OS-T: 8010 Trim Analysis of a Full Aircraft Model
This tutorial demonstrates trim analysis of a full aircraft model.
Preprocessing is done using Altair HyperMesh in the Nastran MSC User profile. A structural model with existing data is used as a base model and this tutorial demonstrates the creation of entities in the Aeroelasticity domain.
- Create Panel Mesh divisions (AEFACT)
- Create Panels (CAERO1)
- Ceate aeroelasticity box list (AELIST)
- Create interpolation splines (SPLINE1)
- Create rigid body motions for aeroelastic TRIM variables (AESTAT)
- Create aerodynamic control surfaces (AESURF)
- Define TRIM variables and link control surfaces (AELINK)
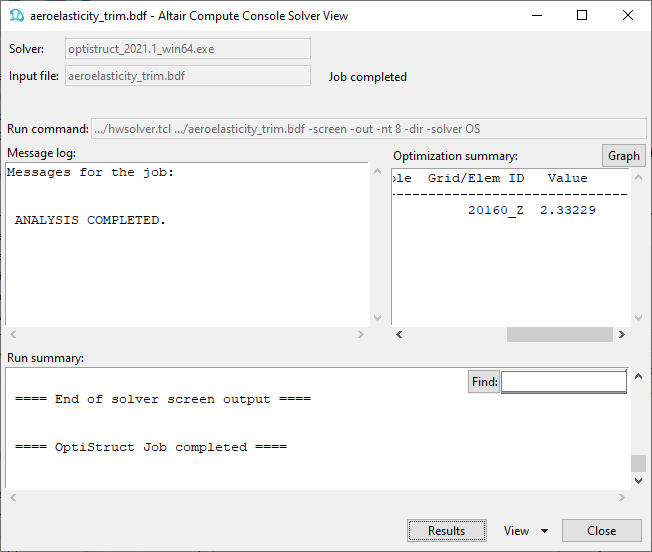
- Submit the job
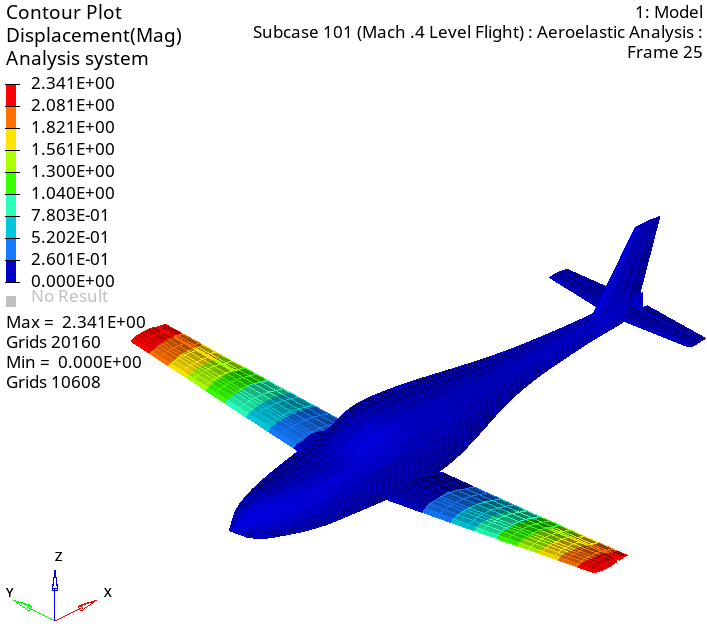
- View the results
Launch HyperMesh and Set the Nastran MSC User Profile
Open the Model and Aeroelasticity Browser
The Aeroelasticity Browser is useful for upcoming tasks in this tutorial.
