RD-E: 5102 Topology Optimization for Solids
This example outlines how to set up a topology optimization for solid elements part. A concentrated load is applied to the entire top of the part by using a rigid body. The lower part of the hook is the design space for the toplogy optimization.
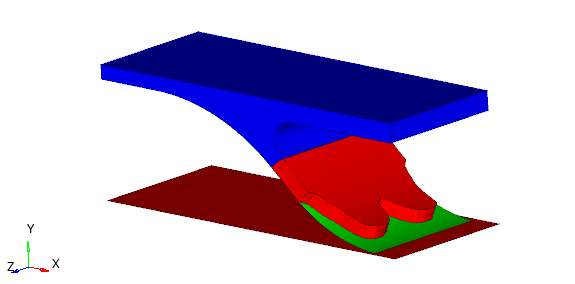
Figure 1.
- Objective (minimize volume of the structure in this example)
- Constraints (maximum displacement less than 5mm in this example)
- Design variables (topology optimization of the design in hook example)
The setup of optimization requires an extra input optimization input file named <name>.radopt which defines the optimization objective, optimization constraints, design variables, and optimization responses.
For more Radioss optimization details, refer to Design Optimization in the User Guide.
Options and Keywords Used
Input Files
Model Description
Units: mm, s, ton, N, and MPa
- Objective: Minimize volume of hook (to saving materials)
- Constraint: Maximum of total displacement in node group 120 less than 5.0 [mm]
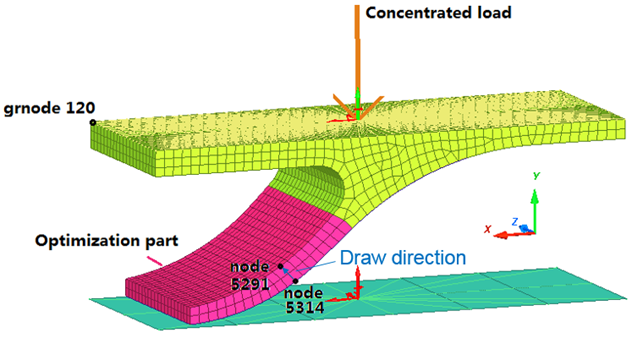
Figure 2. Problem Description
Detailed Optimization Setup
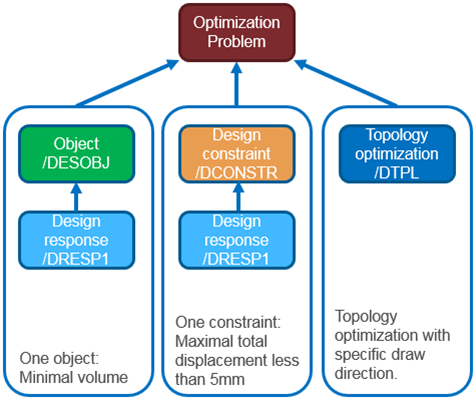
Figure 3. Radioss Optimization Setup
Optimization Objective
/DESOBJ is used to define optimization objective. In this example, the objective is to minimize response #10.
Response #10 defines an optimization response that is the volume of defined optimization part.
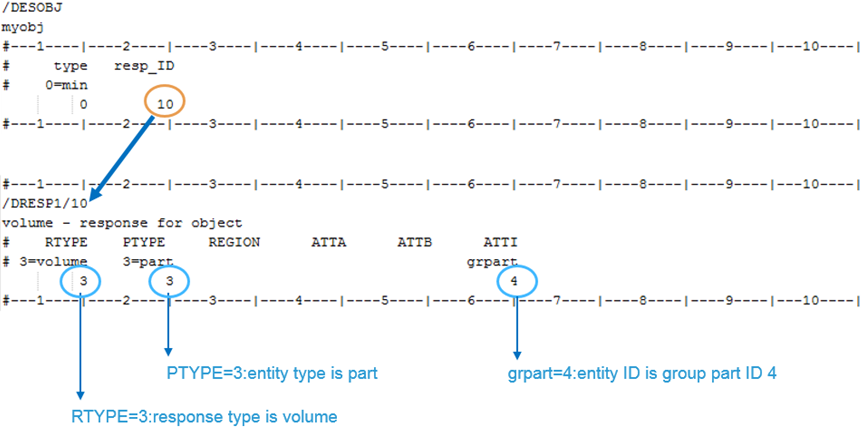
Figure 4. Optimization Objective Setup in Radioss Optimization
Optimization Constraint
In this example, total displacement under concentrated load is limited to less than 5.0 mm to guarantee the quality of hook after topology optimization. In <name>.radopt file set total displacement of selected node group (ID) as response #11 and limit response #11 under maximum value 5.0. Depending on your own optimization criteria, the value in cmax may differ.
