of gravitational acceleration.
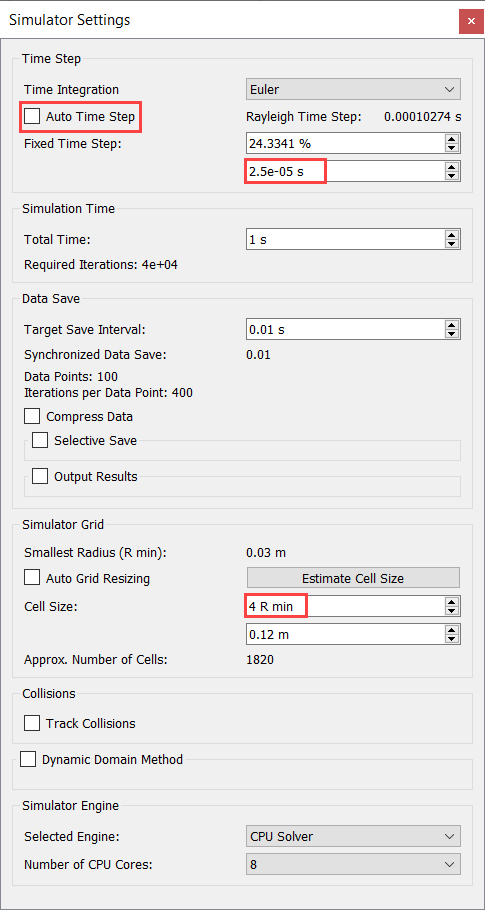
Define the Simulation Settings
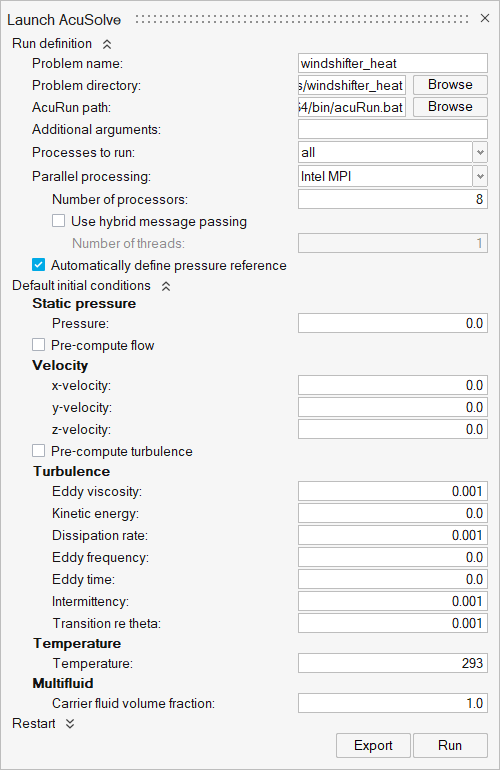
Submit the Coupled Simulation
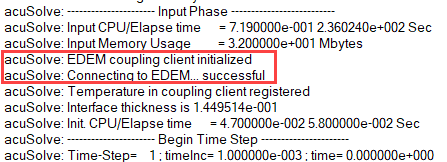
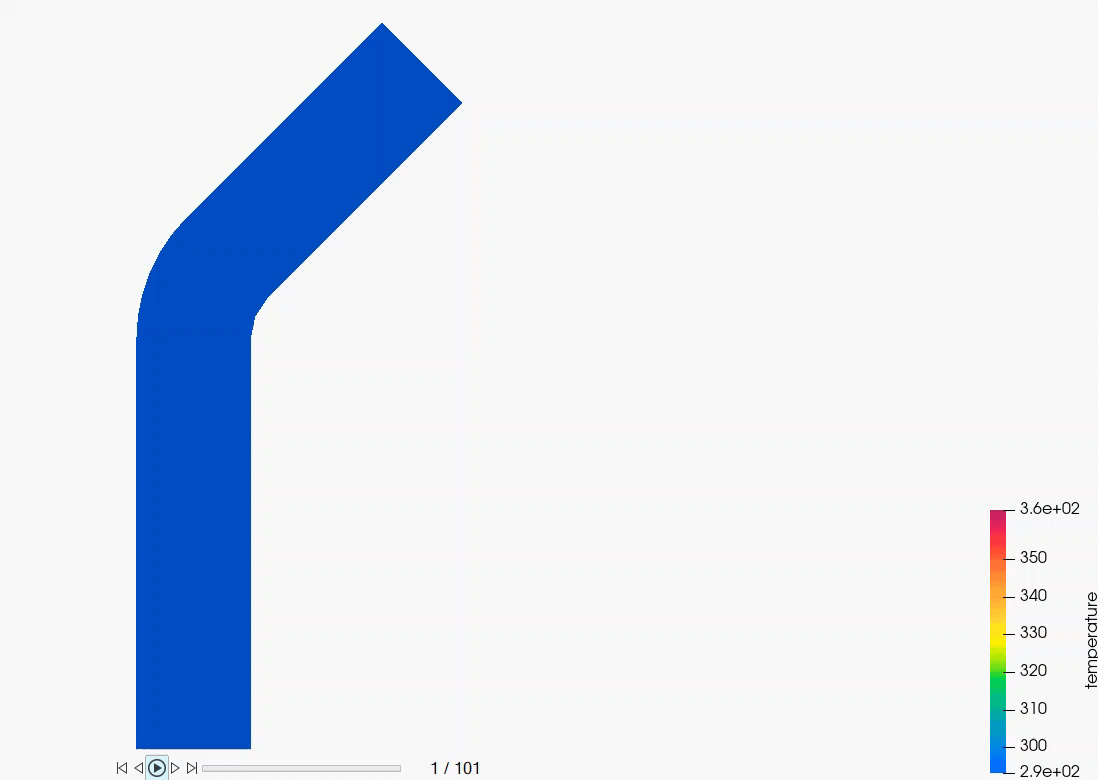