ACU-T: 2000 Turbulent Flow in a Mixing Elbow
Prerequisites
Prior to starting this tutorial, you should have already run through the introductory HyperWorks tutorial, ACU-T: 1000 HyperWorks UI Introduction. To run this simulation, you will need access to a licensed version of HyperMesh and AcuSolve.
Prior to running through this tutorial, click here to download the tutorial models. Extract ACU-T2000_MixingElbow.hm from HyperMesh_tutorial_inputs.zip.
Since the HyperMesh database (.hm file) contains meshed geometry, this tutorial does not include steps related to geometry import and mesh generation.
Problem Description
The problem to be addressed in this tutorial is shown schematically in Figure 1. This is a typical industrial example for mixing in a pipe by injecting high-velocity fluid from a small inlet into relatively low-velocity fluid in the main pipe. It consists of a 90° mixing elbow with water entering through two inlets with different velocities. The geometry is symmetric about the XY midplane of the pipe, as shown in the figure

Figure 1. Schematic of Mixing Elbow
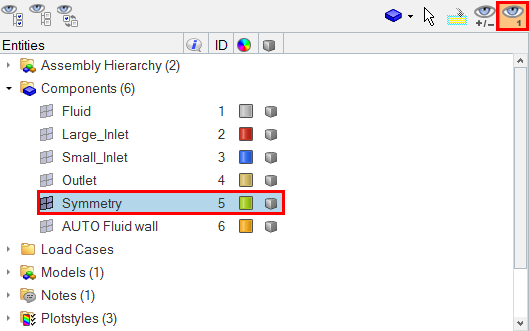
Open the HyperMesh Model Database
Set the General Simulation Parameters
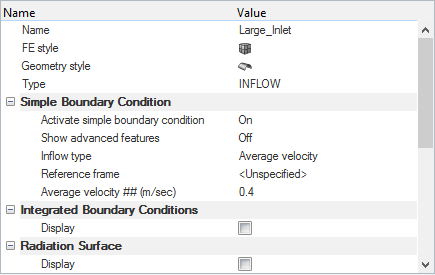
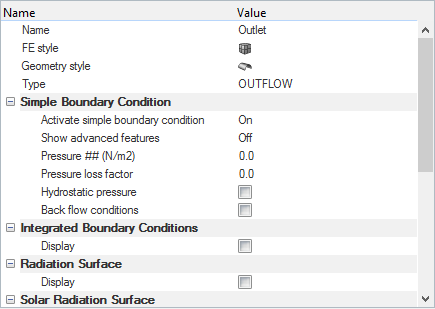
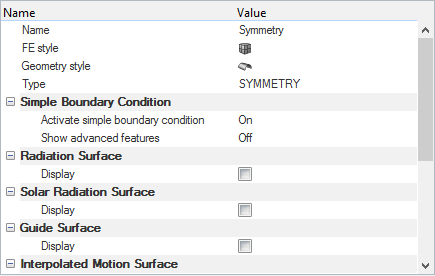
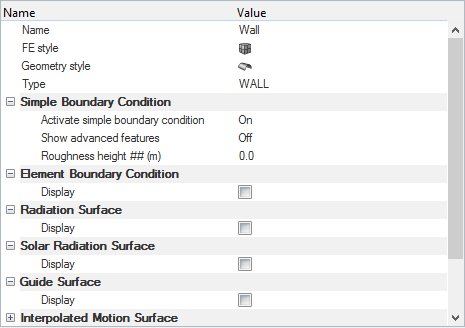
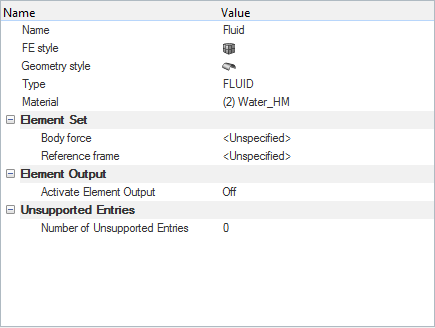
Set Up Boundary Conditions
Compute the Solution
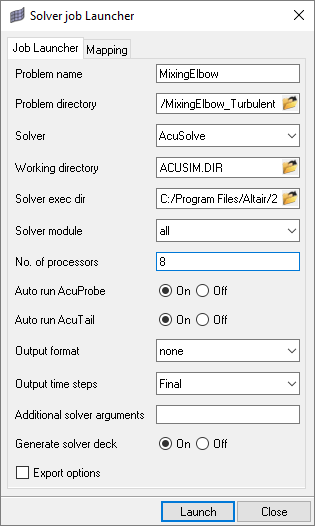
In this step, you will launch AcuSolve directly from HyperMesh and compute the solution.
Run AcuSolve
Post-Process the Results with HyperView
Open HyperView and Load the Model and Results
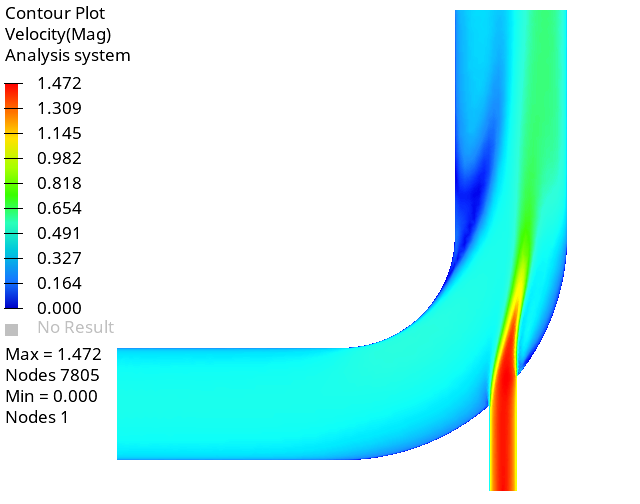
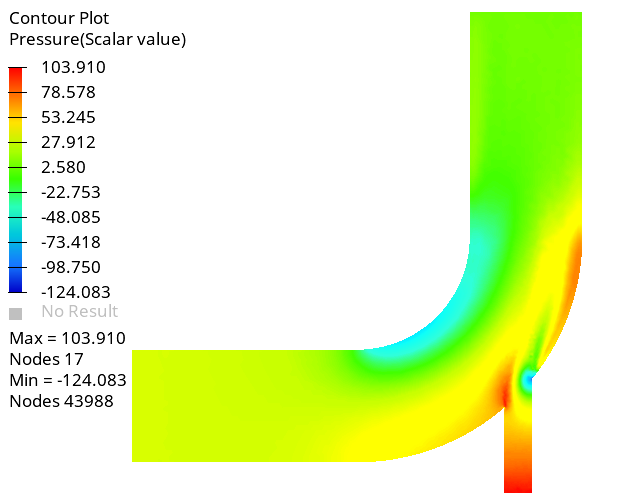
Create Contour Plots of Pressure and Velocity
Summary
In this tutorial, you worked through a basic workflow to set up a CFD model, carry out a CFD simulation, and post-process the results using HyperWorks products, namely AcuSolve, HyperMesh, and HyperView. You started by importing the model in HyperMesh. Then, you defined the simulation parameters and launched AcuSolve directly from within HyperMesh. Upon completion of the solution by AcuSolve, you used HyperView to post-process the results and create contour plots.
 on the Standard Views toolbar.
on the Standard Views toolbar.