Root Cause Analysis
- Modal Contribution
The E-Line method is a time domain analysis approach, using Modal Transient Analysis, also known as the Modal Superposition Method. This enables a transition to the frequency domain.
(1) 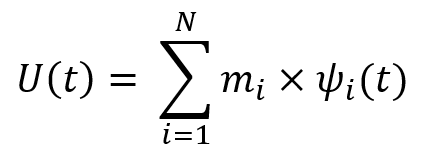
Where:- U(t) is the time domain displacement
- N is the number of modes extracted
- mi is the
Modal displacementfor a mode i - ѱi is the
Participation factorfor mode i
With all the above responses available in the standard outputs from OptiStruct Analysis, the Relative Modal Contribution [%] values can be calculated. These will describe the participation of a mode or modes on a peak of the time domain response.
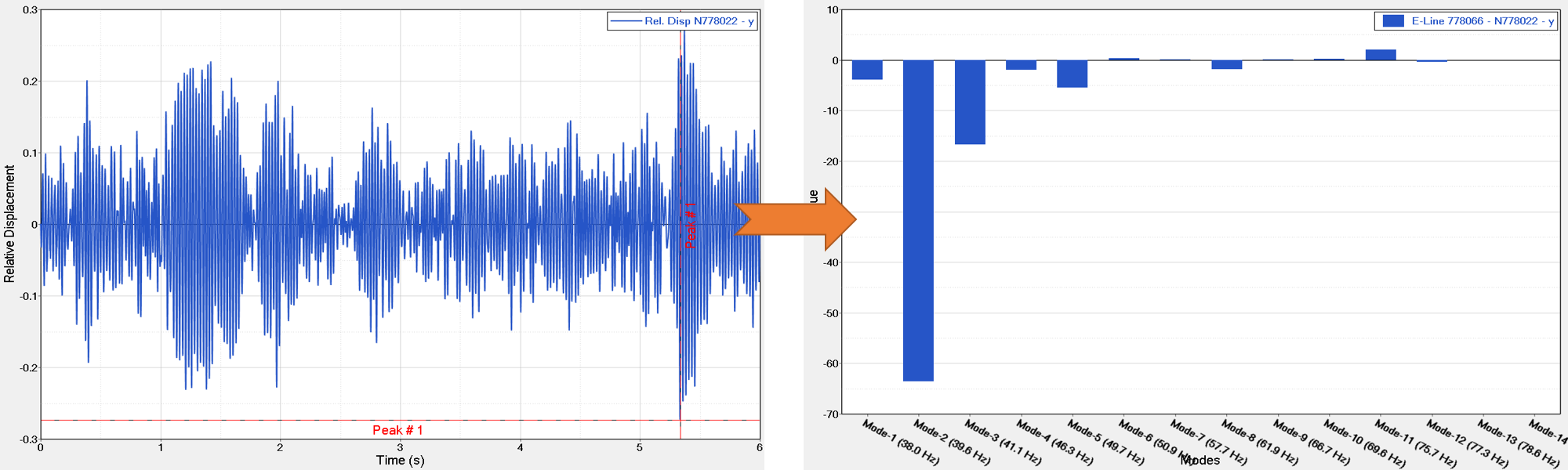 Figure 1.
Figure 1. - Modal Sensitivity
The modal sensitivity allows the analyst to live perform what-if studies by altering the time domain response of an E-Point or complete E-Line. This is achieved by decomposition of the Modal Superposition response, applying a factor (between 0 and 1) on selected modes, damping, canceling or isolating them.
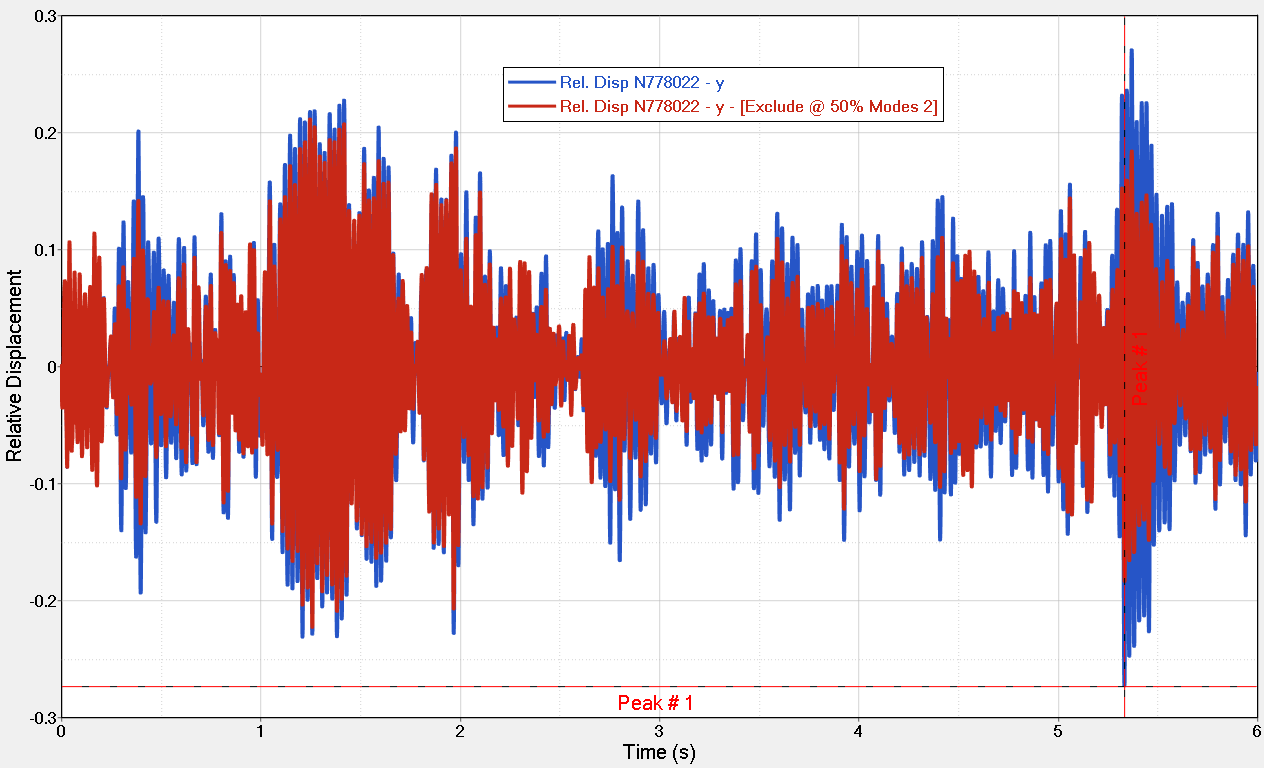
Figure 2.