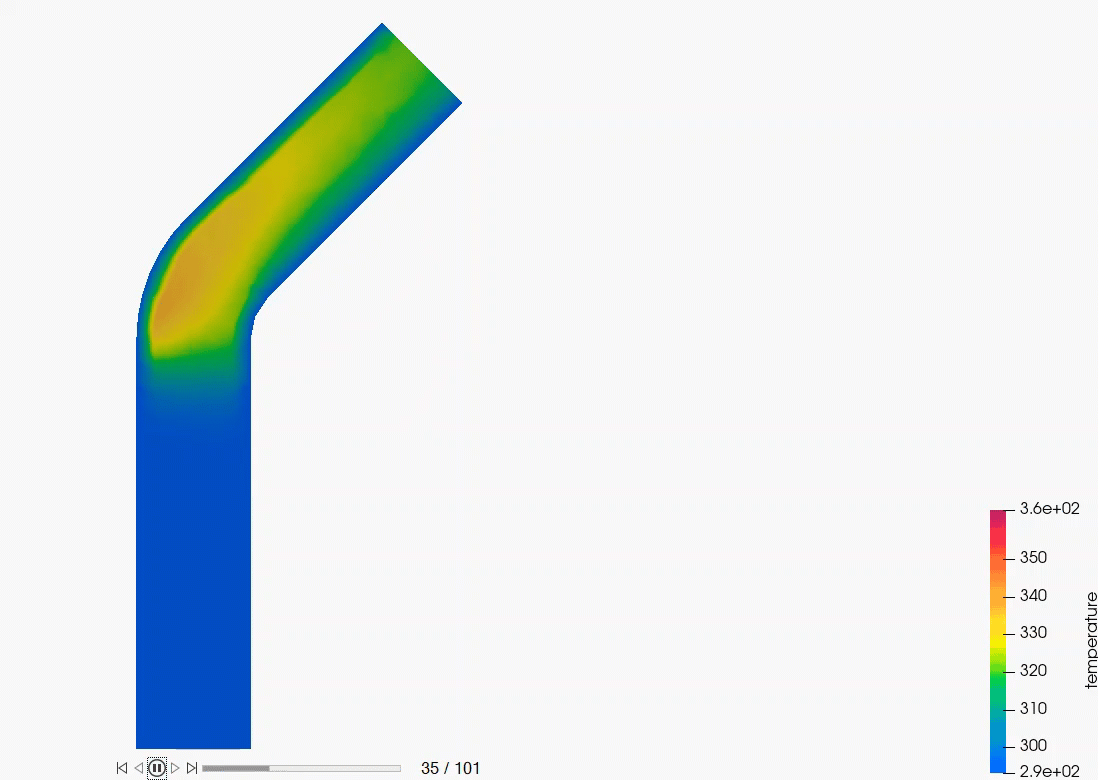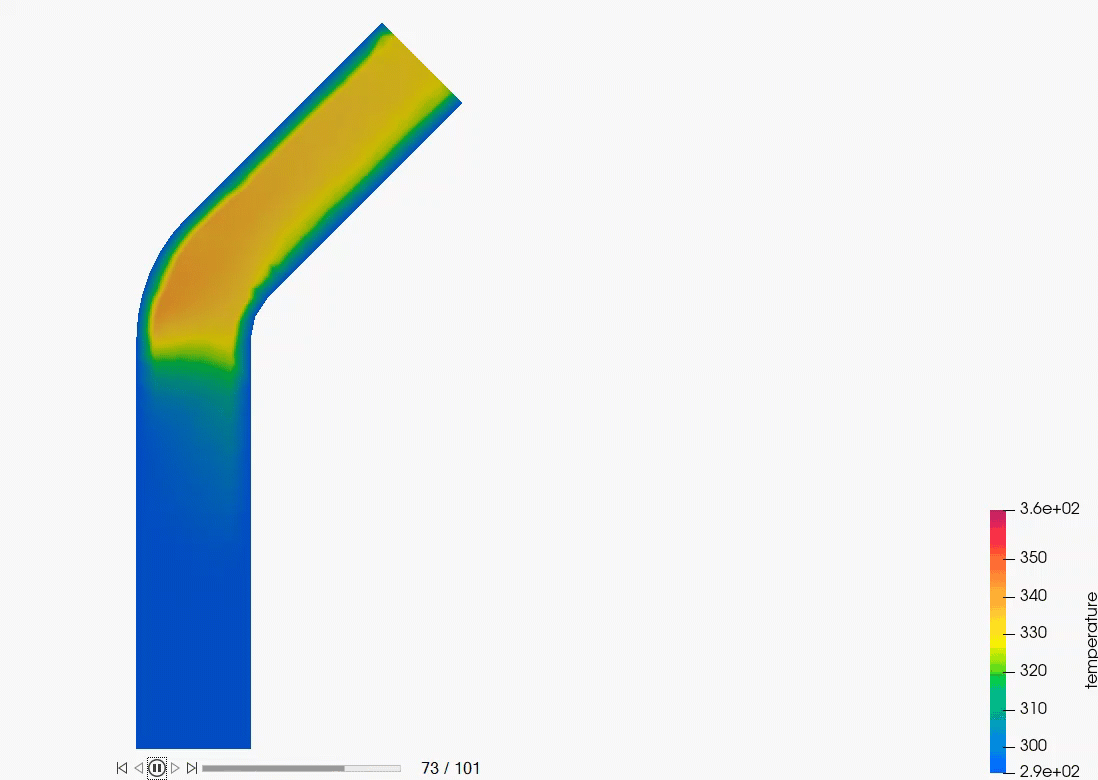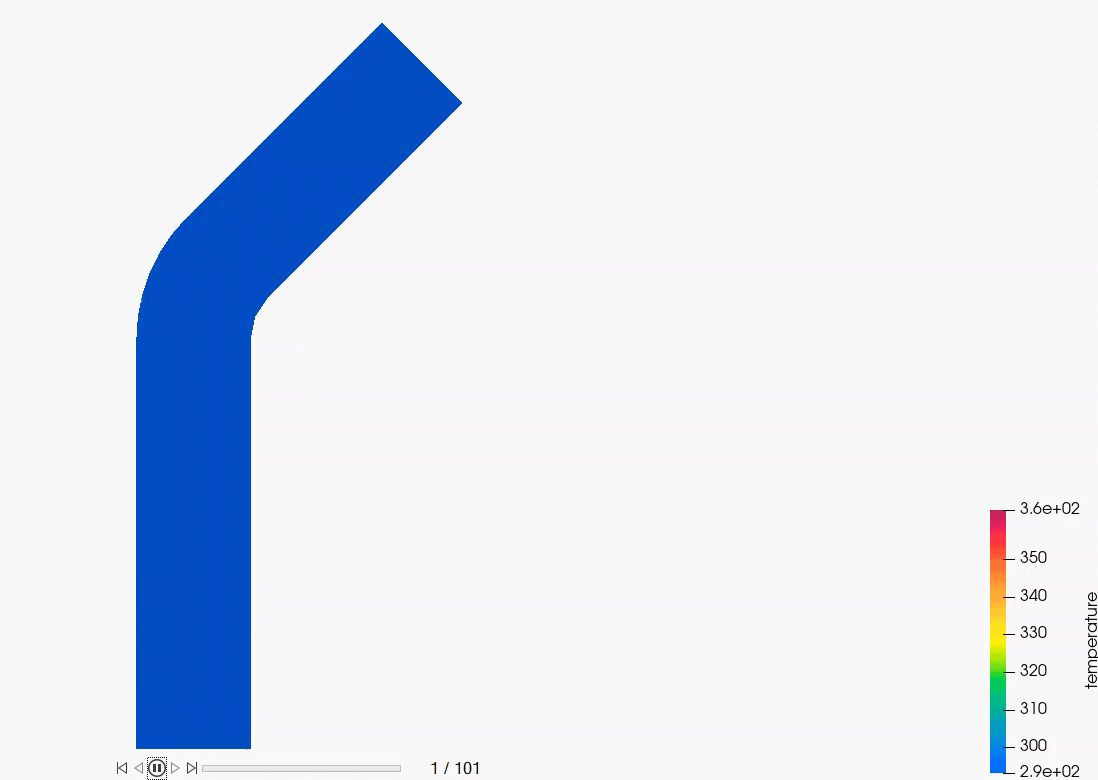
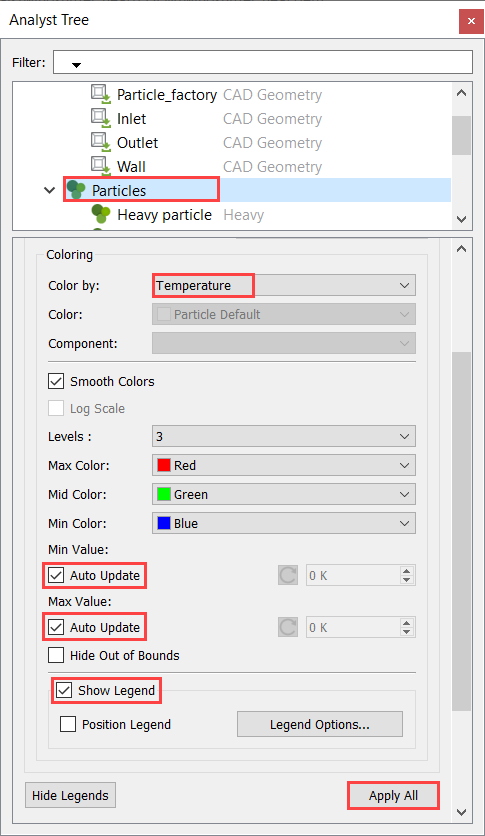
Analyze the Results
AcuSolve Post-Processing
EDEM Post-Processing
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how to set up and run a basic AcuSolve-EDEM bidirectional (two-way) coupling problem with heat transfer. In the first part, set up the AcuSolve model in HyperWorks CFD and exported the geometry. Next, you imported the EDEM input files created by HyperWorks CFD and set up the EDEM model. You learned how to set up the thermal properties for the particles as well as their interaction with other particles and equipment. Once the coupled simulation was completed, you learned how to create animations in both HyperWorks CFD Post and EDEM Analyst.