Set Up the Model
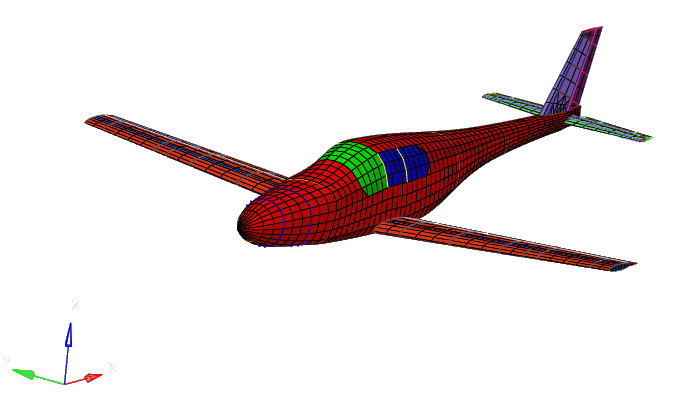
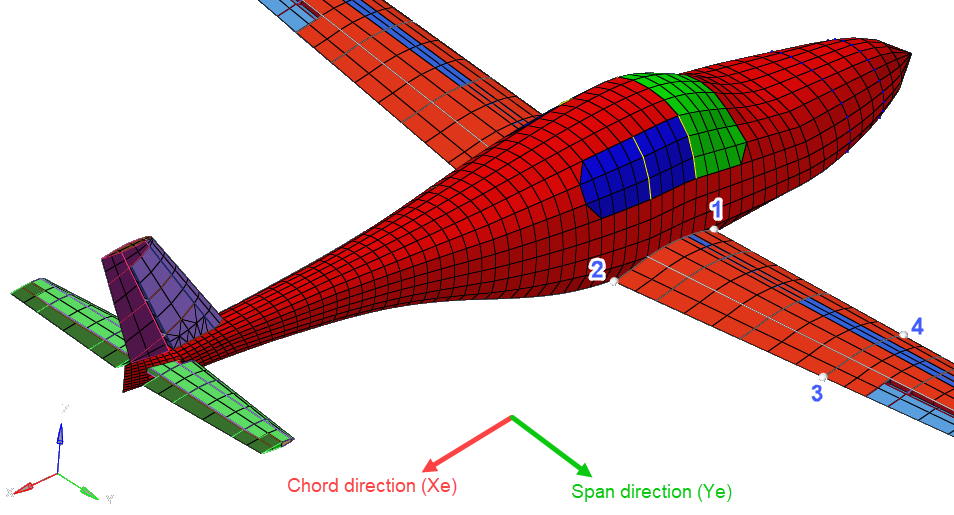
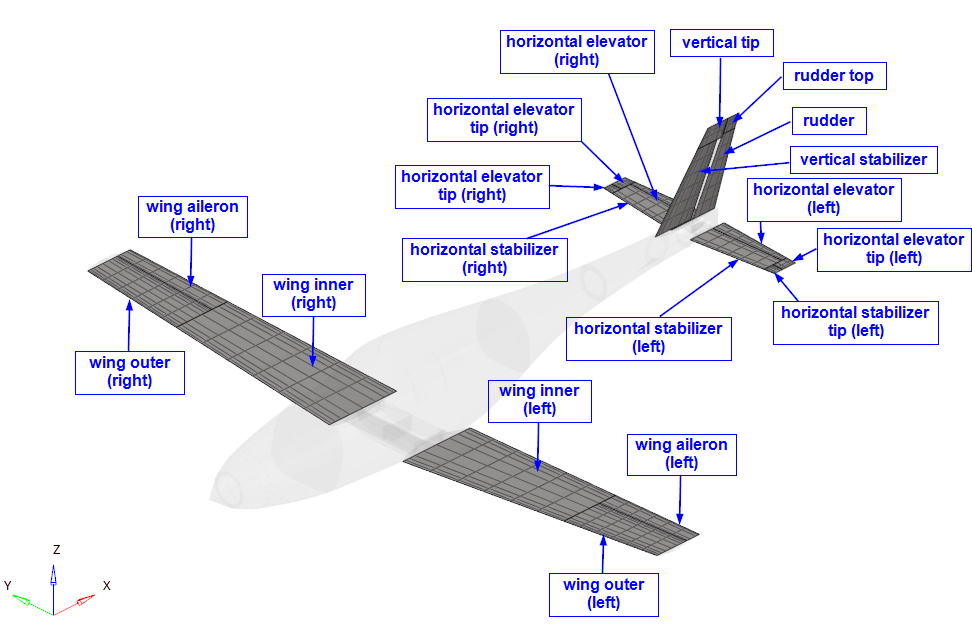
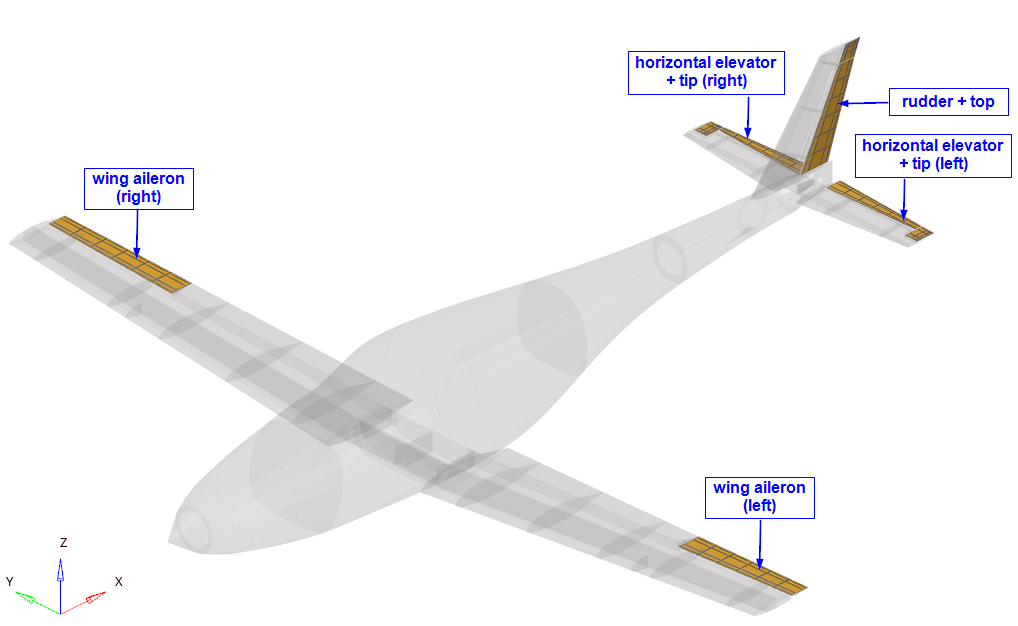
This section is the main portion of this tutorial; the aeroelastic domain is defined. There are 18 entities