HM-3680: Preserve a Shape With Cluster Constraints
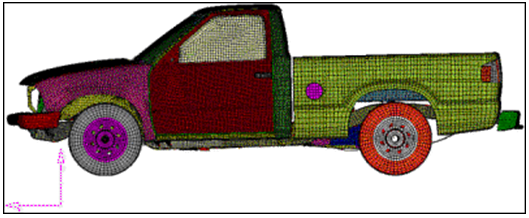
In the tutorial, you will be changing the length of the cab while preserving the shape of the wheel. To facilitate the morphing process you will be employing constraint and symmetry.
When circular features are stretched, they become elliptical in shape. In some cases as in the wheels of a truck, this effect is not desirable. In such cases, using cluster constraints will allow you to translate the features, along with the morph, while maintaining its circular shape.
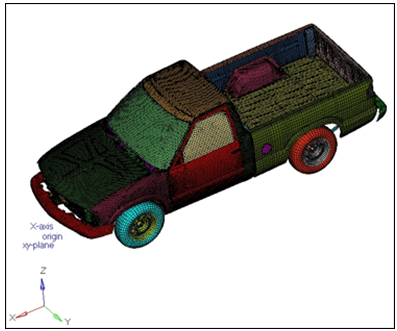
Figure 1.
Open the Model File
In this step, you will open the model file, truck.hm.
- Open the model file, truck.hm.
- Review the model.
Create a Coordinate System
In this step, you will create a coordinate system.
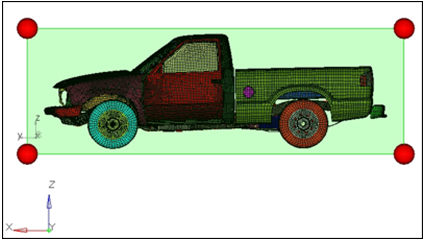
Create and Split Morph Volume
In this step, you will create and split the morph volume.
Create a Symmetry
In this step, you will create a symmetry.
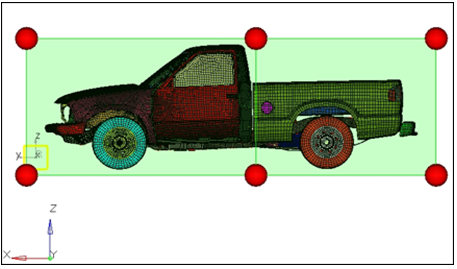
Morph the Part
In this step, you will morph the part.
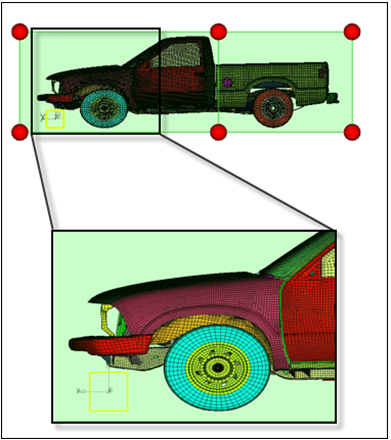
Create a Cluster Constraint
In this step, you will create a cluster constraint.
The front wheels, after morphing, become elliptical. To fix this issue, you will be employing a particular type of constraint, called a cluster constraint, which helps to keep the original shape of a portion of the model while morphing.
Morph the Part
In this step, you will morph the part.
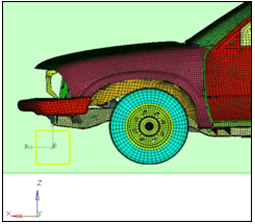
Figure 7.
Using cluster constraints and morph volumes you are able to stretch the cab of the pickup without distorting the wheels.