RD-E: 0500 Beam Frame
A beam frame receives an impact from a mass having initial velocity.
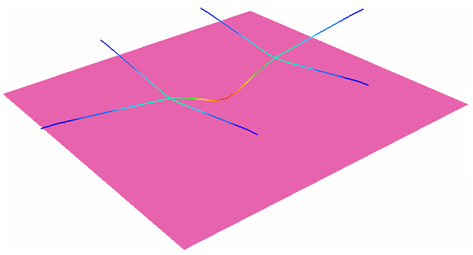
Figure 1.
The explicit approach leads to finding a quasi-static equilibrium of the structure after impact.
Options and Keywords Used
- Beam
- Plasticity and Johnson-Cook material (/MAT/LAW2 (PLAS_JOHNS))
- Boundary conditions (/BCS)
- Initial velocities (/INIVEL)
- Beam element (/PROP/TYPE3 (BEAM))
- Rigid wall (/RWALL)
The impacting mass is simulated using a sliding rigid plane wall (/RWALL) having an initial velocity of 10 ms-1and a mass of 3000 g. Only one secondary node exists: the node O to simulate a point impact.
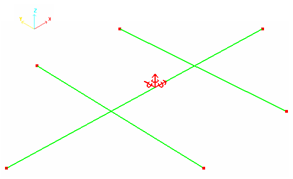
Figure 2. Boundary Conditions
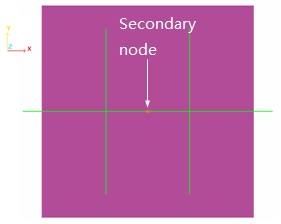
Figure 3. Rigid Wall Type Infinite Plane
Input Files
Refer to Access the Model Files to download the required model file(s).
The model files used in this example include:
FRAME_*.rad
Model Description
The purpose of this example is to perform a static analysis using beam elements.
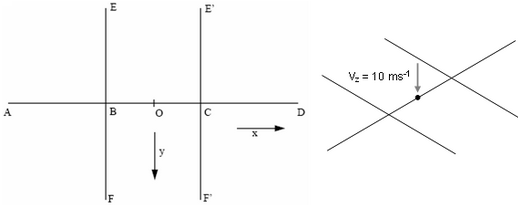
Figure 4. Geometry of the Frame
Dimensions are: AB = BC = CD = BE = BF = E'C = CF' = 90 mm.
- Beam Properties
- Cross section
- 36 mm2
- Moments of inertia in Y and Z
- 108 mm4
- Moments of inertia in X
- 216 mm4
- Material Properties
- Density
- 0.0078
- Young's modulus
- 200 000
- Poisson's ratio
- 0.3
- Yield stress
- 320
- Hardening parameter
- 134.65
- Hardening exponent
- 1.0
All other coefficients are set to default values. Plasticity is taken into account using LAW2 without failure.
Model Method
Figure 5. Mesh of the Frame Showing the Position of the Nodes
Results
Curves and Animations
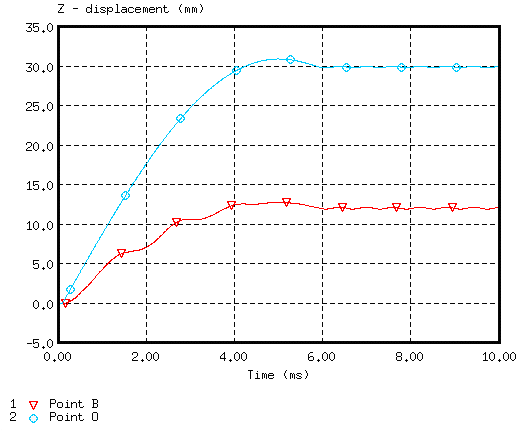
Figure 6. Displacements of Points B and O
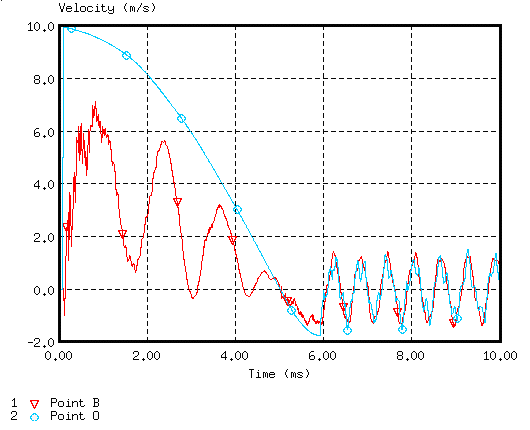
Figure 7. Velocity of Points B and O (stabilization)
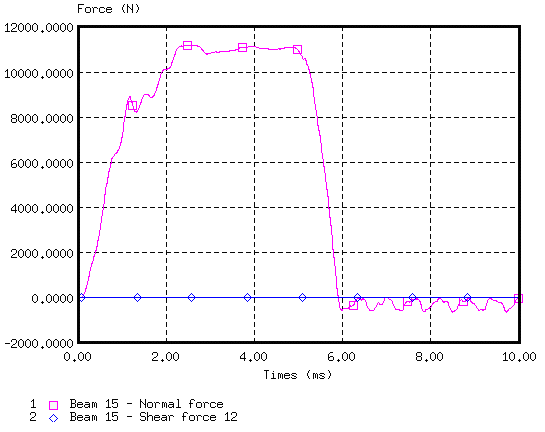
Figure 8. Normal and Shear Force on Beam Element 15 (near to point O)
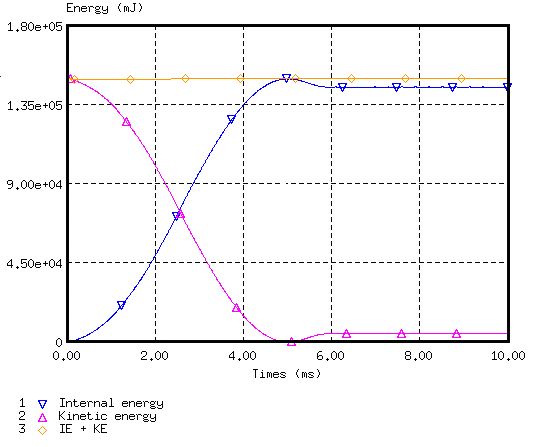
Figure 9. Energy Assessment (stability reached at in 6 ms)
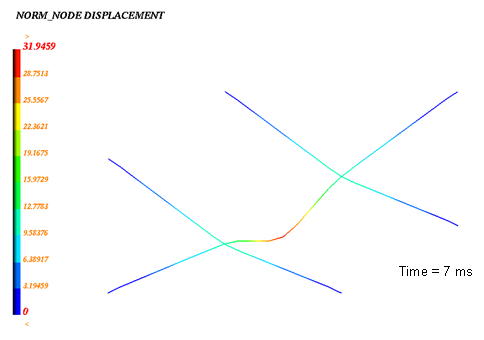
Figure 10. Node Displacement (max. = 30.96 mm)
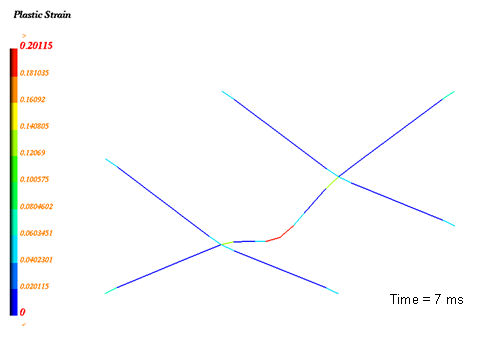
Figure 11. Plastic Strain (max. = 20.1%)