Combine Lines
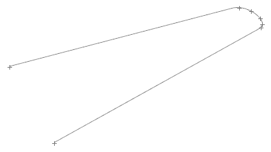
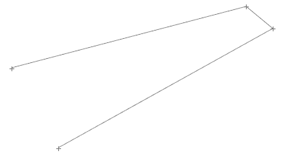
Use the Combine Lines tool to create a new continuous line segment between two existing lines, resulting in a single seamless line.

Figure 1.
View new features for HyperWorks CFD 2022.2.
Learn the basics and discover the workspace.
Discover HyperWorks CFD functionality with interactive tutorials and community resources.
Create, open, import, and save models.
Create, organize and manage parts and subsystems.
Create and edit 2D parametric sketch geometry.
Create, edit, and cleanup geometry.
Convert b-spline models to discrete models then clean up the geometry and mesh.
Review geometric errors in the model's surfaces and solids and fix any defects.
Explore the tools used to create geometry.
Learn about creating, editing, and extracting points and nodes.
A line represents a curve in space and is not attached to any surface or solid. A line is a one-dimensional geometric entity.
Use the Create Lines tool to draw free lines for geometry construction and to generate meaningful snap locations to be used by other tools.
Use the Create Polylines tool to draw polylines for geometry construction and to generate meaningful snap locations to be used by other tools.
Use the Combine Lines tool to create a new continuous line segment between two existing lines, resulting in a single seamless line.
Use the Extend Lines tool to make an existing line longer, following the general vector and/or curvature of the input line. You can specify the distance as a numeric value, or extend the line to a specified node, line, surface, or point.
Use the Midlines tool to create midlines from existing lines, surface edges, or tube solids.
Create and edit circles and rectangles with the Shapes tool.
A surface represents the geometry associated with a physical part. A surface is a two-dimensional geometric entity that may be used in automatic mesh generation.
Solids are closed volume of surfaces that can take any shape. Solids are three-dimensional entities that can be used in automatic tetra and solid meshing.
Use the Midsurfaces tool to extract the midsurface of sheet metal stampings, molded plastic parts with ribs, and other parts that have thickness clearly smaller than width and length.
Drag surfaces, nodes, or lines along their normal direction, a vector, or another line.
Use the Ruled tools to create surfaces/solids by interpolating lines and surfaces either linearly or smoothly.
Explore the tools used to edit geometry.
Clean up problematic areas on geometry.
When performing cleanup or defining simulation parameters, it can be helpful to first find and isolate certain types of geometry. This will give you a better idea of the areas in the model you need to focus on.
Set up the simulation model, materials, domains, and boundaries.
Define radiation conditions and create emissivity models.
Define direct, derived, and constrained mesh motion.
Generate surface/volume mesh by defining mesh controls, or interactively create and edit 2D surface mesh.
Define output conditions, run the simulation, and view the results.
Use the Template Manager to define rule-based logic for groups, geometric operations, and setup and automate simulation processes.
Post-process the simulation results by creating visualizations and measurements.
AcuTrace is particle tracer that runs as a post-processor to AcuSolve.
Click here to access AcuSolve online help.
Create, edit, and cleanup geometry.
Explore the tools used to create geometry.
A line represents a curve in space and is not attached to any surface or solid. A line is a one-dimensional geometric entity.
Use the Combine Lines tool to create a new continuous line segment between two existing lines, resulting in a single seamless line.
Use the Combine Lines tool to create a new continuous line segment between two existing lines, resulting in a single seamless line.

© 2023 Altair Engineering, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Intellectual Property Rights Notice | Technical Support | Cookie Consent