Create E-Lines
Use the Create E-Lines tool to create evaluation lines at component interfaces.
- Define interfaces to be evaluated which has Lines as mandatory input, unless you create an E-Line with the Elem2Elem option.
- Turn off the component(s) that are not applicable for the E-Linecreation and/or deselect them while choosing the appropriate component(s) for creation. Make the display selection ready before entering the workflow.
The Create E-lines tool is used to create E-Lines at the interfaces that shall be evaluated for Squeak and Rattle. Create all E-Lines automatically or switch to Manual mode to create E-Lines one by one with more detailed control.
- Fast Create (Part time Analyst): Use to create many E-Lines at a time to get quick and approximate overview of squeak and rattle risk zones.
- Manual Create (Advanced): Use to manually create one E-Line at a time and control the setup to ensure the accuracy in analysis results.
- Evaluation Points will not be created at the locations where a projection is not found due to a small search tolerance.
- Search Tolerance and Spacing are the two options which decide how and where the E-Lines will be created.
Fast Create E-Lines
Create E-Lines between multiple components at once without much manual intervention.
Use to create many E-Lines at a time and to get a quick and approximate overview of squeak and rattle risk zones.
Manually Create E-lines
Add more control to the creation of E-Lines by selecting Main and Secondary entity (Component or Element) and gap direction.
Create E-Lines Options
There are several options that can be defined via the options menu, these include E-Line and definition of Contact type based on material property.
E-Line Properties
- Spacing
- Defines the spacing between the E-point placements along the created E-Lines.
- Search Distance
- Defines the tolerance or search distance between interface components.
- Gap Direction
- Realization Projection direction.
- Normal to Main
- Z direction will be perpendicular or Normal to Main
component.
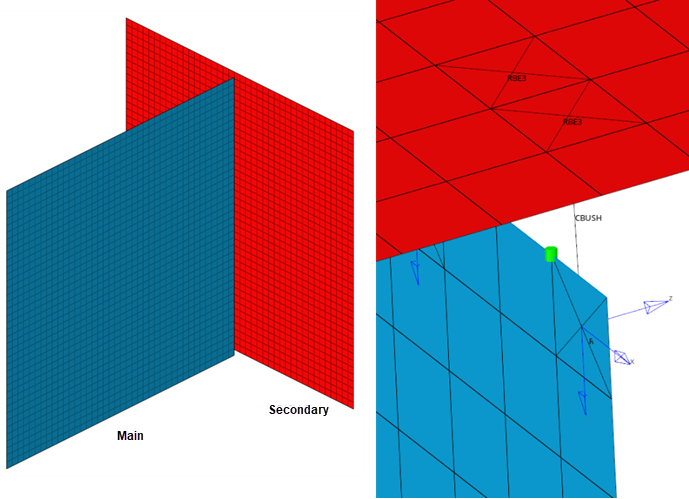 Figure 3.
Figure 3. - In Plane to Main
- Z direction will be In Plane to Main component.
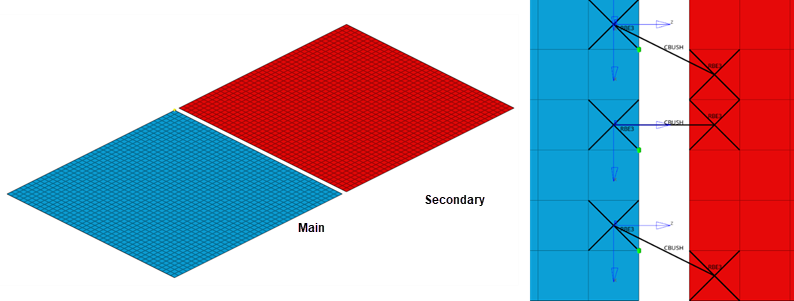 Figure 4.
Figure 4.
- Gap Assignment Method
- Defines which method to use to assign Gap and Tolerance values to E-lines. The assigned gap and tolerance values can be reviewed in E-line Review Table.
Material Property
- Contact Types
- Defined Contact type based on Young's Modulus value.
Advanced
- E-line ID Range
- Define an ID Range for created E-Lines and all entities belonging to them.
- Controlled Spacing
- Define a limit on the spacing to avoid error in solver and numerical issues.
- Controlled Edge
- Select this option when active E-Lines must not create close to E-Line edge.
 to open edit E-line definition
parameters under the Options menu.
to open edit E-line definition
parameters under the Options menu.