total, as shown in Figure 3. The structural domain is shown in light grey.
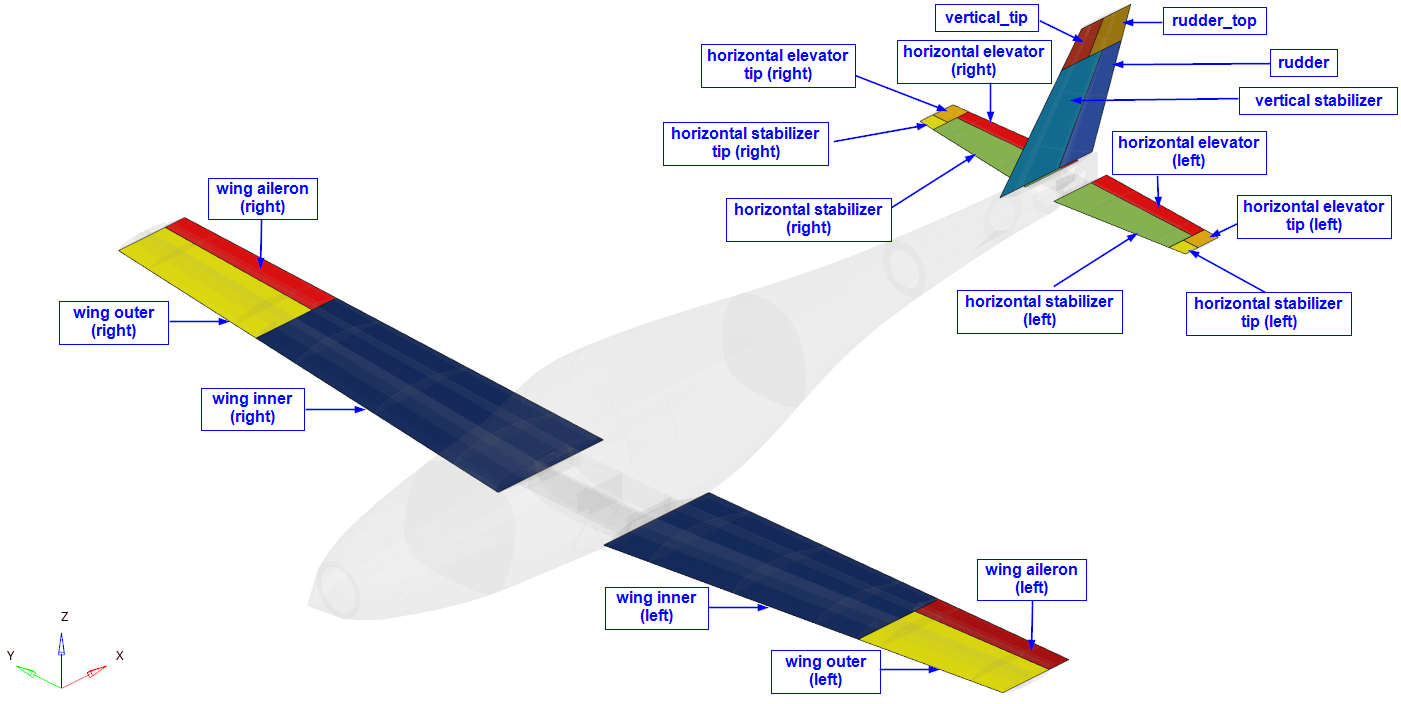
Figure 3. Entities of Aeroelastic Domain
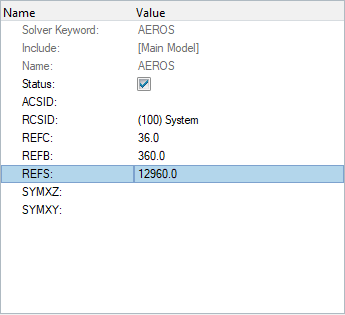
Create AEROS Entry
In this step, basic/references parameters for the simulation are defined.
