Update 1D Element Properties Using Cross Sections
Use the Section Property tools to update properties assigned to bar2 elements (target) using a cross section on various entities as the source.
- A collection of solid geometries
- A collection of surfaces
- A collection of elements (2D & 3D)

Figure 1.
Use the arrow to the right of the tool icon to select the type of beamsection to create.
- Elastic section
- Shell section
- VABS section
Elastic Section
This configuration calculates material weighted moments of inertia considering Young's modulus and the Poisson ratio of each intersected entity. Support is currently limited to isotropic materials with card image MAT1. Gaps between domains are also supported and solved by contact between disconnected regions.
Sectional Property Evaluation Theory
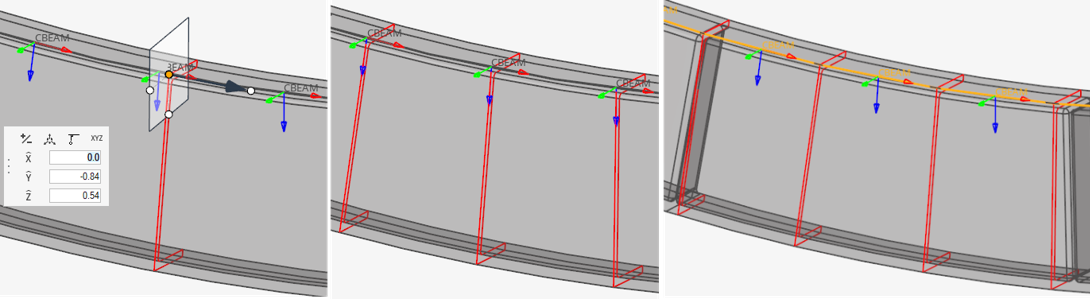
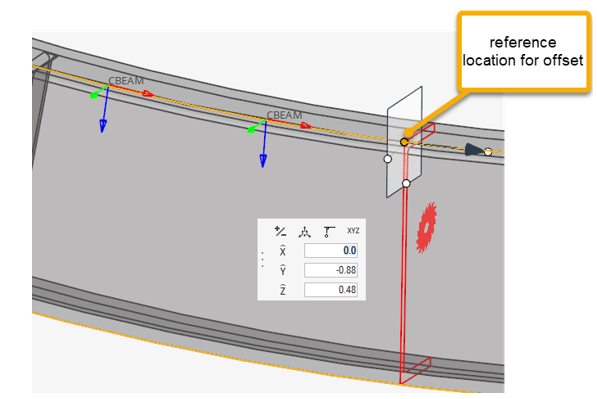
The Section Property tool calculates the intersection between a plane and source entities. It can be a plane per 1D target element or a single cut at a user-defined reference location.
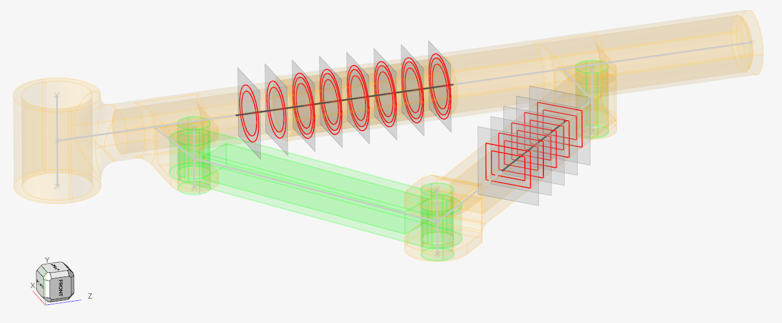
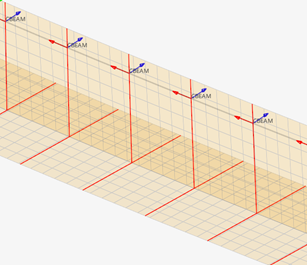 Figure 9. Intersections with shell with thickness |
 Figure 10. Mesh after section inflate |
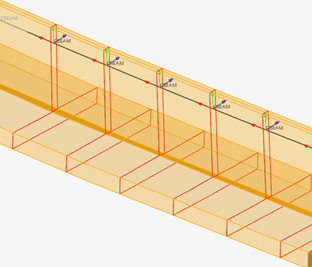 Figure 11. Intersections with solids (geometry) |
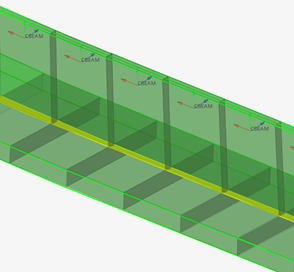 Figure 12. Mesh of solid intersections |
Material info is considered from each intersected entity. If source entities intersected are solids or surfaces, then the material is extracted from the component which holds the intersected geometry. If source entities are elements, then material info is gathered from each element (directly or through component).
