Optimization Setup
The Optimization Setup step allows you to set up objectives and constraints in the Optimization Study.
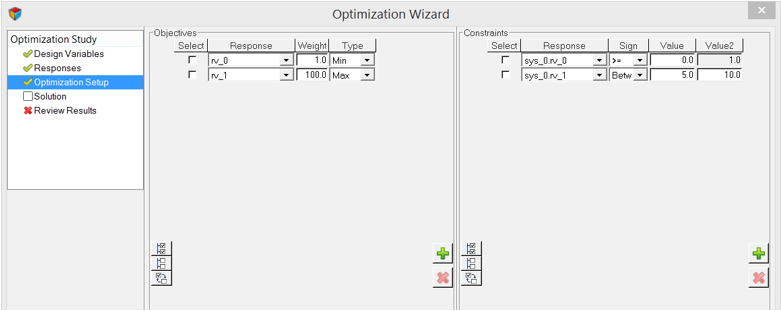
Figure 1.
View new features for HyperWorks 2022.1.
Learn the basics and discover the workspace.
Discover HyperWorks functionality with interactive tutorials.
Start HyperWorks and configure the applications.
Create, open, import, and save models.
Set up sessions and create report templates.
Solver interfaces supported in HyperWorks.
A solver interface is made up of a template and a FE-input reader.
Browsers supply a great deal of view-related functionality by listing the parts of a model in a tabular and/or tree-based format, and providing controls inside the table that allow you to alter the display of model parts.
Create and edit 2D parametric sketch geometry.
Create, edit, and cleanup geometry.
FE geometry is topology on top of mesh, meaning CAD and mesh exist as a single entity. The purpose of FE geometry is to add vertices, edges, surfaces, and solids on FE models which have no CAD geometry.
Different types of mesh you can create in HyperWorks.
Create and edit 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D elements.
Create, organize and manage parts and subsystems.
HyperMesh composites modeling.
Create connections between parts of your model.
Rapidly change the shape of the FE mesh without severely sacrificing the mesh quality.
Create a reduced ordered model to facilitate optimization at the concept phase.
Workflow to support topology optimization model build and setup.
Multi-disciplinary design exploration and optimization tools.
Validate the model built before running solver analysis.
Reduce a full 3D model with axisymmetric surfaces while accounting for imperfections.
Tools and workflows that are dedicated to rapidly creating new parts for specific use cases, or amending existing parts. The current capabilities are focused on stiffening parts.
Tools used for crash and safety analysis.
Airbag solutions offer airbag folder utilities and exports a resulting airbag in a Radioss deck.
Essential utility tools developed using HyperWorks-Tcl.
Import an aeroelastic finite element model with Nastran Bulk Data format.
Framework to plug certification methods to assess margin of safety from the model and result information.
Create evaluation lines, evaluate them, and optimize the interfaces to eliminate squeak and rattle issues.
Panels contains pre-processing and post-processing tools.
Results data can be post-processed using both HyperMesh and HyperView.
HyperGraph is a data analysis and plotting tool with interfaces to many file formats.
MotionView is a general pre-processor for Multibody Dynamics.
MotionView is a general pre-processor for Multi-body Dynamics.
The Model Browser allows you to view the MotionView model structure while providing display and editing control of entities.
The MotionView ribbons allows you to quickly access tools and standard functions, and is located along the top of MotionView.
Create and edit systems, assemblies, and analyses, use wizards to build models quickly, create and edit belt/pullies, NLFE stabars, and NLFE springs, access the EDEM and Track Builder tools.
Create and edit points, bodies, lines (curve graphics), solids (graphics), markers and vectors, edit grounded/ungrounded bodies, create and edit rigid body groups, configure gravity, and select material properties.
Create and edit various model entities.
Create and edit outputs, create and edit templates, run the solver, view reports, access the Load Export utility, use the Optimization Wizard, open HyperStudy, utilize many pre-processing and post-processing capabilities with regards to flexible bodies (or flexbodies), run MS/EDEM cosimulation in batch mode, and generate H3D from EDEM.
Use the Outputs tool to create a result output request to the solver, which writes out the requested data for plotting data.
Use the Templates tool to create and edit blocks of text that contain data fields and programming instructions.
The Run Solver tool allows you to run the solution for the MotionView model using MotionSolve.
The View Reports dialog displays a report list of all reports generated from an analysis task run.
An external module invoked from MotionView. This module allows you to take loads from an ADAMS run and create a tabular summary file or a Nastran input card for those loads.
In the 2022.1 release, MotionSolve has new capabilities for optimizing multibody systems.
The first step in the Optimization process is to identify the Design Variables (DVs) in your model.
The Responses step of the wizard allows you to add Response Variables (RVs) to an optimization study.
The Optimization Setup step allows you to set up objectives and constraints in the Optimization Study.
The Solution step of the wizard allows you to specify optimization and simulation settings and perform an optimization run.
The Review Results step of the wizard allows you to review the results once the optimization solution has successfully completed.
HyperStudy allows you to perform Design of Experiments (DOE), optimization, and stochastic studies in a CAE environment. It allows you to study the different aspects of a design under various conditions, including non-linear behaviors. It can be applied in the multi-disciplinary optimization of a design combining different analysis types.
The FlexBody Prep wizard allows you to create the flex H3D file from several sources, including an ADAMS MNF file, a NASTRAN PCH file, and a mirrored H3D file. You can also generate an H3D file using OptiStruct, a finite element analysis solver.
Generates ADAMS output files from a flexbody transient run, which can then be used in nCODE Fatigue software.
This tool helps to run the cosimulation in batch mode.
This tool helps to convert EDEM particle simulation results to animation H3D that can be visualized in HyperView.
The Model Identification Tool, known as MIT, is a profile in HyperGraph for fitting test data from frequency- and amplitude-dependent bushings to analytical models. This tool operates in conjunction with HyperGraph, MotionView, and MotionSolve to provide you with a comprehensive solution for modeling and analysis.
MotionView supports the importing of several types of CAD and FE formats.
MotionView has many pre-processing and post-processing capabilities with regards to flexible bodies, or flexbodies, for multi-body dynamics models.
From the Preferences dialog, you can access various MotionView options for your model.
Explore the various vehicle modeling tools.
Reference material for the HyperWorks Desktop scripting interface which is a set of Tcl/Tk commands.
Reference materials for the MotionView MDL Language, Tire Modeling, and the MDL Library.
Reference material detailing command statements, model statements, functions and the Subroutine Interface available in MotionSolve.
Reference material for Templex (a general purpose text and numeric processor) and additional mathematical functions and operators.
Reference materials for the MotionView Python Language.
MediaView plays video files, displays static images, tracks objects, and measures distances.
TableView creates an Excel-like spreadsheet in HyperWorks.
TextView math scripts reference vector data from HyperGraph windows to automate data processing and data summary.
Create, define, and export reports.
MotionView is a general pre-processor for Multibody Dynamics.
The MotionView ribbons allows you to quickly access tools and standard functions, and is located along the top of MotionView.
Create and edit outputs, create and edit templates, run the solver, view reports, access the Load Export utility, use the Optimization Wizard, open HyperStudy, utilize many pre-processing and post-processing capabilities with regards to flexible bodies (or flexbodies), run MS/EDEM cosimulation in batch mode, and generate H3D from EDEM.
In the 2022.1 release, MotionSolve has new capabilities for optimizing multibody systems.
The Optimization Setup step allows you to set up objectives and constraints in the Optimization Study.
The Optimization Setup step allows you to set up objectives and constraints in the Optimization Study.

© 2022 Altair Engineering, Inc. All Rights Reserved.