OS-V: 0270 Torsional Creep of Circular Shaft
This benchmark illustrates the structural response of a power law creeping material in a geometrical configuration subjected to pure torsion. OptiStruct examines strain at the edge of the shaft.
- Relaxation at constant twist
- Forward creep at steady twist rate
Relaxation at Constant Twist
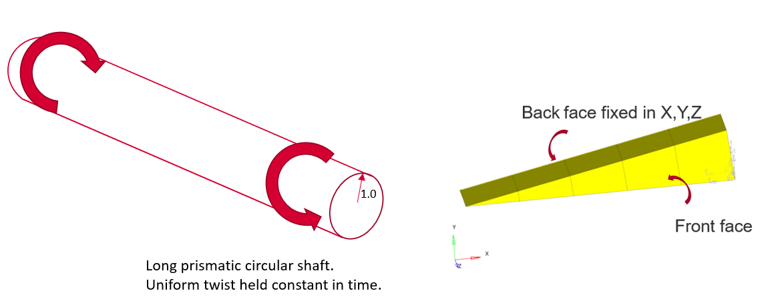
図 1. Model and Loading Description
Benchmark Model
- X, Y displacements given at all nodes of front face using cylindrical system: 0.002 mm
- Rotation is given at mid-side nodes: 0.001 radians
Uniform twist of 0.01 radians/unit length is held constant in time from 0 to 100s.
- Material Properties
- Value
- Young's modulus
- 10 GPa
- Poisson's ratio
- 0.3
- Creep law equation
- Equivalent creep strain rate
- Equivalent stress (Mises)
Nonlinear Static Analysis Results
| OptiStruct | NAFEMS | Normalized Target Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Strain (*10-3) | 5.46 | 5.77 | 0.95 |
| Creep Strain (*10-3) | 4.85 | 4.77 | 1.01 |
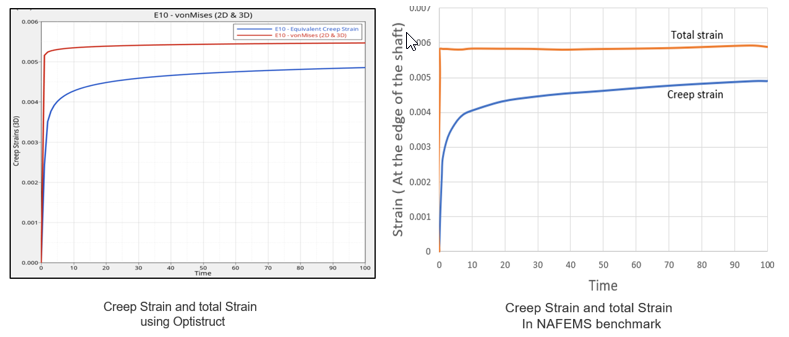
図 2. Comparison of Total Strain and Creep Strain at the Edge of the Shaft
Model Files
必要なモデルファイルのダウンロードについては、モデルファイルへのアクセスを参照してください。
The model file used in this example includes:
Torsional_Creep_Relaxation_at_constant_twist.fem
Forward Creep at Steady Twist Rate
A steadily increasing twist is applied at constant rate to the shaft.
The stresses increase from zero to steady value. The loads, which cause this steady-state behavior are referred as “primary” loads.

図 3. Model and Loading Description
Benchmark Model
- X, Y displacements given at all nodes of front face using cylindrical system: 0.004 mm/unit time
- Rotation is given at mid-side nodes: 0.002 radians/unit time
- Material Properties
- Value
- Young's modulus
- 10 GPa
- Poisson's ratio
- 0.3
- Creep law equation
- Equivalent creep strain rate
- Equivalent stress (Mises)
Nonlinear Static Analysis Results
| OptiStruct | NAFEMS | Normalized Target Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Strain (*10-2) | 1.62 | 1.7321 | 0.94 |
| Creep Strain (*10-2) | 1.27 | 1.1693 | 1.094 |
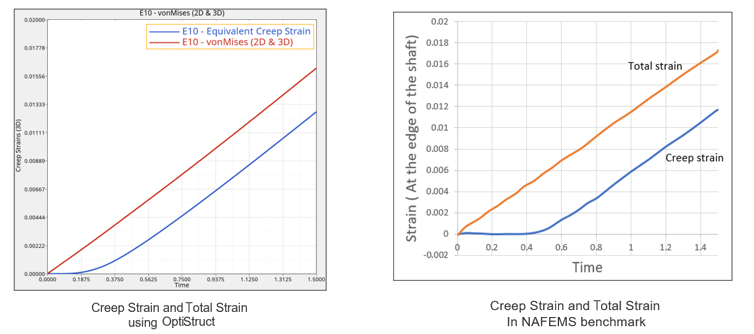
図 4. Comparison of Total Strain and Creep Strain at the Edge of the Shaft
Model Files
必要なモデルファイルのダウンロードについては、モデルファイルへのアクセスを参照してください。
The model file used in this example includes:
Torsional_forward_creep_at_steady_twist_rate.fem
Reference
NAFEMS R0026 - Selected Benchmarks for Material Non-Linearity- Volume 1