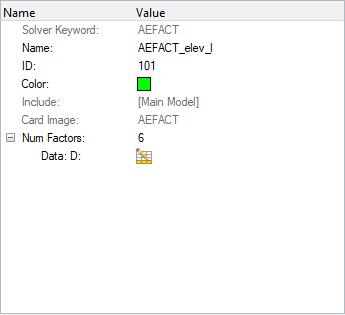
Create AEFACT Entries
The AEFACT entry is used to create tabular data of division points for the Aero panels; these panels are later referenced in the CAERO1 entry.
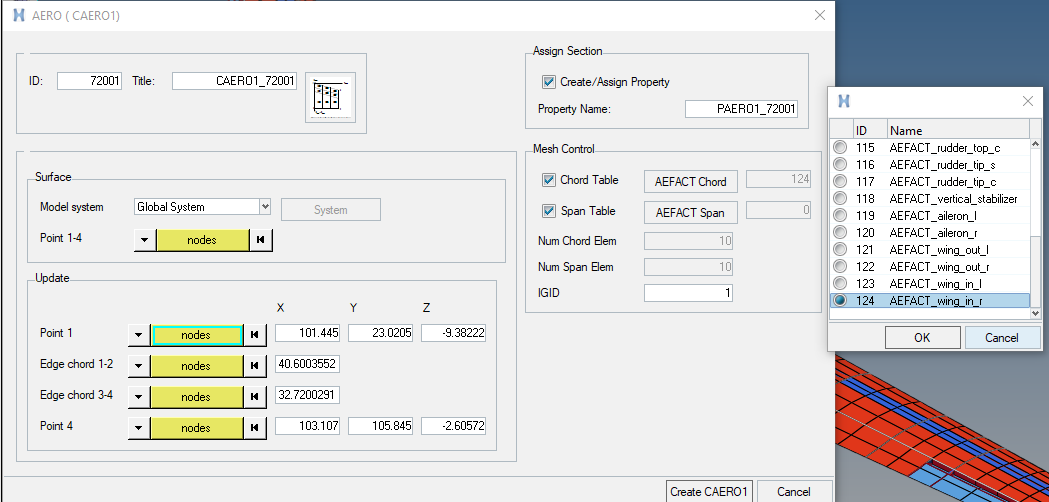
Create Aeroelasticity Panels
The CAERO1 entry is used to create aeroelasticity panel mesh in the base structure model. The AEFACT entries are used to create divisions in the panel mesh along the chord and span directions.
Create Aeroelasticity Box Lists
The AELIST entry is used to create lists of aeroelasticity boxes from the panel mesh (CAERO1).