Sectional properties are hence calculated following theory as described in: “Analysis and Design of Elastic Beams: Computational Methods, Walter D. Pilkey”
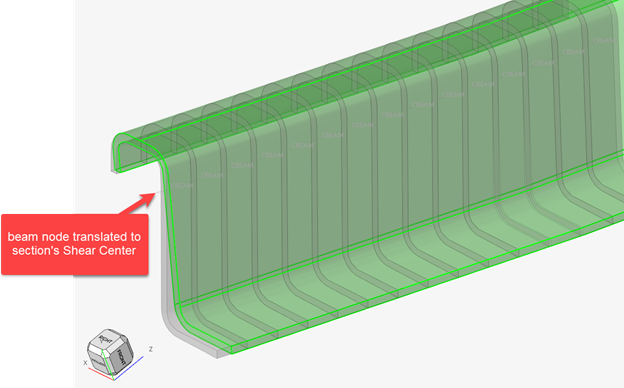
The material neutral axis is calculated along with stiffness terms EIyy, EIzz, GJ, and EA considering local material info. Shear Center and warping properties like torsional constant and warping constant are also calculated.
After sectional properties are calculated accounting for all isotropic materials, a regular homogeneous beam property is created referring to a single (homogenous) material and an elastic beamsection. Regions without a material assigned or with non-isotropic materials (card image other than MAT1) raise a warning. If you continue, such regions will have a material assigned following the “Default material” rule set in the options menu.
You can specify a target material to be used for homogenization or let the tool auto-calculate the material property using effective young modulus. The beam section area and area moments of inertia are set based on the material's Young's modulus to retrieve the same stiffness terms as calculated from the intersected entities.
In turn, if the material is auto-generated, its young modulus is derived from the section product EA and total area A as Eeff= (EA)sec/A. The area moments of inertia are then I=EI/ Eeff; Moments of inertias will deviate from geometric quantities in case of multiple materials, but the section’s Area is correct.
If a target material is provided, then its young modulus will be used; hence all geometric terms A, Iyy, Izz, Iyz may deviate from those calculated by closed form equations for similar geometric shapes.
Orientation and Offset
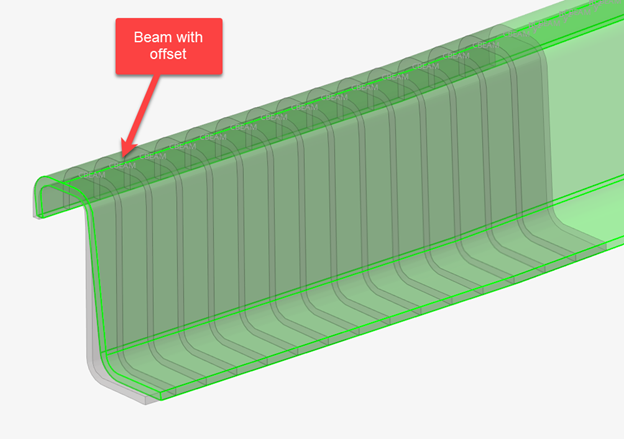
The elemental system of target 1D elements remain unchanged during the update process.
When a cross section is performed on a 1D element, its local X axis is taken as the section plane’s normal. The beamsection local 2D system (Y, Z) matches with the elemental axis (Y, Z). Sectional properties are hence valid in elemental system as defined. If orientation needs to be adjusted, it is advisable to update the element orientation first (see Orient Bar2 Elements).
