Finite element computation, approximation functions
Introduction
- order of the approximation functions: first order / second order
- type of the approximation functions: edge/nodal
Order of elements and approximation functions
- different types of finite elements mesh: 1st order mesh or 2nd order mesh
- different types of approximation functions: linear functions (first order) or quadratic functions (second order)
| Mesh | Position of nodes | Approximation function |
|---|---|---|
| 1st order | Vertexes | Linear (polynomial of first order) |
| 2nd order | Vertexes + middle of edges | Quadratic (polynomial of second order) |
Nodal or edge approximation function
Flux provides to the user:
- the edge approximation functions (computation on the edges of finite element and storage of information in the middle node of edges)
- the nodal approximation functions (computation on the nodes of the finite element)
The edge functions are provided only for the electric vector potential T. The approximation functions for the scalar magnetic potential Φ are of the nodal type.
Therefore, the use of the edge functions is applied to the regions of the solid conductor type (Transient Magnetic and Steady state AC Magnetic applications).
Caution
- solid conductors
- presence of induced currents tangent to the device edges. These edges are the edges of the inside corners of the device.
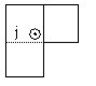
Example: computation of the eddy currents in a solid conductor of the thin plate type in the presence of cracks.
Modifying the default choices
The user does not have to modify the order or the type of the approximation functions. The default choices are adapted to the most situations. However, these choices can be brought to a change under certain particular conditions.
- automatic mode: default choice
- manual mode: user’s choice
Automatic mode
- if the mesh is of the 1st order, the nodal approximation functions are of the first order
- if the mesh is of the 2nd order, the nodal approximation functions are of the second order
If there are regions of the solid conductor type (formulation in electric vector potential), the approximation functions are the edge functions that require a 2nd order mesh. The generation of 2nd order mesh is then automatically carried out.
- Magnetic scalar potential: nodal approximation functions (2nd order)
- Electric vector potential: edge approximation functions
In manual mode
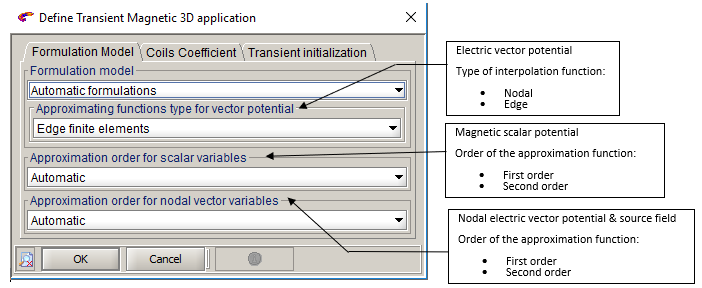
In manual mode, the user can modify the order (1st order / 2nd order) and the type of approximation functions (nodal type/edge type for the electric vector potential). These modifications are carried out in the dialog box of the application definition as presented in the figure below.
Advice
For a huge project, if the memory is not enough during solving process, it is possible to decrease the memory by choosing the vector variables approximation order of first order. It allows earning solving time and memory, despite a light results accuracy degradation.