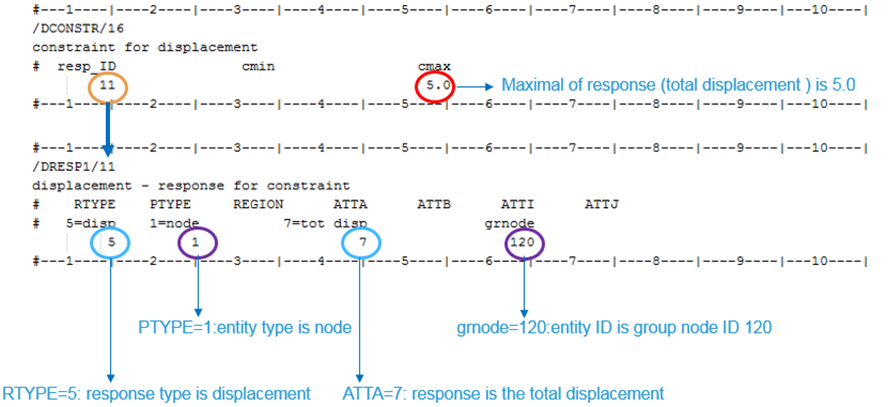
Figure 5. Optimization Constraint Setup in Radioss Optimization
Topology Optimization
- TMIN
- Minimum thickness
- STRESS
- Stress constraint
- MEMBSIZ
- Member Size Conrol
- MESH
- Mesh type
- DRAW
- Draw Direction Constraints
- EXTR
- Extrusion Constraints
- PATRN
- Pattern Grouping
- PATREP
- Pattern Repetition
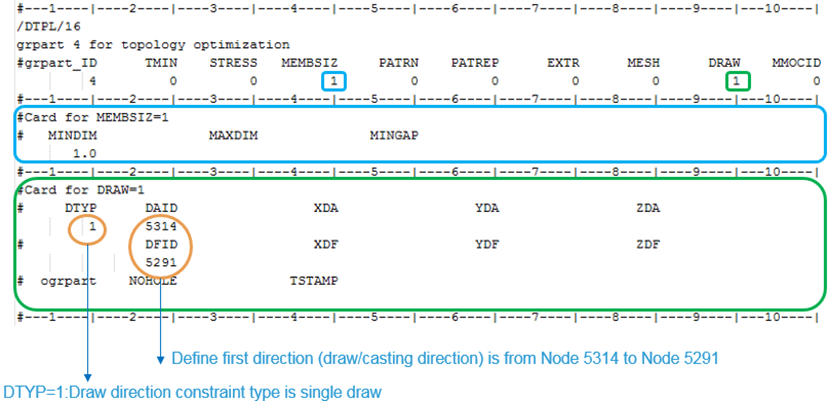
Figure 6. Design Variable Setup in Radioss Optimization
The member size control function is enabled using MEMBSIZ=1 to improve the quality of the topology optimization. In this example the minimum diameter of members is set to MINDIM=2.5. It is recommended that MINDIM be at least 3 times, and no greater than 12 times, the average element size for all elements referenced by that /DTPL.
Draw direction for topology optimization is activated using DRAW=1. This results in a design that can be manufactored easier. DTYP is used to define the draw direction constraint type. In this example a “single die” type (DTYP=1) is used.
Results
- Review the optimization results file to make sure that optimized design is
satisfies the constraints and objective. This information is in the
*.out file (hook_opt.out).
- Design is good
- FEASIBLE DESIGN (ALL CONSTRAINTS SATISFIED)
- Design does not meet the constraints defined
- INFEASIBLE DESIGN (AT LEAST ONE CONSTRAINT VIOLATED)
The Radioss simulation for each design is included in the outer directories created during the simulation. All the animation results can be loaded by opening the hook_opt.mvw session file in HyperView.
- In the *.out file (hook_opt.out), check/verify the optimization definition. Objective Function: Minimize VOLUM, Run Type: Topology Optimization and so on. The Optimization results can be plotted in HyperGraph using the hook_opt.hgdata file.
- By running the Optimization in Radioss, an equivalent OptiStruct model will also be automatically created and named *.fem (hook_opt.fem).

Figure 7. Optimized Results in Each Iterations in *eslout File
- In the original model, the volume is 324.7 mm3
- After topology optimization, the volume is 251.0 mm3
After the topology optimization, the element densities of the different design iterations can be plotted in HyperView using the hook_opt_des.h3d file.
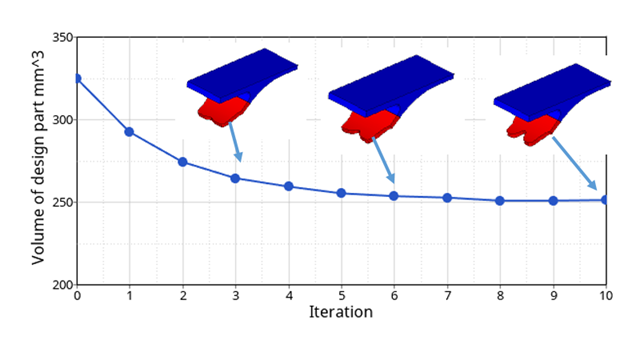
Figure 8. Optimized Results of Hook