Squeak and Rattle
Allows one to identify squeak and rattle issues at various points along the contact surface of neighboring parts.
Terminology
- Rattle
- Rattle is caused when there is a relative motion between components that
come in contact for a short duration of time, due to impact forces.
Rattle generally occurs when the components are loose or overly
flexible.
 Figure 1.
Figure 1. - Squeak
- Squeak is an undesirable sound that occurs when two surfaces interact
under stick-slip phenomenon, and friction induces is caused by a
relative motion between the surfaces. The frictional energy is stored in
the contact surfaces and is released when it exceeds the kinetic
friction, which in turn produces an audible squeak.
 Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Setup
Examples
- Squeak and rattle if the normal gap is below the open-close tolerance and the tangential distance is above the stick-slip tolerance.
- Rattle if the normal gap is below the open-close tolerance and the tangential distance is below the stick-slip tolerance.
- NA if the normal gap is above the open-close tolerance.
Example 1
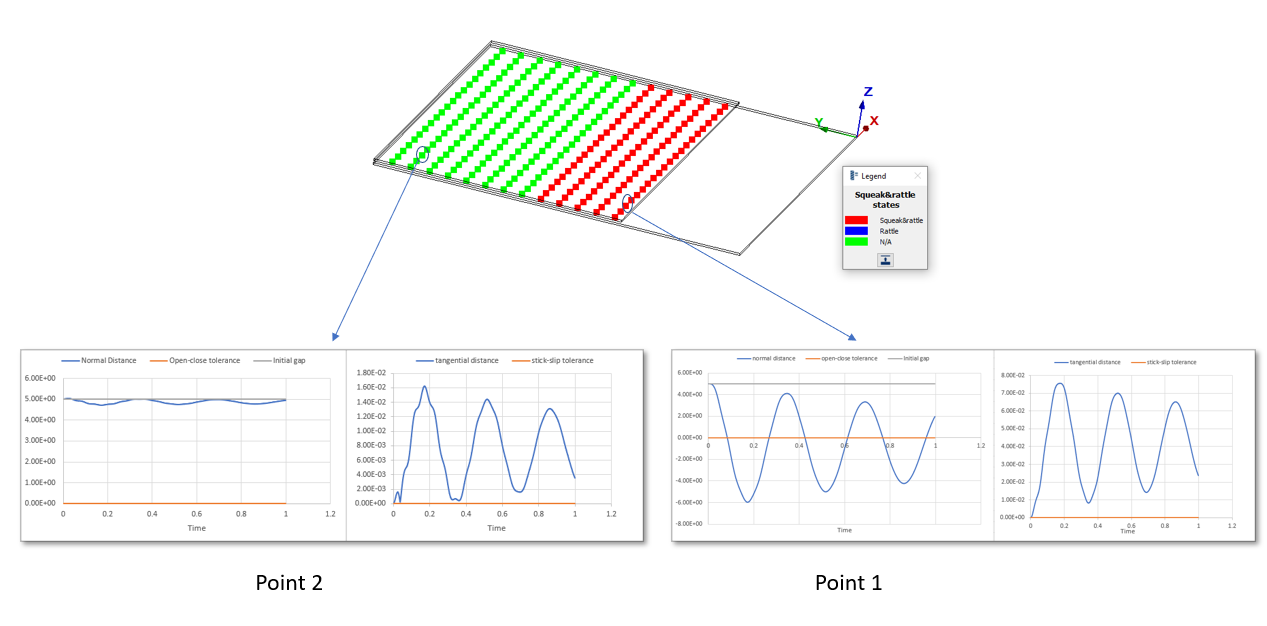
Open-close tolerance = 0
Stick-slip tolerance = 0
Initial gap between the plates = 5mm
Point 1 has both squeak and rattle as the normal gap is below the open-close tolerance and tangential displacement is above the stick-slip tolerance.
Point 2 is green as it has a normal gap much higher than the open-close tolerance. The parts are always separated, so it neither rattles nor squeaks.
