Magneto Static: solved equations (vector model 2D)
Introduction
The vector model is the general model proposed for 2D applications.
This model is used by default (automatically) by:
- the 2D solver of Flux 2D
- the 3D solver of Flux 3D for solving a 2D application
Equation solved with vector model (2D applications)
The Gauss law for magnetism, ![]() , allows the introduction of a magnetic vector potential
, allows the introduction of a magnetic vector potential ![]() , such as:
, such as: ![]()
The equation solved by the finite elements method in a Magneto Static application is written:
![]()
where:
- [νr] is the tensor of the relative reluctivity of the medium
-
ν0 is the magnetic reluctivity of the vacuum, ν0 = 1/μ0 = 1/(4 π 10-7)
(in m/H)
-
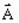 is the vector potential (in Wb/m)
is the vector potential (in Wb/m) -
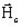 is coercive magnetic field (permanent magnets) (in
A/m)
is coercive magnetic field (permanent magnets) (in
A/m) -
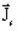 is the density of
current source (in A/m2)
is the density of
current source (in A/m2)
State variable, vector model (2D applications)
The state variable in 2D applications is the magnetic vector potential ![]() .
.
The magnetic field B is written : ![]()
and :
![]() ;
; ![]() ;
; ![]()
In 2D problems, the ![]() vector has a non null component, the normal component to the plane of figure; let
An (or Az)
vector has a non null component, the normal component to the plane of figure; let
An (or Az)
The magnetic field B is written:
![]() ;
; ![]() ;
; ![]()
The state variable, dependent on the problem type, plane 2D or axisymmetric 2D, is given in the table below.
| Type of the problem | State variable |
Notation (in Flux 3D) |
|---|---|---|
| plane | An | AN1* |
| axisymmetric | rAn | RAN1* |