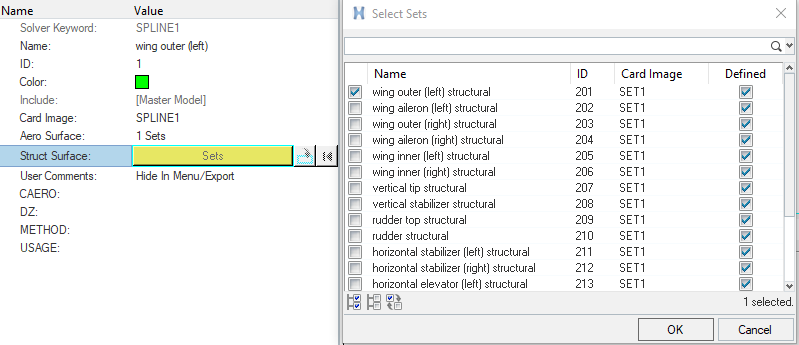
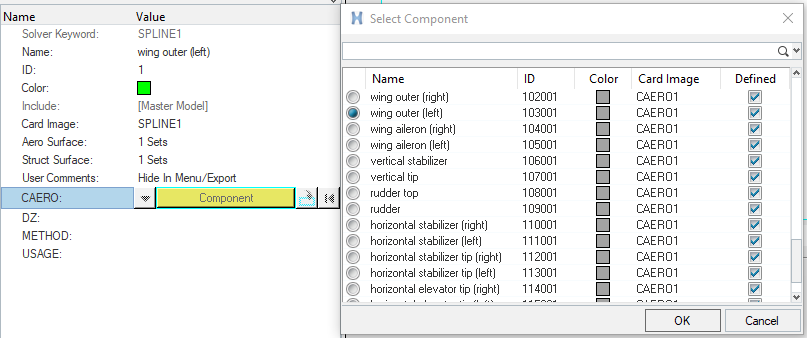
Create Interpolation SPLINES
In this step, SPLINE1 entries are created for interpolating motion and/or forces between the aeroelastic and structural domains. Each SPLINE1 entry is reference to an AELIST set (aeroelastic domain), a node set (structural domain) and the corresponding CAERO1 entry. 18 SPLINE1 entries are created for each of the 18 entities in the aeroelastic domain. The node set for the structural domain is already available in the base model.
Create AESTAT Entries
The AESTAT entry specifies rigid body motions which are used as trim variables in the aeroelastic analysis. This is later referenced in the TRIM Bulk Data Entry.
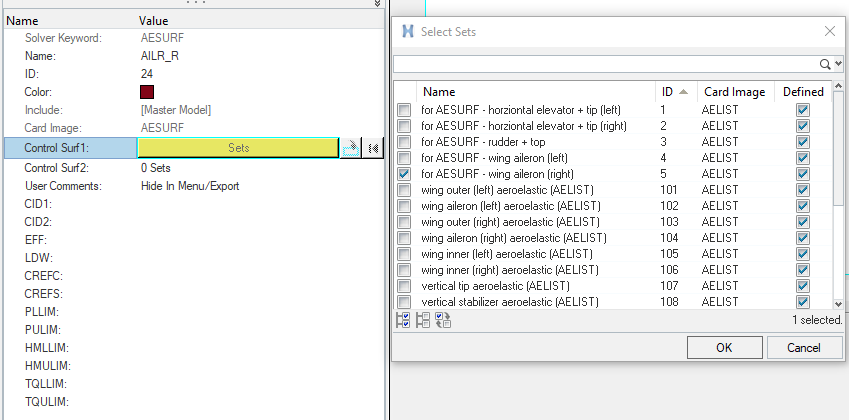
Create AESURF Entries
In this step, the aerodynamic control surface is defined.
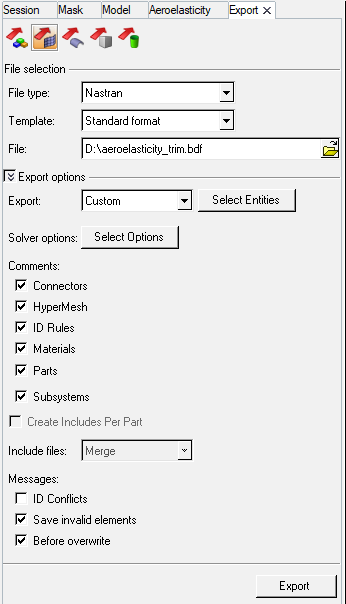
Export the Input File and Add Aeroelastic Entities
In the following steps, certain entities which are not fully supported in HyperMesh are added to the input file manually using a text editor.
Export the Input File
Define TRIM Entry
In this step, the Mach number, Dynamic pressure, and constraint values for the aerodynamic trim variables are defined.
Define AELINK Entry
In this step, the AELINK entries are used to define relationships between the AESURF entries.
Define Aeroelastic Subcase Information Entries
- The TRIM Bulk Data Entry is referenced in the subcase.
- Aeroelastic output requests are added.
- Symmetry flags are added.
Perform Corrections to the Input File
Due to some HyperMesh export issues, the input file requires some manual correction. These issues will be addressed in future releases.
-
In SPLINE1, check that BOX1 ID and BOX2 ID match the upper
and lower bounds of the corresponding CAERO1 entries.
- If the bounds are incorrect, review the CAERO1 entries and correct them in SPLINE1.
-
In SPLINE1 verify that BOX1 ID < BOX2 ID.
- If the values are incorrect, swap them accordingly.
- Change the value of EFF in AESURF from 0.0 to 0.1.