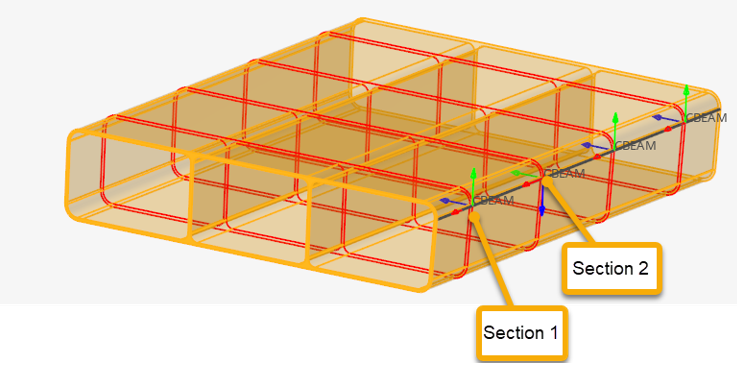
Figure 13. Section cut per element
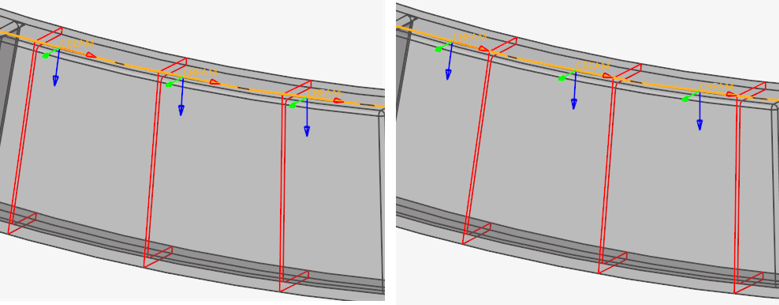
Since a cut is performed per element in Figure 13, each section has its own local system matching the elemental system, as shown in Figure 14 & Figure 15. The origin of the system, from which Centroid and Shear Center coordinates are saved in the beamsection entity, is taken at the center of the bounding of the section in the local system.
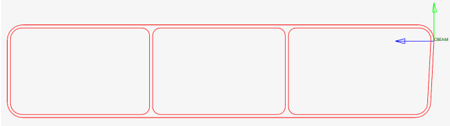
Figure 14. First section

Figure 15. Second section
After proceeding, a 3D detailed visualization of updated beams shows the resulting beam cross section taking into account orientation and offset.
Figure 16. Single section cut on misaligned elements
Default Material
If the “Ignore source material”checkbox is turned off and all regions have a valid isotropic material, then this option has no effect. Otherwise, if some materials are missing or invalid, there is a provision to auto-assign default materials to such regions.
- Max
- The material with the greatest Young's modulus (among those found in the intersection) is assigned to these regions.
- Mean
- The arithmetic average of the Young's modulus and the Poisson ratio of other materials found in the intersection are considered. This is a simple average of materials without accounting for the number of occurrences.
- Nearest
- The material from the nearest region with a valid material is used.
- User
- A user material is used. This implies that the material selector become a mandatory selection and in turn the user material is used for normalization.
However, using such a default is not a good practice in general; you should assign the proper material to account during section cut.
Disconnected Parts
A section cut on a model may lead to disconnected regions. It could be because of separate bodies which are glued or welded, or because section undergoes a hole in model. A valid section needs to be connected to consider it as an equivalent beam section.
In any case, the Section Property tool generates a beamsection with geometric properties like area and second moments of inertia calculated. However, to fully complete the process and calculate shear center position as well as torsional & warping constants, the section need to be “connected”.
The tool provides an option called “contact”.
- Best match - Search contact between domains based on internal tolerance calculated from local mesh size.
- Tolerance - Search contact between domains based on user defined tolerance.
- No contact - No contact searches.
After gluing domains, sectional properties are calculated as described above.
Consolidation
An option for the consolidation of beamsections and properties is available. It is valid when you cut large prismatic solids where properties do not vary a lot. Hence, it reduces the number of beamsections created.
- Area
- Section's Modulus
- Torsional constant
If any of these metrics deviates more than the threshold tolerance given, then a new beamsection is created.
Shell Section
This configuration calculates area moments of inertia considering thinwall theory and uses HyperBeam engines. An option for auto-weld is available to reconnect disconnected domains by spot welds.
VABS Section
This setting is available for the OptiStruct profile only. It creates OptiStruct PBEAML using the VABS file generated by the tool from each intersection with composite shell model.