SS-V: 5080 Rigid Punch Plasticity
Test No. VNL09 Find out reactions at the punch pressed on large block for perfectly plastic and isotropic hardening materials.
Definition
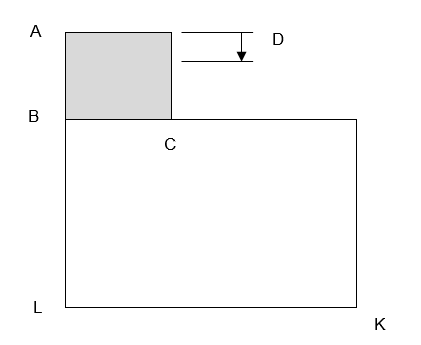
Figure 1.
Dimensions: AB = 40 mm, BC = 80 mm, BL = 160 mm, LK = 200 mm
- Properties
- Value
- Modulus of Elasticity
- 1.e+3 MPa
- Poisson's Ratio
- 0.3
- Elastic perfectly plastic with yield stress 1 MPa
- Isotropic hardening with tangent modulus 0.1e+3 MPa
Results
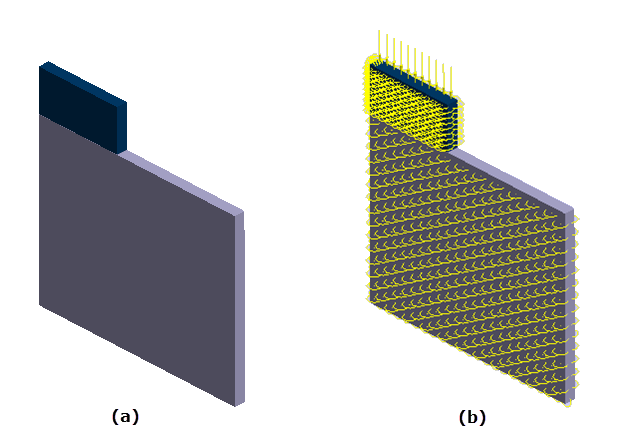
Figure 2.
| SimSolid Reaction, N | Reference Reaction, N | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D, mm | Perfect Plasticity | Hardening | Perfect Plasticity | Hardening |
| 0.04 | 29.57 | 29.57 | 30 | 30 |
| 0.12 | 86.95 | 87.27 | 86 | 87 |
| 0.14 | 99.93 | 100.65 | 99 | 100 |
| 0.16 | 108.22 | 111.17 | 109 | 113 |
| 0.18 | 108.87 | 113.03 | 110 | 114 |
| 0.24 | 111.75 | 122.20 | 111 | 125 |
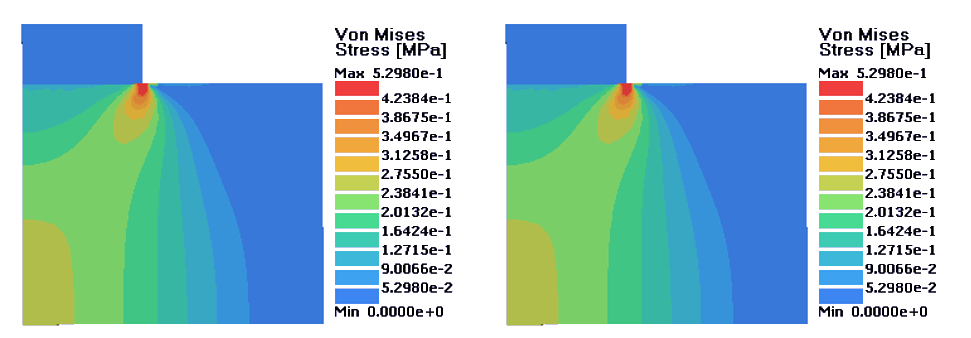
Figure 3. Left: Perfectly Plastic Material; Right: Isotropic Hardening Material. D = 0.04 mm

Figure 4. Left: Perfectly Plastic Material; Right: Isotropic Hardening Material. D = 0.12 mm
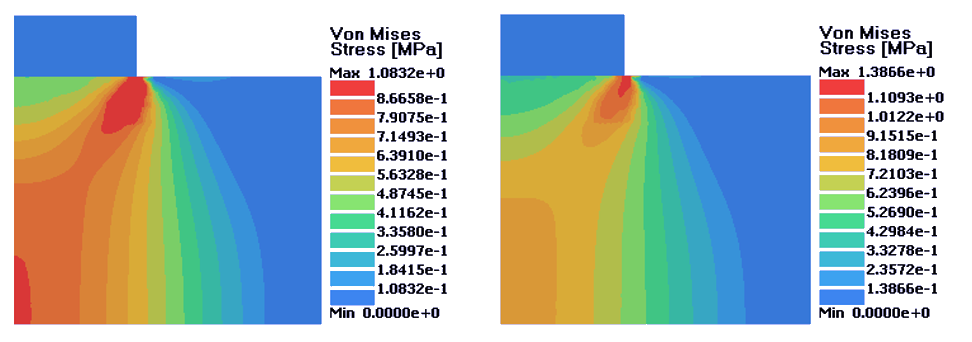
Figure 5. Left: Perfectly Plastic Material; Right: Isotropic Hardening Material. D = 0.14 mm

Figure 6. Left: Perfectly Plastic Material; Right: Isotropic Hardening Material. D = 0.16 mm

Figure 7. Left: Perfectly Plastic Material; Right: Isotropic Hardening Material. D = 0.18 mm

Figure 8. Left: Perfectly Plastic Material; Right: Isotropic Hardening Material. D = 0.24 mm