/MAT/LAW22 (DAMA)
Block Format Keyword This law is identical to Johnson-Cook material (/MAT/LAW2), except that the material undergoes damage if plastic strains reach a user-defined value ( ). This law can be applied to both shell and solid elements.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /MAT/LAW22/mat_ID/unit_ID or /MAT/DAMA/mat_ID/unit_ID | |||||||||
| mat_title | |||||||||
| E | |||||||||
| a | b | n | |||||||
| c | ICC | ||||||||
| Et | |||||||||
Definition
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| mat_ID | Material
identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| unit_ID | Unit Identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| mat_title | Material
title. (Character, maximum 100 characters) |
|
| Initial
density. (Real) |
||
| E | Young's
modulus. (Real) |
|
| Poisson's
ratio. (Real) |
||
| a | Yield stress - should be
strictly positive. (Real) |
|
| b | Hardening
parameter. (Real) |
|
| n | Hardening
exponent. (Real) |
|
| Failure plastic
strain. Default = 1030 (Real) |
||
| Maximum stress. Default = 1030 (Real) |
||
| c | Strain rate coefficient.
Default = 0.00 (Real) |
|
| Reference strain
rate. If , no strain rate effect. (Real) |
||
| ICC | Strain rate computation
flag. 2
(Integer) |
|
| Damage model starts
at
. Default = 0.15 (Real) |
||
| Et | Softening damage slope (
). Default = 0.00 (Real) |
Example (Aluminum)
#RADIOSS STARTER
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/UNIT/1
unit for mat
g mm ms
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
#- 2. MATERIALS:
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/MAT/DAMA/1/1
Alu
# RHO_I
.0027
# E Nu
70000 .3
# a b n Eps_max SIGMA_max0
100 0 1 .2 100
# c Eps_dot_0 ICC
0 0 0
# Eps_dam E_t
.1 -2000
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
#ENDDATA
/END
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|Comments
- Damage is isotropic, its effect
are the same in tension and compression.
(1) Where,- Plastic strain
- Strain rate
- ICC is a flag of the strain rate
effect on material maximum stress
.
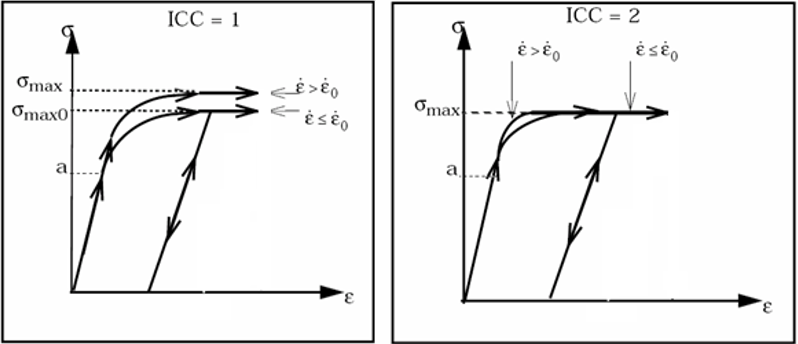
Figure 1. - The damage appears in the
material when the strain is larger than a maximum value
:
(2) If , Law 22 is identical to law /MAT/LAW2.
If and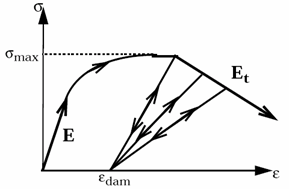
Figure 2. - For solid elements, the damage law can only be applied to the deviatoric stress tensor sij and .
- When
reaches
in one integration point, then based on the element
type:
- Shell elements: The corresponding shell element is deleted.
- Solid elements: The deviatoric stress of the corresponding integral point is permanently set to 0, however, the solid element is not deleted.