Batch Create Module
Create assembly hierarchy and assign ID ranges to the modules from external .csv files.
It is also possible to assign ID ranges manually. It shows the detailed summary of module ID ranges in terms of assignment, validity and conflicts. Right-click on a module in the Assembly Browser and select Batch Create Module to open the dialog.
Assembly Hierarchy Creation and ID Assignment from an External CSV File
Click Import to open the Import modules and id ranges dialog. Load a .csv file that has assembly hierarchy and ID assignment definition. Select the modules and click OK to create modules in hierarchy and assign ID ranges.
Figure 1.
Assignment, Validity and Conflicts Status of Module ID Ranges
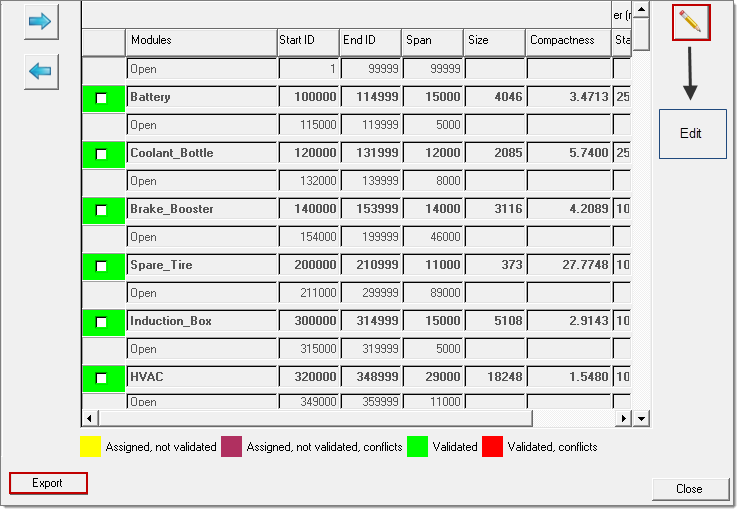
Figure 2.