Piezoelectric Analysis
Piezoelectric materials are a class of materials in which structural deformation triggers electrical potential and vice versa.
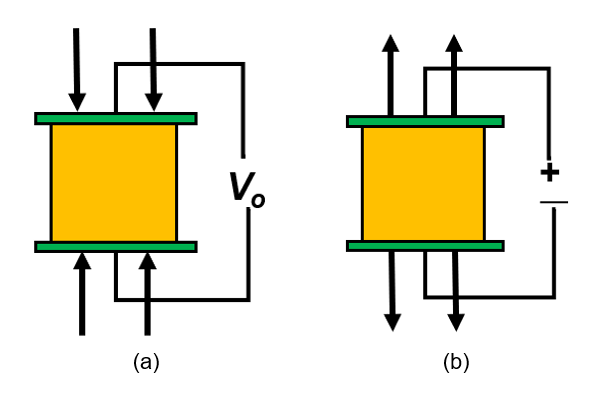
Figure 1. (a) A piezoelectric material subject to structural loading (applied stress) generates electric potential. Conversely, (b) when electric potential is applied, it induces mechanical strain
Piezoelectric Analysis in OptiStruct
Piezoelectric Analysis in OptiStruct involves two-way coupling in which a mechanical excitation will generate an electrical response. Conversely, an electrical excitation will generate a mechanical response. The coupling is strong, which means that both mechanical and electrical responses are solved simultaneously.
Support Information
Piezoelectricity phenomenon is not modeled by a separate analysis type. It is modeled by structural materials, piezoelectric materials, and a coupling definition between the two domains in a structural analysis.
- Linear and Nonlinear Static (SMDISP)
- Normal Modes
- Direct Complex Eigenvalue
- Direct and Modal Frequency Response
- Linear and Nonlinear Transient (SMDISP)
- Element Type
- Order
- Solids
- 1st and 2nd order
Input
Input file entries for piezoelectric coupling definition.
Bulk Data Entries - Material Definitions
- Entry
- Purpose
- MAT1PT
- Defines isotropic permittivity and damping for dielectric materials.
- MAT2PT
- Defines anisotropic permittivity and damping for dielectric materials.
- MATPZO
- Defines the piezoelectric coupling matrix between dielectric and structural components.
- MATT1PT
- Defines a temperature dependent version of MAT1PT.
- MATT2PT
- Defines a temperature dependent version of MAT2PT.
- MATTPZO
- Defines a temperature dependent version of MATPZO.
Bulk Data Entries - Loads, Constraints, and Boundary Conditions
- Entry
- Purpose
- CHARGE
- Defines a point charge.
- CHGAREA
- Defines charge density over an area.
- CHGVOL
- Defines charge density over a volume.
- SPC
- Can be used to define a zero electric potential, by setting C=V.
- SPCD
- Can be used to define a prescribed electric potential, by setting C=V.
- MPC
- Can be used to model an electric conductive surface, by setting C=V.
- TLOAD1/TLOAD2
- Can be used to define a dynamic load.
- When TYPE=LOAD, it can point to CHARGE, CHGARE or CHGVOL
- When TYPE=DISP, it can point to SPCD with C=V
- RLOAD1/RLOAD2
- Can be used to define a dynamic load.
- When TYPE=LOAD, it can point to CHARGE, CHGARE or CHGVOL
- When TYPE=DISP, it can point to SPCD with C=V
Bulk Data Entries - Miscellaneous
- Entry
- Purpose
- PARAM, VAPMTV
- Defines the vacuum permittivity for piezoelectric materials. This is required when relative permittivity is defined in MAT1PT or MAT2PT.
Problem Setup
$ *************************************************************
$ EXAMPLE: LINEAR STATIC ANALYSIS WITH PIEZOELECTRIC COUPLING
$ ************************************************************
DISPLACEMENT = ALL
SPCFORCE = ALL
GPFORCE = ALL
OLOAD = ALL
SUBCASE 1
ANALYSIS STATIC
SPC = 2
LOAD = 3
BEGIN BULK
$--1---><---2--><---3--><---4--><--5---><--6---><---7--><--8---><---9-->
PSOLID 1 2
MAT4 2 1000.0
MAT1PT 2 1000.0
CHARGE 3 163 1.0
SPC 2 2890 V 0.0
SPC 2 2875 V 0.0
..