Block Format Keyword Describes moving frames. Relative motion with respect to a reference frame. Moving frame
definition differs from /FRAME/MOV . 8
Format
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
/FRAME/MOV2 /frame_ID
frame_title
node_ID 1 node_ID 2 node_ID 3
Definition
Field
Contents
SI Unit Example
frame_ID Reference frame identifier
- must be different from all skew identifiers.(Integer, maximum
10 digits)
frame_title Reference frame
title(Character, maximum 100 characters)
node_ID 1 Node identifier
N 1 (Integer)
node_ID 2 Node identifier
N 2 (Integer)
node_ID 3 Node identifier
N 3 (Integer)
Comments
Let a moving reference frame
Λ
t
(
A , u , v , w
)
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaeu4MdW0aaS
baaSqaaiaadshaaeqaaOWaaeWaaeaacaWGbbGaaiilaiaahwhacaGG
SaGaaCODaiaacYcacaWH3baacaGLOaGaayzkaaaaaa@3FF7@
For each time t ,
the frame position and orientation are determined via its original position
x
A
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaamiEamaaBa
aaleaacaWGbbaabeaaaaa@37E6@
R
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCOuaaaa@36D1@
.
Let
w MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaC4Daaaa@36F7@
λ
.
For each time t ,
the local coordinates of
x
l
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCiEamaaBa
aaleaacaWGSbaabeaaaaa@3815@
a point M with respect to the
frame are related to its coordinates
x
G
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCiEamaaBa
aaleaacaWGhbaabeaaaaa@37F0@
into the global system, as:(1)
x
G
=
x
A
+
R
x
l
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCiEamaaBa
aaleaacaWGhbaabeaakiabg2da9iaahIhadaWgaaWcbaGaamyqaaqa
baGccqGHRaWkcaWHsbGaaCiEamaaBaaaleaacaWGSbaabeaaaaa@3ED8@
The relative displacement
u
l
=
x
l
−
x
l
0
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCyDamaaBa
aaleaacaWGSbaabeaakiabg2da9iaahIhadaWgaaWcbaGaamiBaaqa
baGccqGHsislcaWH4bWaa0baaSqaaiaadYgaaeaacaaIWaaaaaaa@3F10@
of M between time 0 and
t , with respect to the frame is related to its
displacement with regard to the global system, as:(2)
u G
=
u A
+ (
R −
R 0
)
x l
+ R
u l
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCyDamaaBa
aaleaacaWGhbaabeaakiabg2da9iaahwhadaWgaaWcbaGaamyqaaqa
baGccqGHRaWkdaqadaqaaiaahkfacqGHsislcaWHsbWaaWbaaSqabe
aacaaIWaaaaaGccaGLOaGaayzkaaGaaCiEamaaBaaaleaacaWGSbaa
beaakiabgUcaRiaahkfacaWH1bWaaSbaaSqaaiaadYgaaeqaaaaa@46F6@
The relative velocity of
M with respect to the frame is related to its velocity
with regard to the global system, as:(3)
R
v
l
=
v
G
−
v
e
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCOuaiaahA
hadaWgaaWcbaGaamiBaaqabaGccqGH9aqpcaWH2bWaaSbaaSqaaiaa
dEeaaeqaaOGaeyOeI0IaaCODamaaBaaaleaacaWGLbaabeaaaaa@3F01@
Where,
v e
=
v A
+ ω × A M
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCODamaaBa
aaleaacaWGLbaabeaakiabg2da9iaahAhadaWgaaWcbaGaamyqaaqa
baGccqGHRaWkcaWHjpGaey41aqRaaCyqaiaah2eaaaa@4105@
M at time t and fixed with respect
to the reference frame.