Example 2
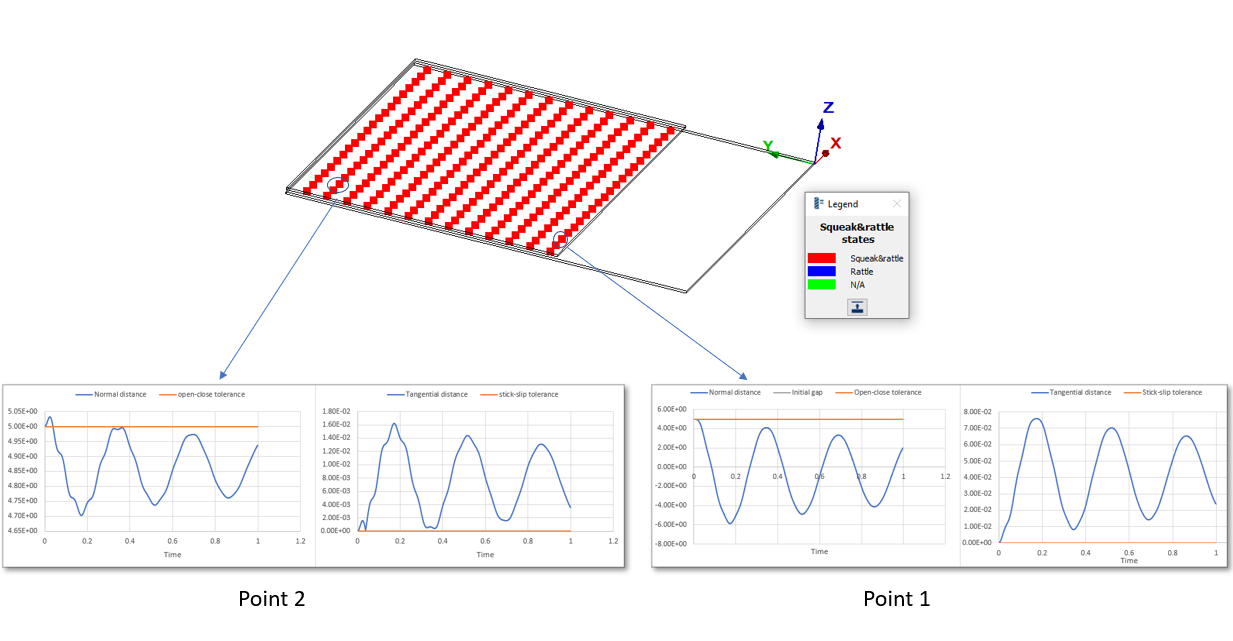
Open-close tolerance = 5 mm
Stick-slip tolerance = 0
Initial gap between the plates = 5mm
Point 1 and Point 2 are identified to squeak and rattle as the normal gap is below the open-close tolerance and tangential displacement is above the stick-slip tolerance.
Example 3
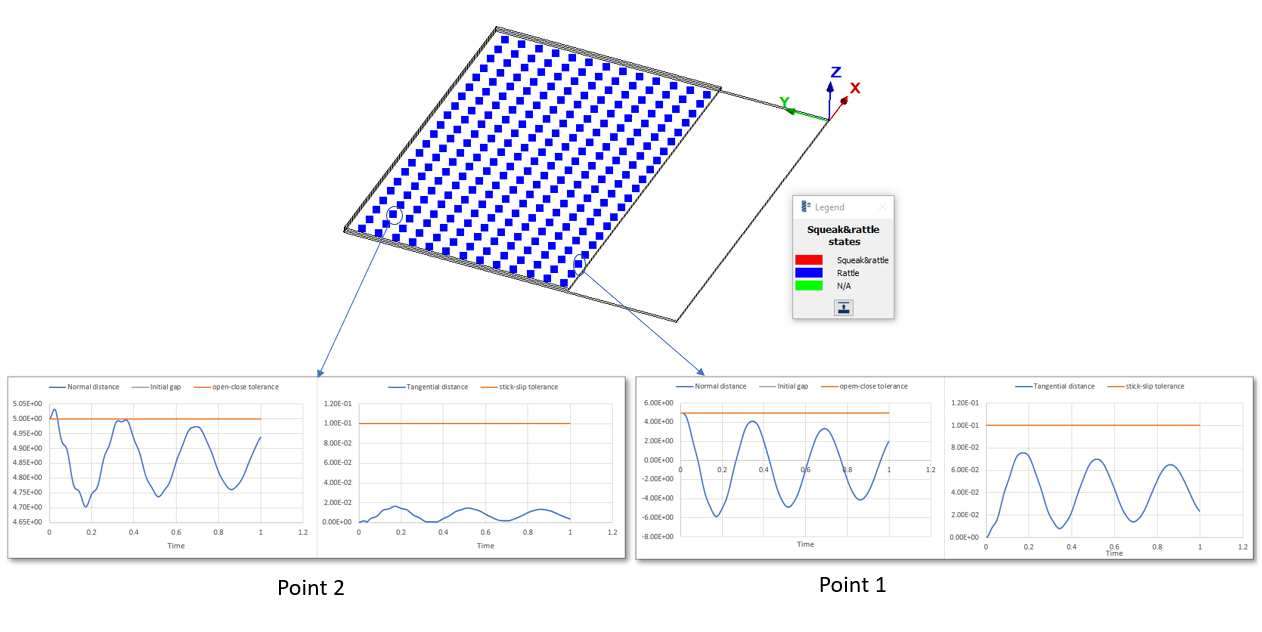
Open-close tolerance = 5
Stick-slip tolerance = 0.1
Initial gap between the plates = 5mm
Point 1 and Point 2 are identified to rattle only as the normal gap is below the open-close tolerance and tangential displacement is below the stick-slip tolerance.
Hence no squeak and the points' final state is set to Rattle only.