COMMU1 Type
The airbag simulation used by Radioss adopts a special uniform pressure airbag. Hence, regardless of the state of inflation or shape, the pressure is uniform.
Perfect gas law and adiabatic conditions are assumed. Injected mass and temperature are defined as a time function. A sensor can define the inflate start time.
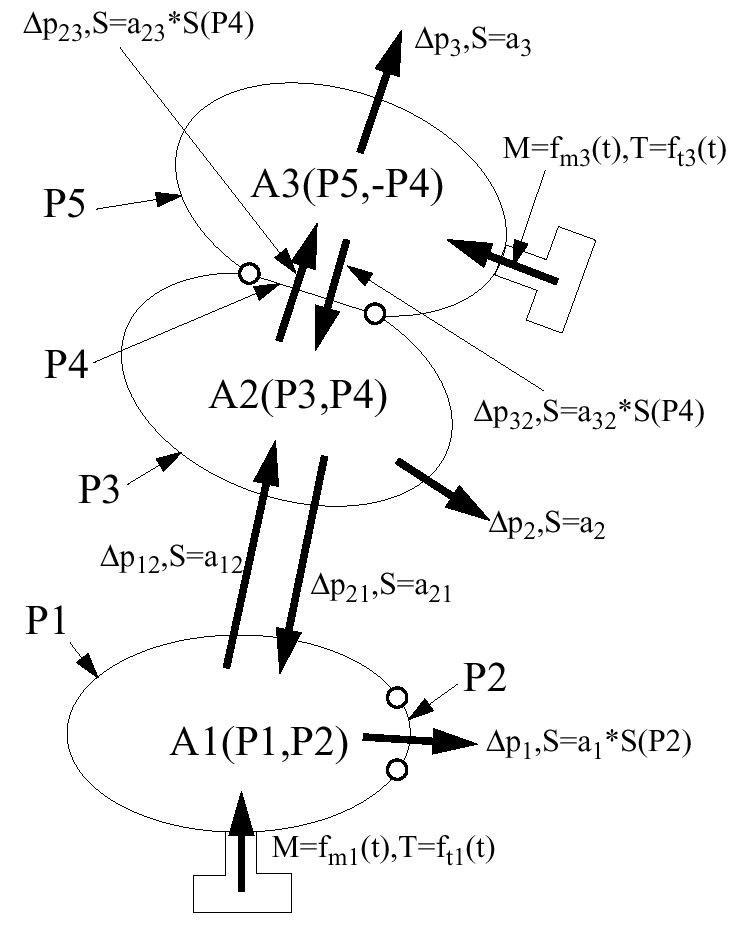
Figure 1. Chambered Airbag Schema
- Uniform airbag pressure kinetic energy is negligible
- Adiabatic conditions
- Injection of energy and mass
- Bag mechanics (that is, unfolding, expansion, membrane tension, impacts, ...)
- Exhaust through vent holes
This option is used to simulate chambered airbags and may be used to unfold an airbag.
Each COMMU1 type monitored volume works like an AIRBAG type monitored volume with possible vent communication with some other monitored volume of COMMU1 type. A chambered airbag is therefore modeled with two or more COMMU1 type monitored volumes.
Each monitored volume can have an inflater and an atmospheric vent hole.
Monitored volume 1 can communicate with monitored volume 2 with or without communication from 2 to 1. Communicating area, deflation pressure or time from 1 to 2 can be different from corresponding values from 2 to 1. It is thereby possible to model a valve communication.
͢͢Thermodynamical Equations
Same equations as for AIRBAG type monitored volume are used. Refer to Thermodynamical Equations.
External Work Variation
Same equations as for AIRBAG type monitored volume are used. Refer to Energy Variation Within a Time Step.
Mass Injection
Same equations as for AIRBAG type monitored volume are used. Refer to Mass Injection.
Venting
Same equations as for AIRBAG type monitored volume are used. Refer to Venting Outgoing Mass Determination.
These mass and energy flux are removed from the current volume and added to the communicating volume at next cycle.