The relative acceleration of
M with respect to the frame M is
related to its acceleration with regard to the global system, as:
(4)
R
γ
l
=
γ
G
−
γ
e
−
γ
c
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaCOuaiaaho
7adaWgaaWcbaGaamiBaaqabaGccqGH9aqpcaWHZoWaaSbaaSqaaiaa
dEeaaeqaaOGaeyOeI0IaaC4SdmaaBaaaleaacaWGLbaabeaakiabgk
HiTiaaho7adaWgaaWcbaGaam4yaaqabaaaaa@430B@
Where,
γ
e
=
γ
A
+
d
ω
d
t
×
A
M
+
ω
×
(
ω
×
A
M
)
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaC4SdmaaBa
aaleaacaWGLbaabeaakiabg2da9iaaho7adaWgaaWcbaGaamyqaaqa
baGccqGHRaWkdaWccaqaaiaadsgacaWHjpaabaGaamizaiaadshaaa
Gaey41aqRaaCyqaiaah2eacqGHRaWkcaWHjpGaey41aq7aaeWaaeaa
caWHjpGaey41aqRaaCyqaiaah2eaaiaawIcacaGLPaaaaaa@4F45@
Driving acceleration
γ
c
=
2
ω
×
v
r
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aqatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn
hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr
4rNCHbGeaGqiVu0Je9sqqrpepC0xbbL8F4rqqrFfpeea0xe9Lq=Jc9
vqaqpepm0xbba9pwe9Q8fs0=yqaqpepae9pg0FirpepeKkFr0xfr=x
fr=xb9adbaqaaeGaciGaaiaabeqaamaabaabaaGcbaGaaC4SdmaaBa
aaleaacaWGJbaabeaakiabg2da9iaaikdacaWHjpGaey41aqRaaCOD
amaaBaaaleaacaWGYbGaamyzaiaadYgacaWGHbGaamiDaiaadMgaca
WG2bGaamyzaaqabaaaaa@4631@
Acceleration, due to Coriolis forces
For a moving reference frame, the
reference frame position and orientation vary with time and are defined by
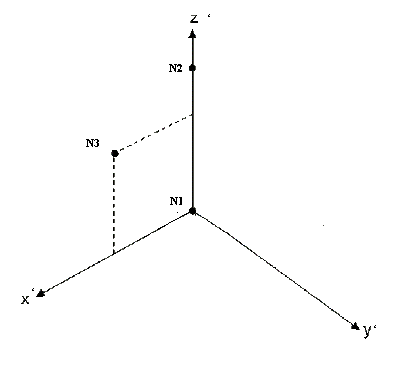
N 1 , N 2 and
N 3 .The origin of the frame is defined by
the position of N 1 .
node_ID 1 node_ID 2
Z
′
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbwvMCKf
MBHbqefqvATv2CG4uz3bIuV1wyUbqedmvETj2BSbqefm0B1jxALjhi
ov2DaebbnrfifHhDYfgasaacH8akY=xipgYlh9vqqj=hEeei0xXdbb
a9frFf0=yqFf0dbba91qpepeI8k8fiI+fsY=rqaqpepae9pg0Firpe
pesP0xe9Fve9Fve9qapdbaGaaiGadiWaamaaceGaaqaacaqbaaGcba
GabCOwayaafaaaaa@3AC5@
node_ID 1 and
node_ID 3 define
X "
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbwvMCKf
MBHbqefqvATv2CG4uz3bIuV1wyUbqedmvETj2BSbqefm0B1jxALjhi
ov2DaebbnrfifHhDYfgasaacH8akY=xipgYlh9vqqj=hEeei0xXdbb
a9frFf0=yqFf0dbba91qpepeI8k8fiI+fsY=rqaqpepae9pg0Firpe
pesP0xe9Fve9Fve9qapdbaGaaiGadiWaamaaceGaaqaacaqbaaGcba
GaaCiwaiaackcaaaa@3B5D@
(5)
Y
'
=
Z
′
Λ
X
"
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbwvMCKf
MBHbqefqvATv2CG4uz3bIuV1wyUbqedmvETj2BSbqefm0B1jxALjhi
ov2DaebbnrfifHhDYfgasaacH8akY=xipgYlh9vqqj=hEeei0xXdbb
a9frFf0=yqFf0dbba91qpepeI8k8fiI+fsY=rqaqpepae9pg0Firpe
pesP0xe9Fve9Fve9qapdbaGaaiGadiWaamaaceGaaqaacaqbaaGcba
GaaCywaiaacEcacqGH9aqpceWHAbGbauaacqqHBoatcaWHybGaaiOi
aaaa@4054@
(6)
X
'
=
Y
'
Λ
Z
'
MathType@MTEF@5@5@+=
feaagKart1ev2aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbwvMCKf
MBHbqefqvATv2CG4uz3bIuV1wyUbqedmvETj2BSbqefm0B1jxALjhi
ov2DaebbnrfifHhDYfgasaacH8akY=xipgYlh9vqqj=hEeei0xXdbb
a9frFf0=yqFf0dbba91qpepeI8k8fiI+fsY=rqaqpepae9pg0Firpe
pesP0xe9Fve9Fve9qapdbaGaaiGadiWaamaaceGaaqaacaqbaaGcba
GaaCiwaiaacEcacqGH9aqpcaWHzbGaai4jaiabfU5amjaahQfacaGG
Naaaaa@40F8@
Figure 1.
Reference frame identifier must be different from all skew
identifiers.