Post-processing quantities
Introduction
The post-processing quantities are of two types:
- local quantities, analyzed in all points of the study domain,
- global quantities*, resulting from an integration, analyzed over the entire study domain or on a part of this domain.
Usual quantities
Usual local quantities available are presented on the table below.
| Usual quantities |
Flux formula |
Flux Unit | Explanation | Application | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D plane | 2D axi | 3D | ||||
| Temperature | Temp(Tkelvin) | K |
|
|
|
|
| Temperature (gradient) | mGradT | K/m |
|
|
|
|
| Heat capacity (volume): ρCP | RhoCp | J/(m3 .K) |
|
|
|
|
| Thermal conductivity: k | Kth | W/(m.K) |
|
|
|
|
| Thermal flux (surface density): |
dFluxTh | W/m2 |
or
|
|
|
|
Advanced use
Usual local quantities available in advanced use are presented on the table below.
|
Quantities (advanced use) |
Flux formula | Flux Unit | Explanation | Application | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D plane | 2D axi | 3D | ||||
| Temperature (Kelvin): TKelvin | TKelvin | K |
|
|
|
|
| Temperature (Celsius): TCelsius | TCelsius | °C | TCelsius = TKelvin -273.15 |
|
|
|
| Heat (volume density): q | dHeatV | W/m3 |
|
|
|
|
| Heat (surface density): q | dHeatS | W/m2 |
|
|
|
|
| Heat (line density): q | dHeatL | W/m |
|
|
|
|
| Heat transfer (convection coefficient): h | Hconv | W/(m2.K) |
|
|
|
|
| Hconv2s | (on both sides, for regions with double heat exchange) | |||||
| Heat transfer (radiation coefficient): ε | Hrad | W/(m2 .K4) |
|
|
|
|
| Hrad2s | (on both sides, for regions with double heat exchange) | |||||
|
Ambiante temperature (for convectif exchange) |
Tamb | K |
|
|
|
|
| Tamb2s | (on both sides, for regions with double heat exchange) | |||||
| Heat transfer (surface density): |
dExchangeS | W/m2 | 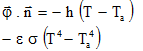 * * |
|
|
|
Global quantities
Global quantities are not directly available. They can be calculated by integration (See § Explanation of results)