Supersonic Outlet Flow
Same equations as for AIRBAG type monitored volume is used. Refer to Supersonic Outlet Flow.
Jetting Effect
Same explanation as for AIRBAG type monitored volume is used. Refer to Jetting Effect.
Reference Metric
Same explanation as for AIRBAG type monitored volume is used. Refer to Reference Metric.
COMMU1 Type Examples
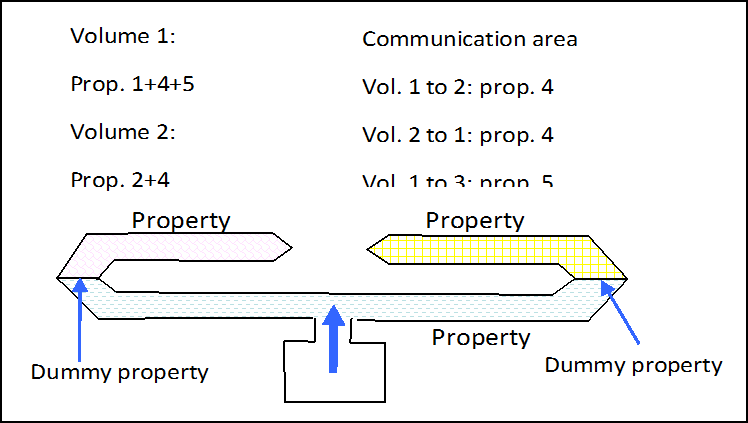
Example: Communication between the 2 Volumes
Volume 1 communicates with volume 2 and vice-versa.
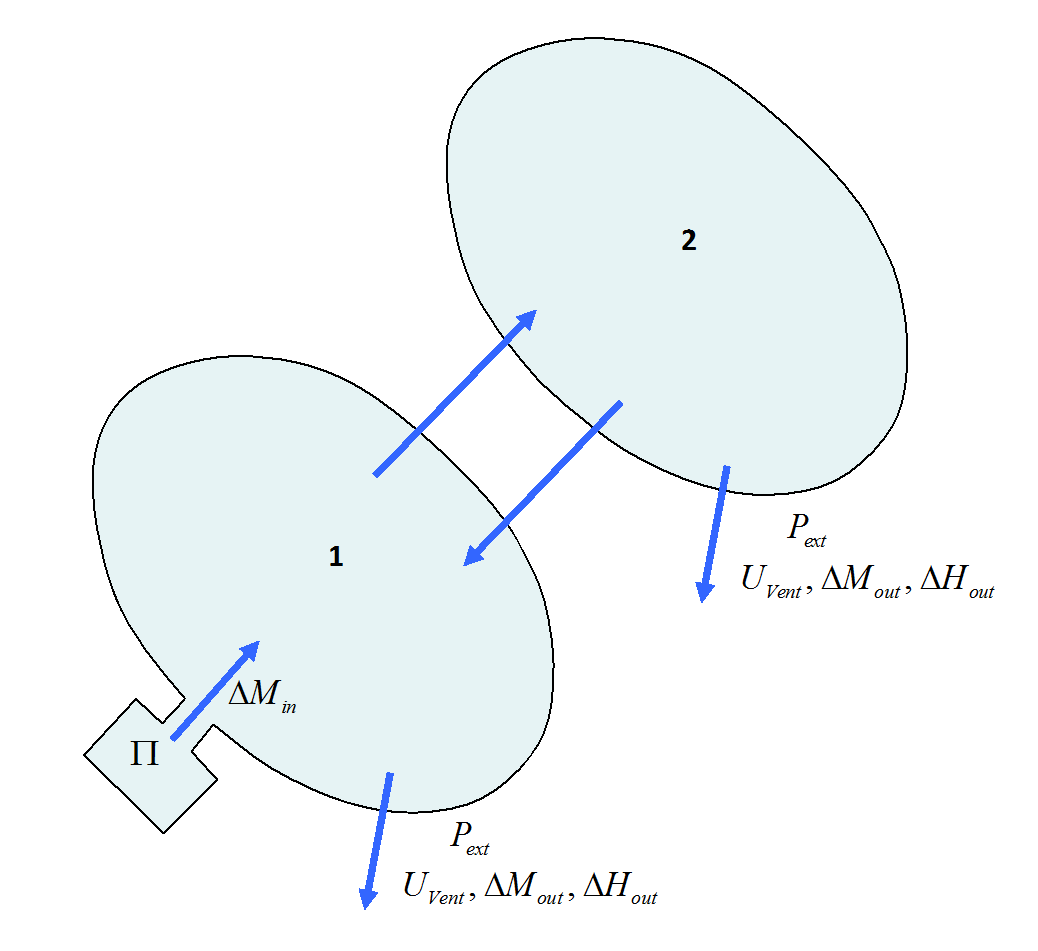
Figure 2. Communication between the 2 Volumes
Example: No Communication between 2 and 3
Volume 1 communicates with volume 2 and volume 2 with volumes 1 and 3, but there is no communication from 3 to 2.
