Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics Panel
Use the Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics panel to perform SPH analysis on a component with volume, such as airbags or fuel tanks.
Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) is a technique used to analyze bodies that do not have high cohesive forces among themselves and undergo large deformation, such as liquids and gases.
In SPH Finite Point Method (SPH FPM), a given volume of the body of interest is discretized into particles, called SPH elements. These elements are node-like particles which have no geometric connectivity among themselves. Each SPH element has an effective mass. The summed mass of all particles in the filled volume of the body should be equal to the mass of the filled volume.
Panel Options
| Option | Action |
|---|---|
| entity selector | Select the entities that define the volume to be filled with SPH elements. |
| use reference | SPH elements are
generated at the corners/face centers of the cubes which fall
within the user defined criteria. Select this checkbox to specify which point the generation of cubes should be started. The base point defines the starting point for
cube generation, and is utilized by the mesher as a starting
point.
|
| mesh orientation | Choose a method for
defining the orientation of SPH elements.
|
| pitch | Choose a method for
specifying the distances between each SPH particle.
Note: Smaller numbers will result in more elements within
the same space, but this will not affect the mass or density
of the substance (gas, fluid, and so on) that the particles
represent.
|
| material density= / filled volume mass= | Choose a method for
specifying the quantity of fluid.
|
| volume definition | Choose which elements
to generate SPH elements for.
|
| partial fill | Model a fluid or gas
that does not completely fill the selected volume. If
enabled, perform the following steps:
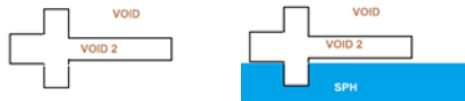 Figure 1. |
| wall offset | Create SPH particles
up to a distance that you specify. The thickness of SPH elements is created from input. The distance between the SPH particles is driven by the pitch. 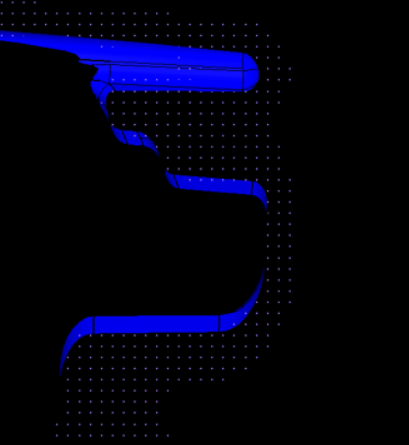 Figure 2. |
| external to volume | Create SPH particles
outside of the defined volume. Note: Available when wall offset
is enabled, which enables the capability to offset SPH
elements from selected volume surfaces.
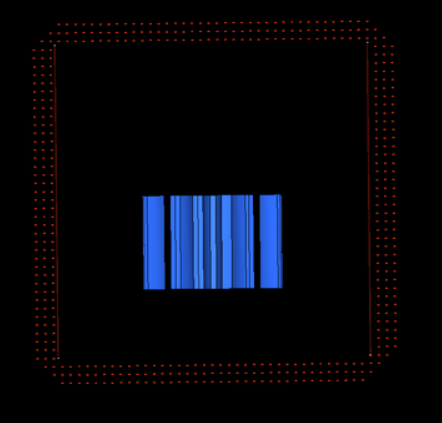 Figure 3. |
| wall clearance | Create SPH particles
from the specified distance. Tip: Useful when you are
trying to avoid contact of SPH elements with walls at the
beginning of the solver run (1st iteration) and want the
solver to run smoothly.
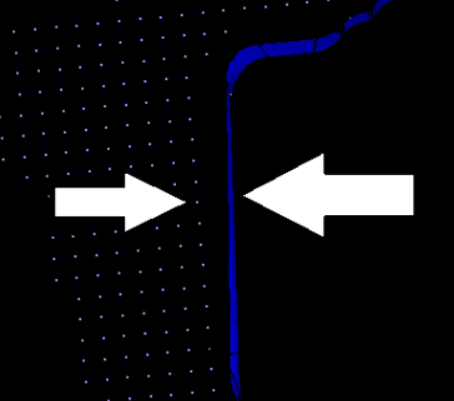 Figure 4. |
Command Buttons
| Button | Action |
|---|---|
| create | Create a new SPH analysis. |
| reject | If the particle fill
is incorrect, click reject. Note: Once you exit the panel you will no longer be
able to reject the fill.
|
| return | Exit the panel. |