Two COMMU1 type monitored volume communications can have common nodes or common shell property sets but this is optional.

Figure 3. No Communication between 2 and 3
Example: Monitored Volume with Communication Coefficient
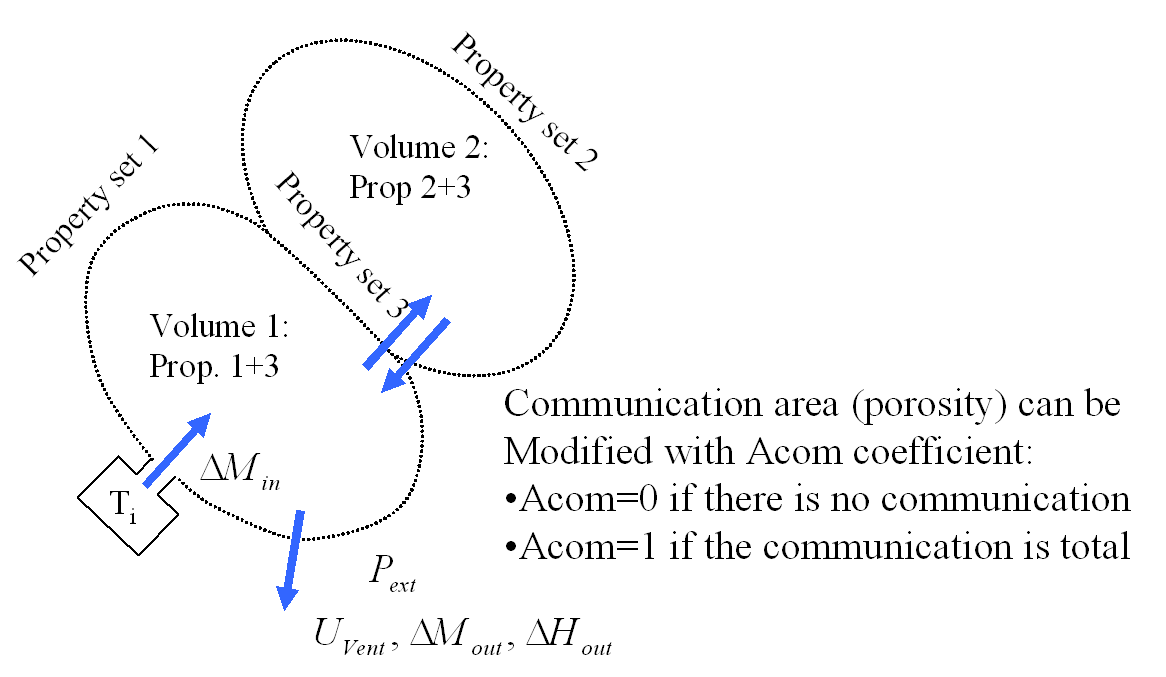
Figure 4. Monitored Volume with Communication Coefficient
Example: Folded Airbag